Wireshark and Snort are two widely used tools in the field of network security. Both are used to monitor and analyze network traffic, but they have some key differences that make them suitable for different use cases.
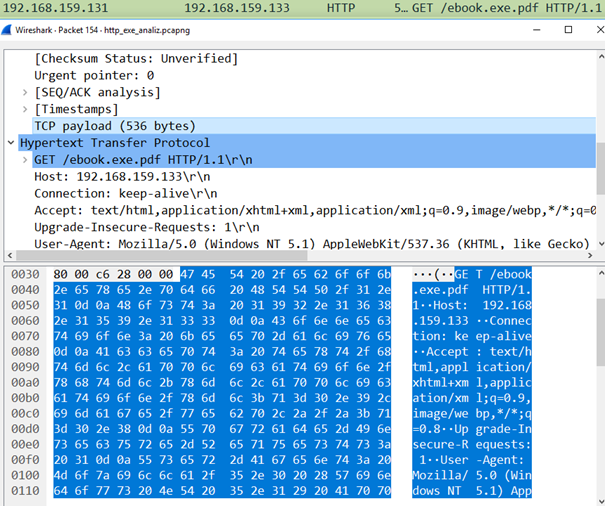
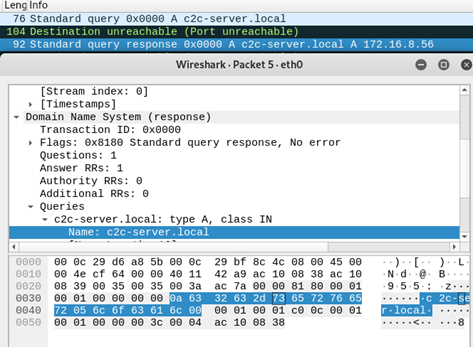
Wireshark is a packet analyzer that allows users to capture and inspect network traffic in real-time. It is widely used by network administrators and security professionals to troubleshoot network issues, identify security vulnerabilities, and analyze traffic patterns. Wireshark is a graphical tool that displays the details of each packet in a human-readable format, making it easy for users to understand the contents and structure of the traffic.
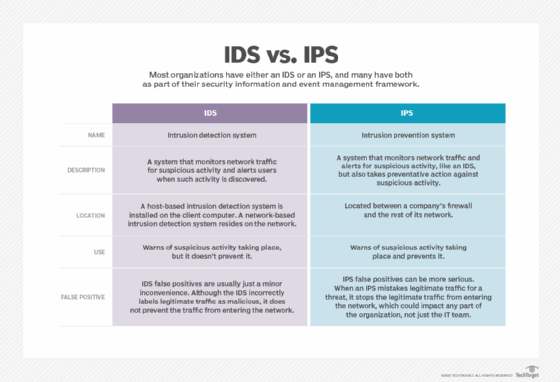
Snort, on the other hand, is a network intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS). It is used to detect and prevent malicious activity on a network by analyzing network traffic and comparing it to a set of rules or patterns that are indicative of malicious activity. Snort is often used to detect and block attacks such as denial of service (DoS), port scans, and other types of threats. It can also be configured to take specific actions, such as blocking or alerting, in response to detected threats.
One key difference between Wireshark and Snort is that Wireshark is a passive tool, while Snort is an active tool. Wireshark simply captures and displays network traffic, while Snort actively monitors the traffic and takes action based on its analysis. This makes Snort better suited for detecting and preventing attacks, while Wireshark is more useful for analyzing traffic and understanding what is happening on the network.
Another difference between the two tools is that Wireshark is primarily a diagnostic tool, while Snort is a security tool. Wireshark is used to troubleshoot and understand the behavior of network traffic, while Snort is used to protect networks from attacks and other malicious activity.
In conclusion, Wireshark and Snort are both important tools in the field of network security, but they serve different purposes. Wireshark is a packet analyzer that is used to capture and inspect network traffic, while Snort is a network intrusion detection and prevention system that is used to detect and prevent attacks. Both tools have their own unique features and capabilities, and they can be used together or separately depending on the needs of the user.
Snort and Wireshark

However, if a simple configuration and set of rules are being used, it may be possible to limit by IP ranges e. The Snort post-dissector can show which packets from a pcap file match snort alerts, and where content or pcre fields match within the payload. Unfortunately at this time there isn't a Suricata post-dissector. These days, there are a ton of great blogs already on understanding them, such as this one by Rapid7. Depending on the rule, Snort is able to prevent or log the traffic. It allows you to capture and interpret network traffic. The author has not tried running it on a Mac.
How do I use a Snort rule to search or filter PCAP in Wireshark?

To answer the Qbot question, provide the Snort SID for the rule that detected the password being sent in clear text. All other trademarks, including those of Microsoft, CompTIA, VMware, Juniper ISC 2 , and CWNP are trademarks of their respective owners. It is also possible to create artificial alerts from configuration and rules - this was done using rule2alert. TODO: find examples from Laura's lab kit and wiki captures that result in interesting alerts. Defaults to usual platform defaults.
Snort

They are typically used to analyze and view custom or maybe new network protocols. Note that for WireViz to work you also have to have GraphViz and GraphViz libraries installed. It should also highlight where in the frame it thinks the content and pcre fields matched. My typical workflow is to identify suspicious traffic in Netwitness, then download the PCAP to open it with Wireshark for deeper analysis. That said, there is advantage in using the plugin, in that it can quickly identify locations, in a packet capture, that make good starting points for further investigation. Rather than showing the alert in the frame where it was detected, if it was a TCP segment that is later reassembled into an upper-level PDU, show the alert in that frame instead. That can be a painful task when there are hundreds of packets matching tens of different Snort rules as the above steps have to be repeated many times… That is why WireShnork was created for: applying Snort rules on all packets of a PCAP file and adding a new kind of filter to Wireshark.
Wireshark · Display Filter Reference: Snort Alerts

As a result, use of the Snort plugin for Wireshark is limited to after-the-fact types of packet capture analyses e. I suggest that you probably either got a corrupt, half-finished download, or have downloaded something bogus masquerading as Wireshark. Jul 25, 2007 Snort and Wireshark - although they can perform similar functions - are completely different. Primarily, those rules allow users to monitor traffic in a more flexible way. Configuring Wireshark Now - we'll need to configure Wireshark to see our Snort binary as well as a few other settings. This information was added by Wireshark and includes the information provided by Snort the alert, the rule information, etc. But did you know that you can use Wireshark to find which specific packet triggered a Snort rule within a few seconds, from within the Wireshark GUI giving you all of the surrounding context that a PCAP can give you.