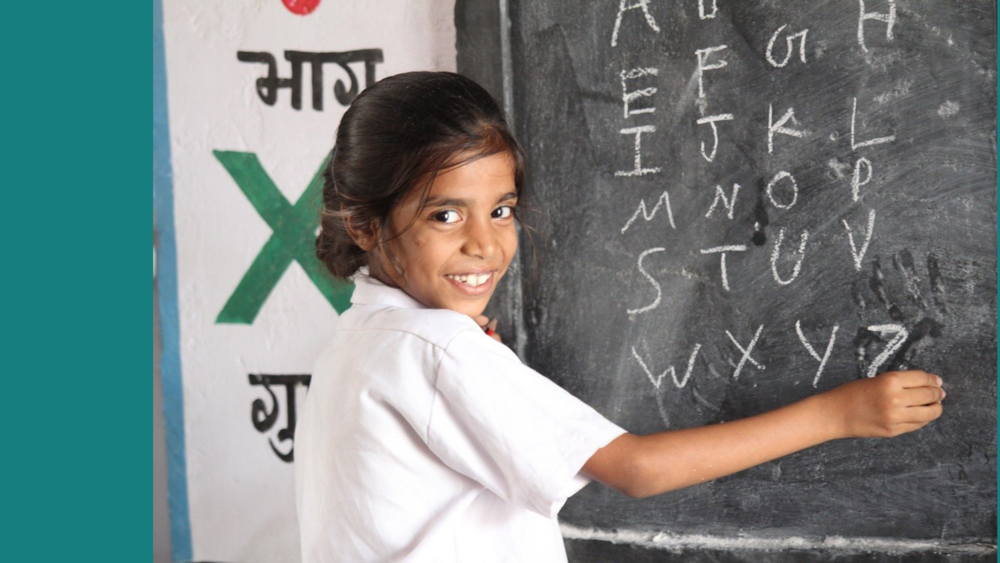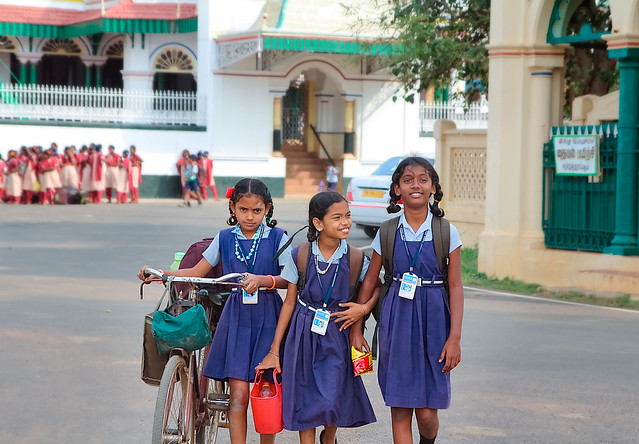Women's education in India has come a long way since the country gained independence in 1947. While there were significant improvements in women's literacy rates over the past few decades, there are still many challenges that need to be addressed in order to ensure that all women in India have equal access to education.
One of the main challenges facing women's education in India is the low enrollment and retention rates of girls in schools. According to data from the Ministry of Education, only about 90% of girls in India are enrolled in primary school, compared to about 95% of boys. This gap widens at higher levels of education, with only about 82% of girls enrolling in secondary school, compared to about 87% of boys.
There are several reasons for this gap in enrollment and retention rates. One factor is the traditional societal roles assigned to women, which often prioritize household duties and caregiving over education. Another factor is the lack of access to schools in rural and remote areas, which disproportionately affects girls. Many girls in these areas have to travel long distances to get to the nearest school, which can be unsafe and discourage them from continuing their education.
Poverty is also a major barrier to education for girls in India. Many families, especially in rural areas, cannot afford the costs associated with education, such as uniforms, books, and other supplies. This can lead to girls dropping out of school early in order to help contribute to their family's income.
There have been efforts to address these challenges and improve women's education in India. The Indian government has implemented a number of initiatives, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, which aims to provide universal access to primary education for all children in India. There are also non-governmental organizations that work to improve education for girls, such as the Pratham Education Foundation and Room to Read.
Despite these efforts, there is still much work to be done to ensure that all women in India have equal access to education. To address the challenges facing women's education in India, it is important to continue investing in initiatives that provide access to schools and other learning opportunities, and to work to change societal attitudes towards the value of education for girls and women. Overall, investing in women's education is not only a social responsibility, but also a smart economic decision, as it has been shown to have positive impacts on the overall development and prosperity of a community.
Why Are So Many Girls in India Not Getting an Education?

Gender prejudice is maintained. While cooking and looking after the home did not require a strong educational background, going out of the house to do business demanded an education. It is education which makes a female competent enough to handle the issues of her life, to be self-sufficient, to become an able daughter who can have economic independence and support her family, to stand by her husband in difficult times, and to rear up her children with the right education. Manockjee Cursetjee In 1859, Manockjee Cusetjee started an English school for girls to promote education among women in India. Although in the Vedic period women had access to education in India, they had gradually lost this right. Education provides more strength to women. With two sections of society at the two ends of a balance.
Women Education in India

Literacy Rate of India Census 2011 : Census year Total Population per cent Males per cent Females per cent 1951 18. The major goal of the overall educational program is to educate every girl kid. He empathetically lamented the deep distress of Indian womanhood, while campaibning for widow-remarraige: "The country, whose male population is unkind, unreligious and unaware of the distinction between the good and the evil and don't care about justice and fairness and where abiding the rituals is the chief preoccupation of religion, should not give birth to girls! Women in ancient times rarely went out of their homes. The holistic approach towards the working environment makes them dazzle even in the lame light. Many prestigious Universities were established, and women got enrolled in allied courses to study. One scholar drives home the point that "The lives of Indian women began to change significantly in the late nineteenth century when the colonial government, critical of the treatment of both Indeed, reformist stalwarts like Raja Rammohun Roy formed a coalition power with the British to abolish the social abuse, Sati.
Women Education in India: An Analysis

Calcutta witnessed the contribution of J. It involves changing social mindsets and making housework a task shared among all genders. Read more about Obstacles to Women's Education Obstacles include geographical, socio-cultural, health, economic, religious, legal, political, administrative, and educational reasons, as well as measures by governments, non-governmental organizations, and other organizations to overcome female educational disadvantages. The schools expanded their work under the finances funded by the Hindu aristocracy. We will also study the government initiatives in different cities to improvise the situation.