Women in ancient times played a variety of roles in society, depending on the culture and historical period in which they lived. In some societies, women were highly respected and held positions of power and influence, while in others they were marginalized and treated as second-class citizens.
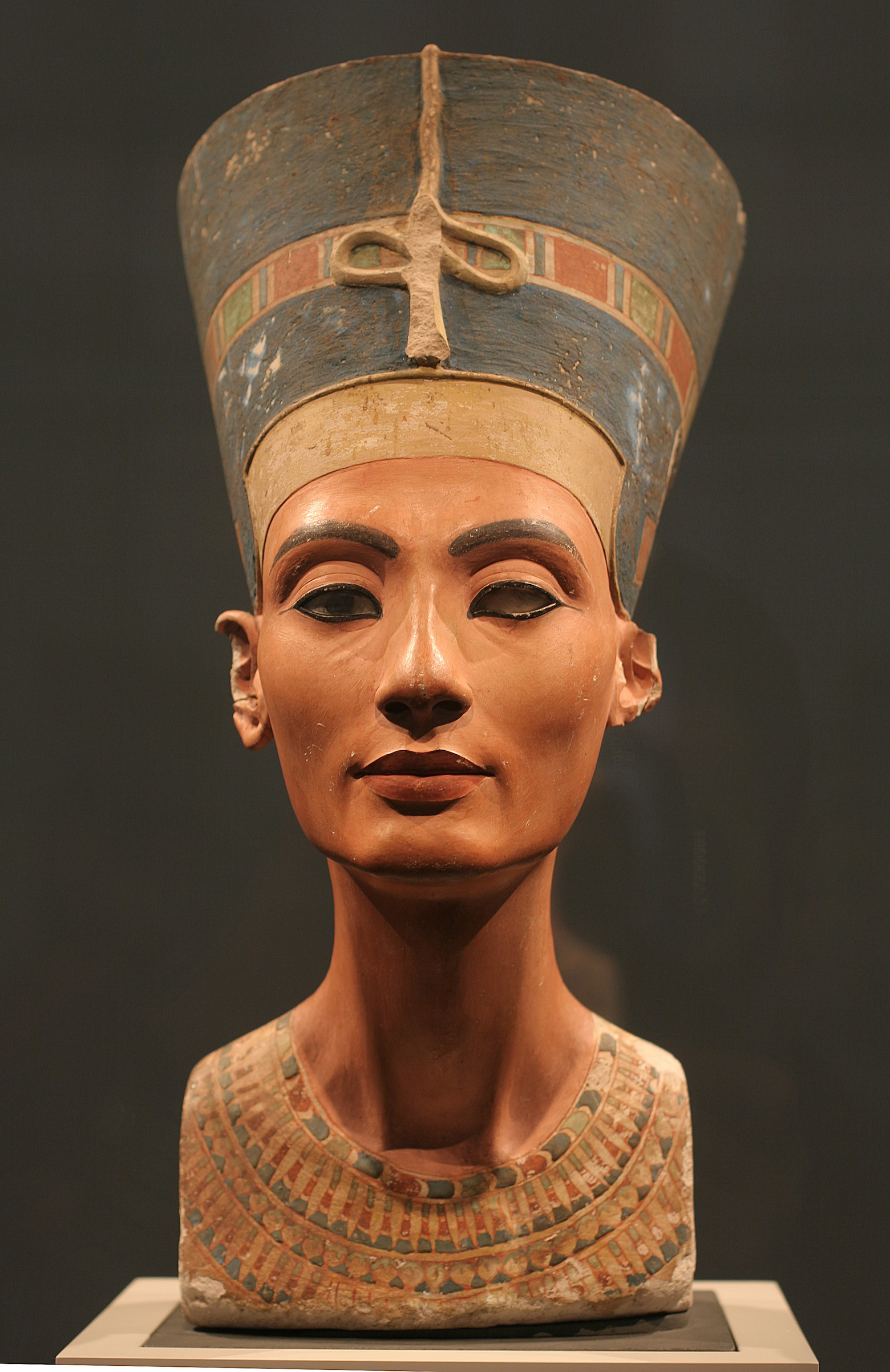
One of the earliest societies in which women played a prominent role was ancient Egypt. During this time, women could inherit property, own businesses, and hold high positions in the government and temple hierarchy. Queen Cleopatra, who ruled Egypt from 51 to 30 BCE, is perhaps the most well-known example of a powerful woman in ancient times. She was a skilled politician and negotiator, and her actions had a significant impact on the course of history.
In ancient Greece, women were not afforded the same rights and privileges as men. They were expected to marry, bear children, and manage the household, and they were not allowed to participate in politics or hold public office. However, some women did achieve fame and success in their own right, such as the philosopher Sappho, who was known for her poetry and her influential role in the development of literature and art.
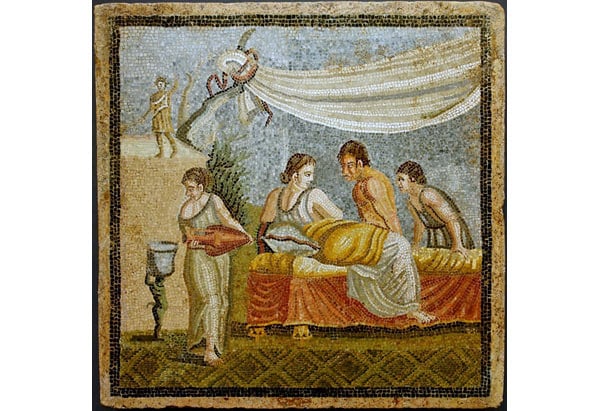
In ancient Rome, women had a somewhat higher status than in Greece, but they were still considered inferior to men. They were allowed to own property and manage their own financial affairs, but they were not allowed to vote or hold public office. Some Roman women, such as the empress Livia, were able to wield significant influence behind the scenes, but this was the exception rather than the rule.
Throughout ancient history, the role of women varied greatly from culture to culture. In some societies, women were respected and held positions of power, while in others they were marginalized and treated as inferior. Despite these differences, women have always played a vital role in the development and progress of human civilization.





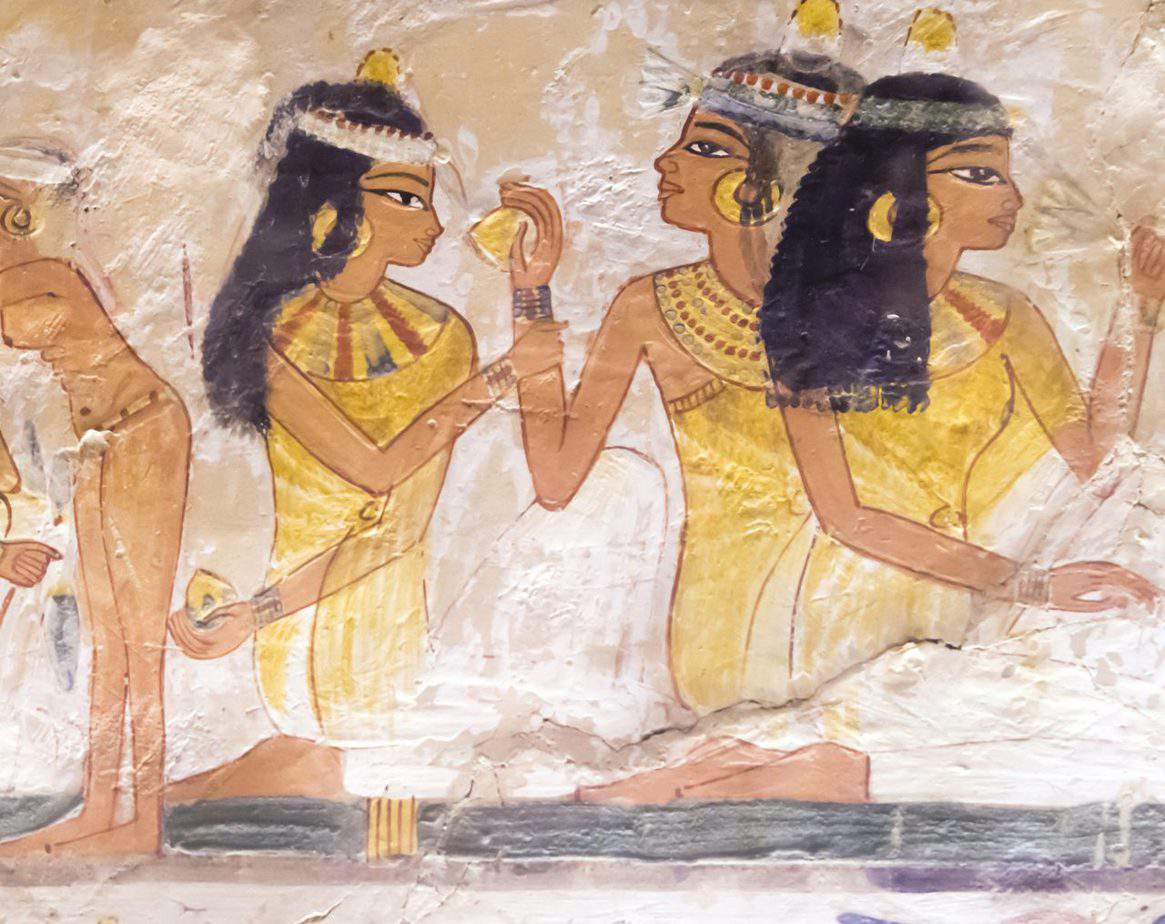

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Boudicca-463982161x-56aa21e55f9b58b7d000f7d3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Zenobia-486776647x-56aa25675f9b58b7d000fd07.jpg)