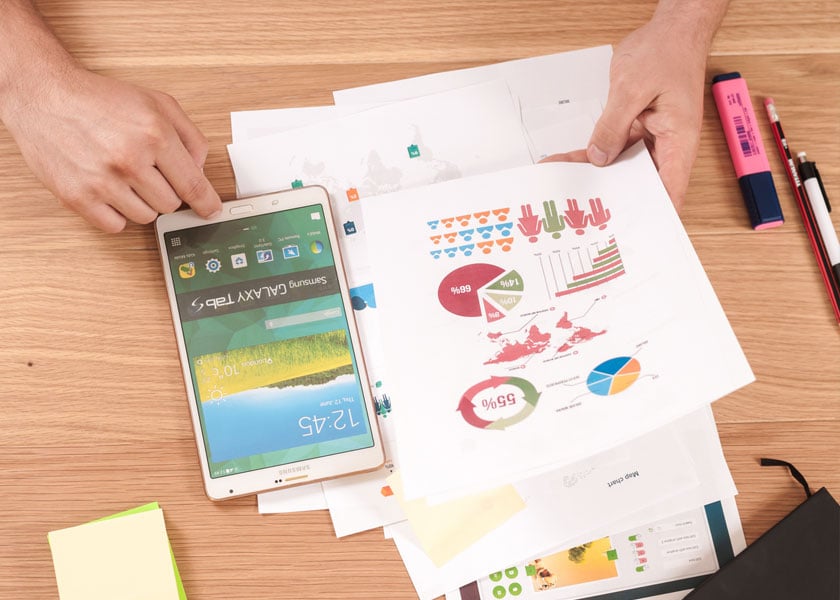
Obedience is a crucial aspect of any society, as it allows individuals to coexist peacefully and work together towards common goals. Without obedience, chaos and anarchy would reign, leading to a breakdown of social order and the inability to accomplish anything as a community.
One of the main benefits of obedience is that it helps to maintain law and order. When people follow rules and laws, they create a sense of stability and predictability in society. This allows people to feel safe and secure, knowing that they can go about their daily lives without fear of harm or disruption.
In addition to maintaining law and order, obedience also promotes efficiency and productivity. When people follow instructions and rules, they can work together effectively and accomplish tasks more efficiently. This is especially important in organizations and institutions, where teamwork and cooperation are essential to success.
Obedience is also important for the development of personal character and values. By learning to follow rules and authority, individuals can learn discipline, responsibility, and respect for others. These values are essential for leading a productive and fulfilling life, both personally and professionally.
However, it is important to note that obedience should not be blindly followed. It is important to critically evaluate the rules and authority figures one is asked to obey, and to question and challenge them when necessary. This helps to ensure that obedience is not used as a tool for oppression or injustice.
In conclusion, obedience is an important aspect of any society, as it helps to maintain law and order, promotes efficiency and productivity, and fosters the development of personal character and values. However, it is important to critically evaluate the rules and authority figures one is asked to obey, and to challenge them when necessary.
Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development outlines eight stages that individuals go through as they develop and mature. The first stage, trust versus mistrust, occurs during the first year of life and is characterized by the development of trust or mistrust in others.
During this stage, infants are dependent on their caregivers for basic needs such as food, warmth, and comfort. If these needs are consistently met in a reliable and predictable manner, the infant will develop a sense of trust in their environment and the people around them. On the other hand, if their needs are not consistently met, or if they are subjected to neglect or abuse, the infant may develop a sense of mistrust and insecurity in their environment and the people around them.
The development of trust versus mistrust is important because it lays the foundation for future relationships and emotional development. Trust allows individuals to feel safe and secure in their relationships, and to be open to new experiences and challenges. Mistrust, on the other hand, can lead to feelings of insecurity, anxiety, and an inability to form close relationships with others.
It is important for caregivers to be attentive and responsive to the needs of infants in order to foster a sense of trust. This can involve providing a consistent and predictable routine, responding to the infant's cries and needs in a timely manner, and being emotionally attuned and supportive.
Erikson's theory of psychosocial development suggests that the development of trust versus mistrust in the first year of life has a lasting impact on an individual's emotional development and relationships. By providing a secure and supportive environment for infants, caregivers can help lay the foundation for a lifetime of trust and healthy relationships.