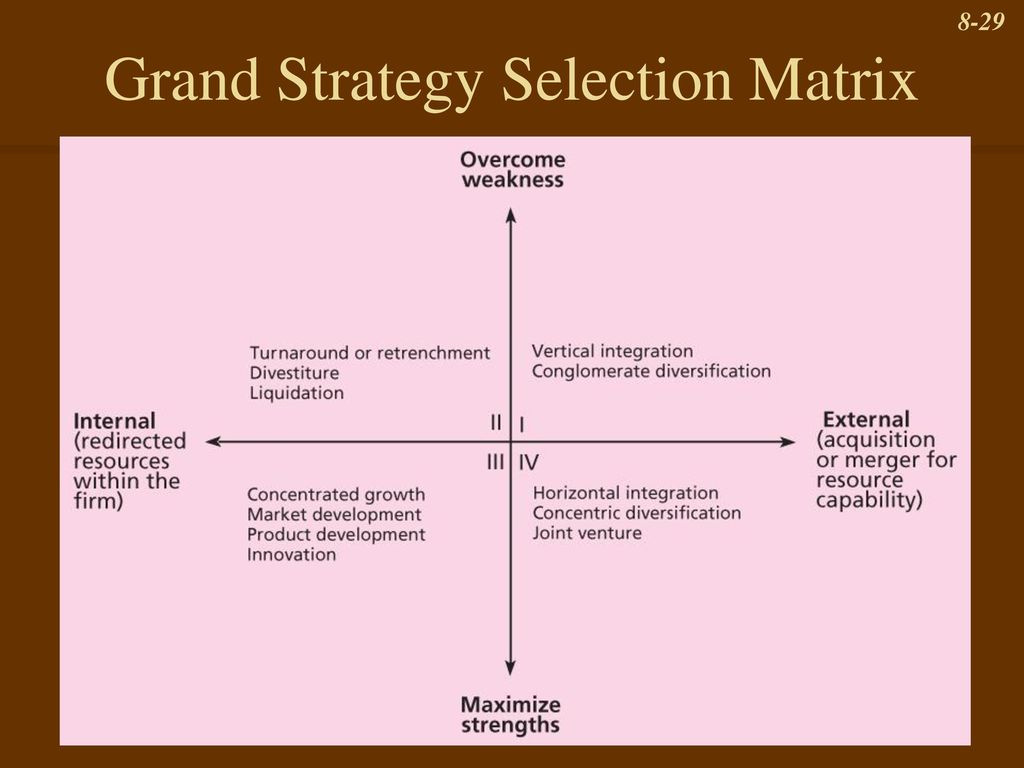
The 15 grand strategies identified by Pearce and Robinson are a set of general strategies that organizations can use to achieve their goals and objectives. These strategies are broad in scope and can be applied to a wide range of organizations, including businesses, non-profits, and government agencies.
The first grand strategy is differentiation, which involves developing and promoting unique products or services that offer value to customers. This strategy can be used to differentiate an organization from its competitors and create a competitive advantage.
The second grand strategy is cost leadership, which involves reducing the costs of producing and delivering products or services in order to offer them at a lower price than competitors. This strategy can be used to increase market share and profitability.
The third grand strategy is focused low cost, which involves targeting a specific market segment and offering products or services at a lower price than competitors in that segment. This strategy can be used to gain a competitive advantage in a specific market.
The fourth grand strategy is focused differentiation, which involves targeting a specific market segment and offering unique products or services that meet the needs and preferences of that segment. This strategy can be used to create a strong brand and loyal customer base in a specific market.
The fifth grand strategy is integrated low cost/differentiation, which involves offering a combination of low prices and unique products or services to customers. This strategy can be used to appeal to a broad range of customers and create a strong competitive advantage.
The sixth grand strategy is market niche, which involves targeting a small, specific market segment and offering products or services that meet the needs of that segment. This strategy can be used to create a strong brand and loyal customer base in a niche market.
The seventh grand strategy is innovation, which involves introducing new products or services to the market or finding new ways to deliver existing products or services. This strategy can be used to create a competitive advantage and increase market share.
The eighth grand strategy is customer intimacy, which involves building close relationships with customers and providing personalized products or services to meet their specific needs. This strategy can be used to create a loyal customer base and increase customer satisfaction.
The ninth grand strategy is operational excellence, which involves maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste in all aspects of the organization's operations. This strategy can be used to reduce costs and increase profitability.
The tenth grand strategy is product leadership, which involves continuously innovating and improving products or services in order to maintain a competitive advantage. This strategy can be used to keep customers interested in an organization's products and services.
The eleventh grand strategy is financial strength, which involves maximizing financial resources and minimizing financial risk in order to increase the organization's financial stability. This strategy can be used to increase the organization's ability to invest in growth and expansion.
The twelfth grand strategy is human resource management, which involves effectively managing and developing the organization's human resources in order to increase productivity and achieve strategic goals. This strategy can be used to create a positive work culture and attract top talent.
The thirteenth grand strategy is corporate social responsibility, which involves considering the social and environmental impacts of the organization's actions and making efforts to be a responsible corporate citizen. This strategy can be used to improve the organization's reputation and build customer loyalty.
The fourteenth grand strategy is globalization, which involves expanding the organization's operations into new international markets. This strategy can be used to increase market share and profitability.
The fifteenth grand strategy is global standardization, which involves adapting products or services to meet the needs of different international markets while maintaining a consistent brand and approach. This strategy can be used to increase the organization's global reach and appeal.
In conclusion, the 15 grand strategies identified by Pearce and Robinson offer a wide range of