Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are the basic unit of communication in the nervous system. They are responsible for transmitting and processing information throughout the body. A nerve cell consists of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axons.
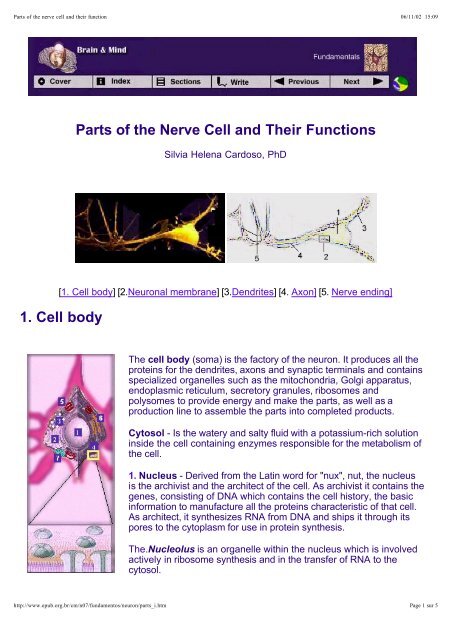
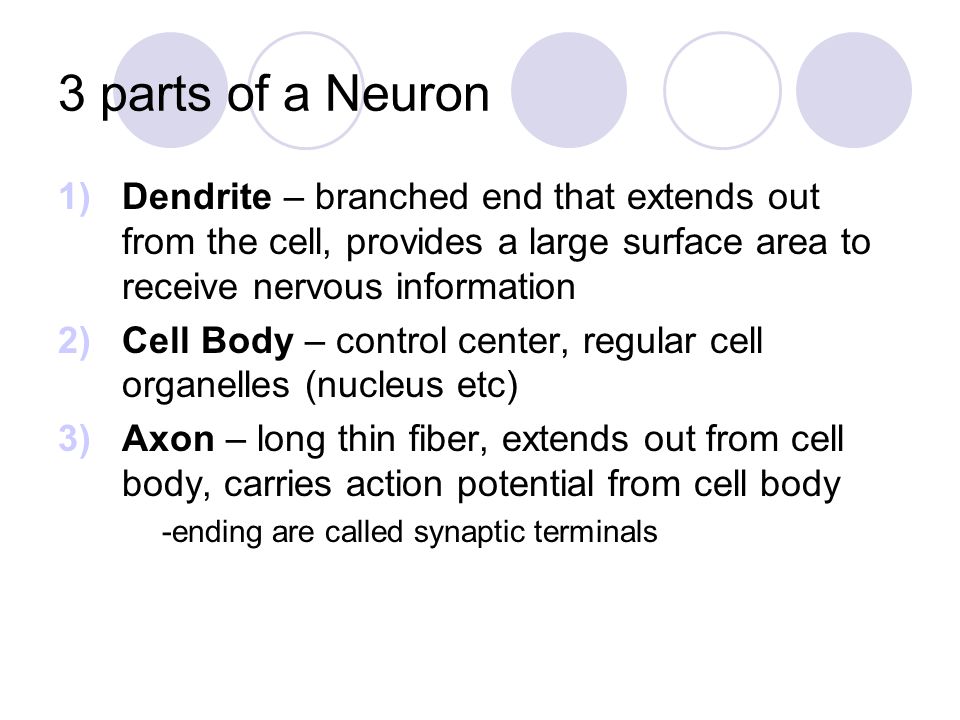
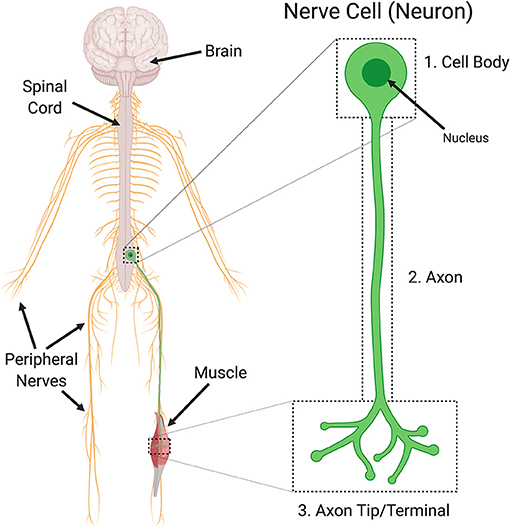
The cell body, also known as the soma, is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the cell's survival, such as mitochondria and ribosomes. The cell body also receives inputs from other neurons through dendrites.
Dendrites are thin, branching processes that extend from the cell body. They are responsible for receiving electrical signals from other neurons and transmitting them to the cell body. Dendrites are highly specialized and are able to detect and respond to specific types of stimuli, such as chemical signals or changes in temperature.
The axon is a long, thin process that extends from the cell body and is responsible for transmitting signals to other neurons or to muscles or glands. Axons can be quite long, with some reaching up to a meter in length in some animals. They are surrounded by a protective layer called the myelin sheath, which helps to insulate the axon and increase the speed of signal transmission.
In summary, the three main parts of a nerve cell are the cell body, dendrites, and axons. The cell body is the central part of the neuron and contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the cell's survival. Dendrites receive inputs from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body. Axons transmit signals to other neurons or to muscles or glands. Together, these three parts work together to transmit and process information throughout the body.
What are the main parts of a nerve cell quizlet?

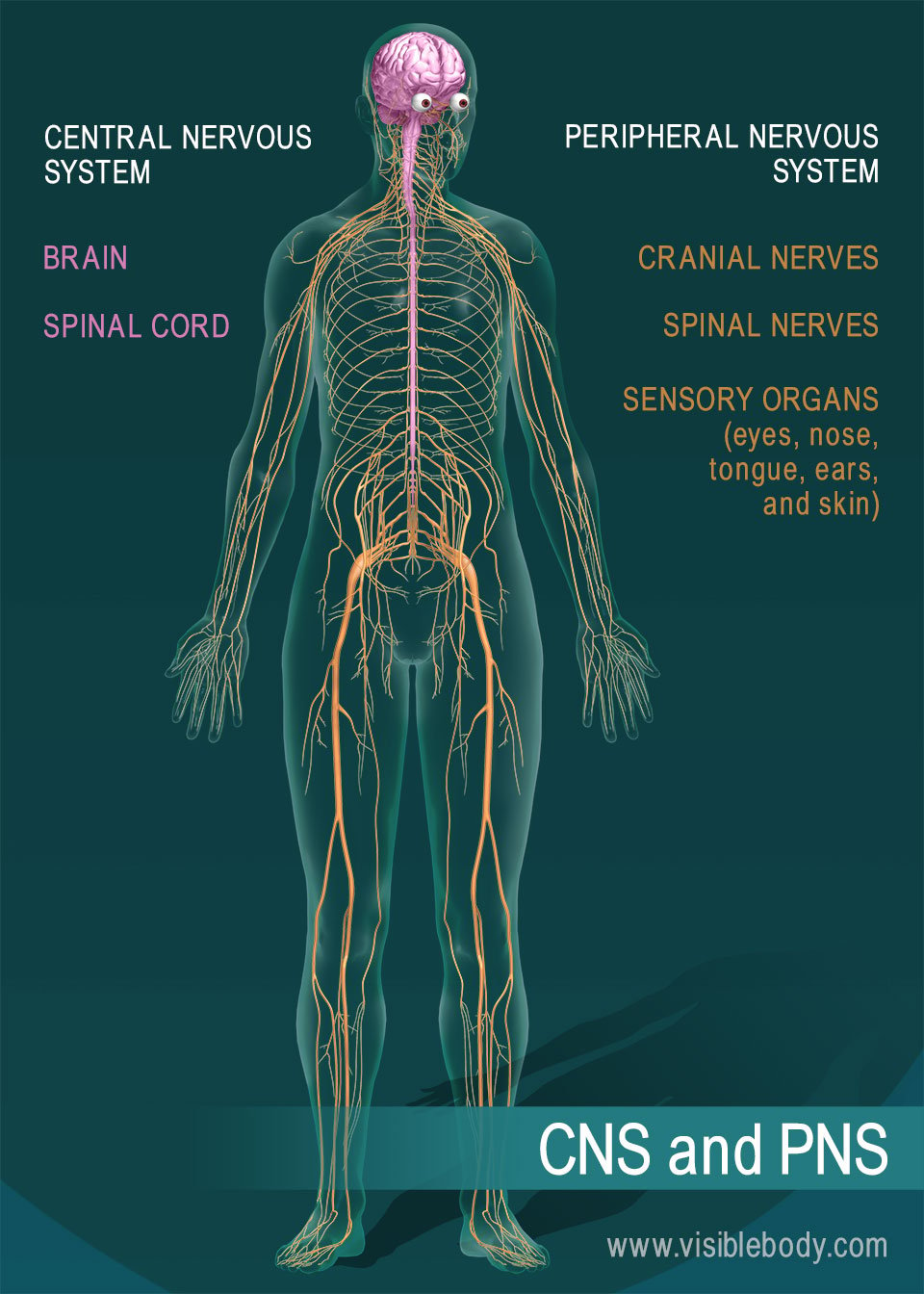
Conditions and Disorders What conditions and disorders affect the nerves? This period is known as the refractory period. The functioning of the nervous system is vital for the control, coordination, and balance of one's body. A neuron has 4 major parts: the dendrites, the cell body, the axon and the axon terminal. What is the main job of nerve cells? The myelin sheath is the outer protective layer of a nerve cell that provides insulation for the smooth transmission of the electric impulses through the axon. There are three major types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons.
Nerve Cell

What is the role of the nerve cell? What is the function of an axon in a nerve cell? Essentially, nerve cells, also known as a neurons, are the active component of the nervous system. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. Arising from the cell body are dendrites branched while the axon extends from one side of the cell body Dendrites Dendrites are the tree-like branched structures that arise from the nerve cell body. Apart from connecting the dendrites and axons, which allows for nerve impulses to be transmitted from one cell to another, the soma is also the site of protein synthesis proteins are synthesized within Nissl body of the rough E. What is the Nervous System? Compared to dendrites, the axon is straighter in appearance and has a smoother surface. The membranes are wrapped tightly around the axon, forming a multilayered sheath.
What are the four parts of a nerve cell?
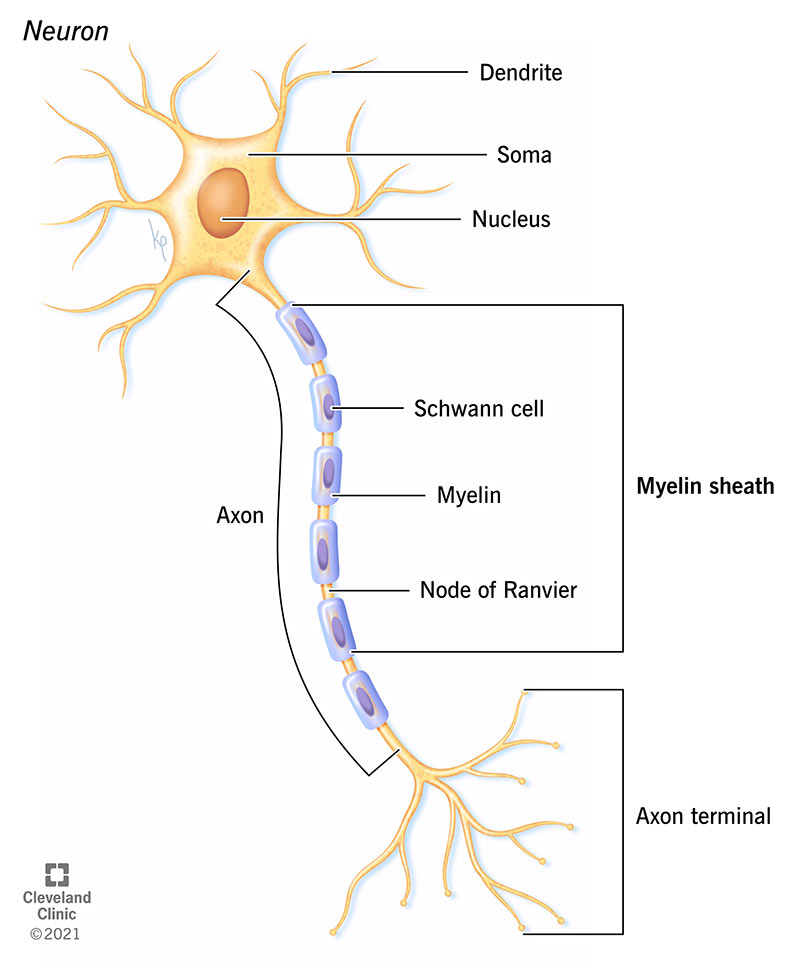
The neurons are those specialized cells that can transmit electrical or chemical signals throughout the body. In addition, compared to dendrites which tend to be highly branched, each neuron has a single axon that extends and branches at its end. The axon is primarily involved in carrying the electrical signals from the cell body to the neuron ending and transmitting it to other surrounding neurons. These cells have three principal parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and one axon. You can improve the health of your entire nervous system by practicing healthy habits, like eating nutritious foods and exercising regularly. Signal transmission in the endocrine system is slow, since hormones must travel through the bloodstream, but the responses tend to last longer.