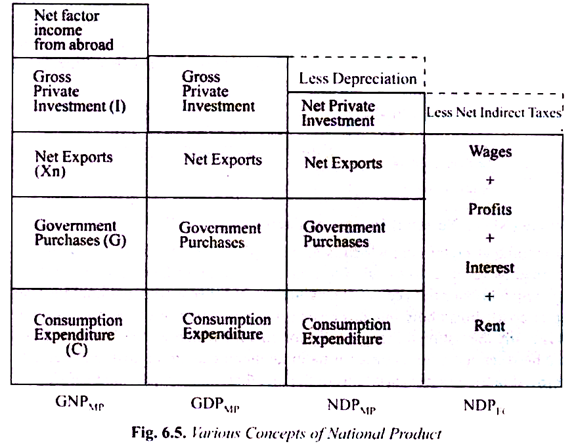
National income is the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given period of time. It is a key measure of a country's economic performance and serves as an indicator of the overall standard of living in a society.
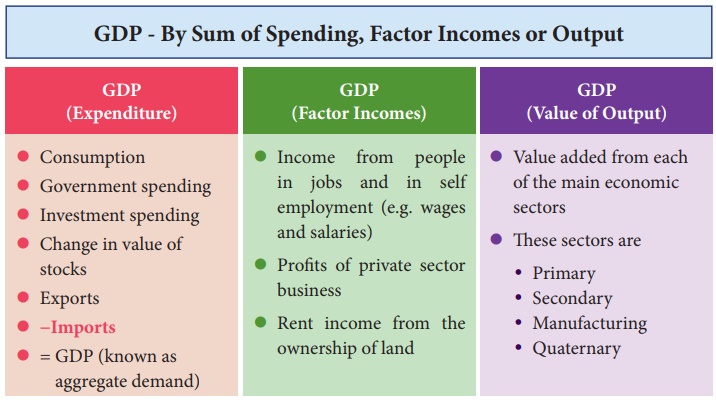
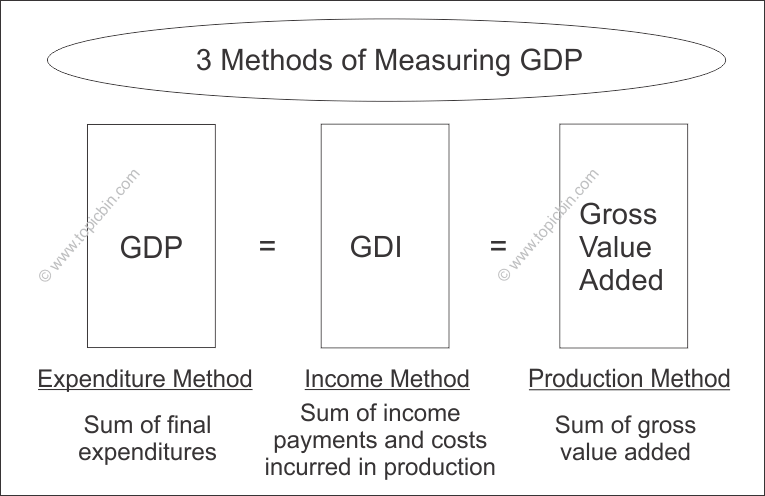
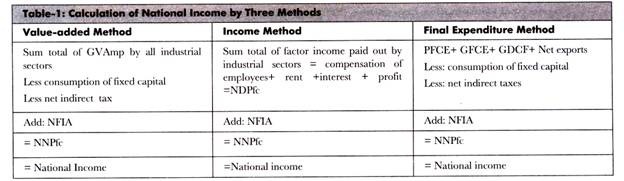
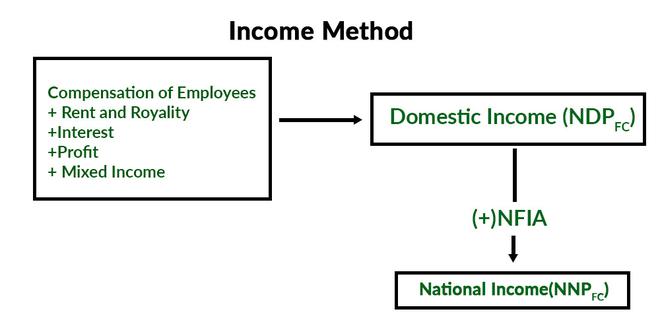
There are several ways to calculate national income, but the most commonly used method is to sum the total value of all goods and services produced in a country, also known as gross domestic product (GDP). This includes both the goods and services produced by the government and those produced by the private sector. GDP can be calculated using either the expenditure approach, which adds up all spending on goods and services, or the income approach, which adds up all the income earned from the production of goods and services.
Another way to measure national income is to use gross national product (GNP), which measures the total value of goods and services produced by a country's citizens, regardless of where they are located. This includes not only the goods and services produced within the country's borders, but also those produced by citizens living abroad.
National income is an important concept for both policymakers and economists because it helps to understand the overall health and growth of an economy. By analyzing national income trends over time, governments can identify areas of strength and weakness within the economy and implement policies to address any issues. Additionally, national income is often used to compare the economic performance of different countries and to assess the overall well-being of a society.
While national income is a useful measure of economic performance, it is not without its limitations. For example, national income does not take into account the distribution of income within a society, meaning it does not consider the gap between the rich and the poor. It also does not account for the value of unpaid work, such as caring for children or the elderly, which can be significant in some societies. Additionally, national income does not consider the negative impacts of economic activity, such as pollution or resource depletion, which can have long-term consequences for both the environment and the economy.
In conclusion, national income is the sum of all goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given period of time. It is a key measure of a country's economic performance and serves as an indicator of the overall standard of living in a society. While useful, national income does have its limitations and should be considered in conjunction with other measures of economic performance and well-being.