4 types of jurisdiction. What are the 4 types of jurisdiction? 2022-12-29
4 types of jurisdiction
Rating:
4,8/10
759
reviews
Jurisdiction refers to the authority of a court or other judicial body to hear and decide cases. There are four main types of jurisdiction:
Personal jurisdiction: This type of jurisdiction refers to the authority of a court to hear cases involving specific individuals or organizations. Personal jurisdiction can be based on the defendant's physical presence in the court's territory, or on their consent to be sued in that jurisdiction.
Subject matter jurisdiction: This type of jurisdiction refers to the authority of a court to hear cases involving certain types of legal issues. For example, federal courts have subject matter jurisdiction over cases involving federal laws or the U.S. Constitution, while state courts have jurisdiction over cases involving state laws.
Territorial jurisdiction: This type of jurisdiction refers to the authority of a court to hear cases that occur within its geographic boundaries. For example, a state court will typically have jurisdiction over cases that take place within the state, while a federal court will have jurisdiction over cases that occur on federal land.
Appellate jurisdiction: This type of jurisdiction refers to the authority of a higher court to review and potentially reverse the decisions of lower courts. Appellate courts have the power to review the legal reasoning and decisions of lower courts, and can either affirm the lower court's decision or remand the case for further proceedings.
In summary, jurisdiction is an important concept in the legal system, as it determines the authority of a court to hear and decide cases. Understanding the different types of jurisdiction can help individuals and organizations navigate the legal system and ensure that their cases are heard by the appropriate court.
The 5 Types of Jurisdiction That May Apply to Your Criminal Case

Therefore, for the purposes of any appeal from or revision of his decision in the exercise of extended jurisdiction, such resident magistrate is deemed to be a judge of the High Court and the court presided over by him while exercising extended jurisdiction shall be deemed to be the High Court. State Courts have subject matter jurisdiction over all suits unless specifically prohibited. Who has jurisdiction over a divorce? That means those courts shall have equal powers when it comes to matrimonial proceedings. . Article 139A of the Constitution of India allows certain cases involving fundamental rights disputes to be transferred from a High Court or multiple High Courts to the Supreme Court.
Next
What are the 4 types of jurisdictions?
Whether+they+share+power+to+hear+the+case+with+State+Courts+or+not..jpg)
However, the individual state plays a leading role in the world organization, although it has multilateral agreements and centralized agreements. State jurisdiction refers to the capacity of a State to prescribe rules of law, enforce them, as well as adjudicate. Jurisdiction is the term that refers to the limits of a legal authority. Before a court can exercise power over a party, the U. These rules of law are applicable to persons, property and events, generally within the territory of the State - land, the State's airspace, as well as internal and territorial water. Can you get divorced in a different state than you were married? International crimes against the international community are punishable under international law. The US Court of Appeals Circuit Courts are the intermediate appellate courts of the federal Judicial Branch.
Next
10 Types Of Jurisdiction (guide + Examples)
What do you understand of doctrine of primary jurisdiction? The Constitution and laws of each state establish the state courts. Definition of jurisdiction 1 : the power, right, or authority to interpret and apply the law a matter that falls within the court's jurisdiction. With territorial jurisdiction, A District Court has jurisdiction within the district in which it is situated, and a court of a resident magistrate has jurisdiction in the region within which it is situated. What is the state jurisdiction? Articles 132 and 133 of the Constitution of India establish the appellate jurisdiction of the Supreme Court. What is preclusion law? Enforcement jurisdiction is the ability of a State to effectively enforce its law through the exercise of executive and judicial power. It is also a kind of criminal justice, but we will deal with that principle separately. What is limited original jurisdiction? Constitution requires that the party has certain minimum contacts with the forum in which the court sits.
Next
What are the different types of courts and their jurisdictions?
Mississippi, South Dakota and Tennessee are the only states that require mutual consent for no-fault divorce. . Private jurisdiction is the right of an individual or a legal entity to establish courts of law. What does limited jurisdiction mean? Answer and Explanation: The two types of jurisdiction exercised by courts are original jurisdiction and appellate jurisdiction. The jurisdiction of a nation over its sovereign territory is exclusive and perfect. What are the four types of state courts? This immunity is a creation of customary international law, which derives from the principles of the independence and equality of sovereign States. What is administrative law Philippines? Each of the states except for Tasmania also has three levels of courts of general jurisdiction: the state Supreme Court, the District Court called County Court in Victoria and the Local Court.
Next
What are 3 types of jurisdiction?
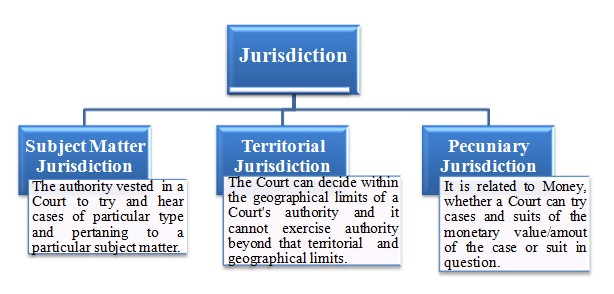
Justices hold office during good behavior, typically, for life. This means that if a person is charged with both felony and misdemeanor counts, the felony court can hear both cases — but not vice versa. What is jurisdiction of a court? Under sub-clause 2 of section 13 of the Act, there are available four ground on which the wife alone can file a divorce petition. Pecuniary Jurisdiction Pecuniary Jurisdiction means a limitation of the powers of a court by the value of the subject matter in issue. Determining jurisdiction helps define how a case shall be tried, and at what level of the courts. . United States Courts of Special Jurisdiction These courts cover the Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces, the Court of Federal Claims, the Court of International Trade, the Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims, the Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation and the Tax Court.
Next
Types of Jurisdiction of Supreme Court

Briefly explain the Advisory Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of India. . According to the principle of universality, each State has jurisdiction over international crimes committed by human beings. The court at the trial level hears original jurisdiction. Due to the statutory limitations imposed, even though states have the power to decide over whom their courts may exercise jurisdiction, before the exercise of such jurisdiction, courts should look into the state law to determine whether the court can properly exercise personal jurisdiction. Types of Jurisdiction The following are the types of jurisdiction; Original Jurisdiction Original Jurisdiction refers to the power of a court to hear or try a case as a matter of the first instance. Property that was brought into your marriage is yours to keep, but any increases in the value of this property during the duration of marriage must be shared.
Next
Types of Jurisdiction in International Law

A federal Supreme Court judge can only be removed from their position by retirement, death, or by impeachment. The Constitution confers federal question jurisdiction on federal district courts. There are four main types of jurisdiction arranged from greatest Air Force authority to least : 1 exclusive federal jurisdiction; 2 concurrent federal jurisdic- tion; 3 partial federal jurisdiction; and 4 proprietary jurisdiction. The Constitution states that the Supreme Court has both original and appellate jurisdiction. The applicant argued that the seizure was null and void and without the authorisation of a court. What are the 4 types of cases where the Federal Court has original jurisdiction? Judicial activism is the assertion or, sometimes, the unjustified assertion of the power of judicial review to set aside government acts.
Next
What are the 6 types of jurisdiction?

What are the 2 types of court system in the world? The two types of judicial systems increasingly predominant in the contemporary world Civil and Common Law share a basic common, though distant, root: Roman Law, Justinianean and Classic, respectively van Caenegem 1988. Special jurisdiction, courts which have the power to hear only certain types of cases, or are clothed with special powers for the performance of specified duties beyond which they have no authority of any kind. Prescriptive jurisdiction is the power to regulate an activity and prescribe certain behaviours. Writs of Certiorari The primary means to petition the court for review is to ask it to grant a writ of certiorari. In practice, this limits prescriptive jurisdiction because one State cannot apply its prescriptive jurisdiction in another State; The work of the police and the judiciary is limited to the territory of the State.
Next
What are the four types of court jurisdiction?

Further, the case of R. Supreme Court and gives Congress the authority to create the lower federal courts. As a result of the ongoing proceedings, the passport was confiscated by the defendant. How many jurisdiction are there? There are varying types of jurisdiction in the legal system: original, appellate, exclusive, and concurrent. However to exercise in rem jurisdiction, the property must generally be located within physical boundaries of the state. The doctrine of primary jurisdiction requires the court to allow for a referral to the agency by staying further judicial proceedings so as to give the parties a reasonable opportunity to seek an administrative ruling. If the court discovers, on reading the charge, or in the course of the trial, that the offence was committed outside its territorial jurisdiction, it must immediately make an order transferring the case to the court within whose jurisdiction the offence was committed.
Next

Whether+they+share+power+to+hear+the+case+with+State+Courts+or+not..jpg)






