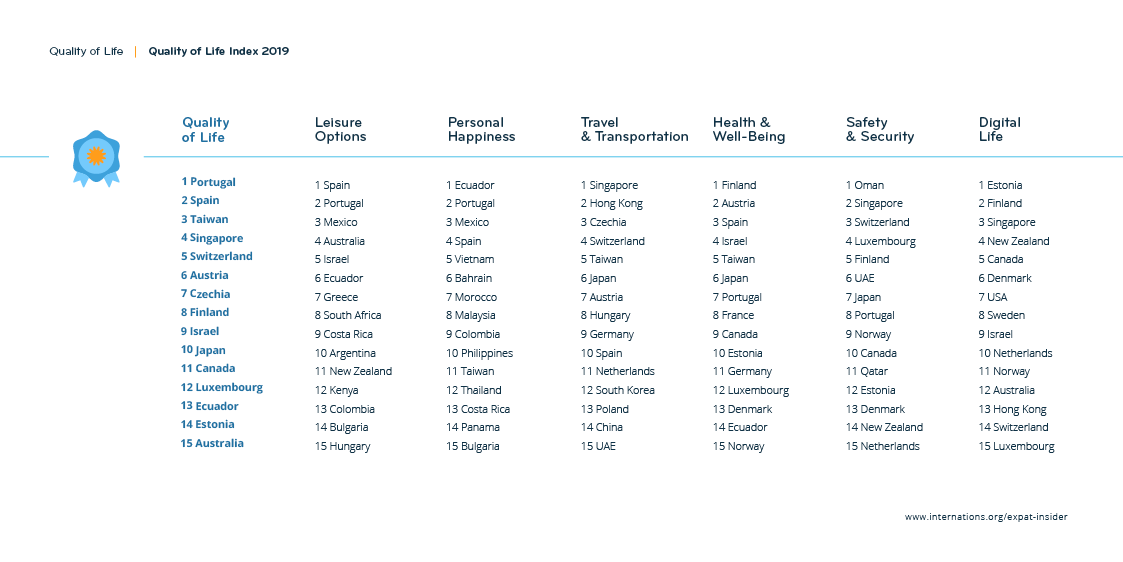
A nation state is a sovereign state that consists of a particular nation or ethnic group and occupies a defined territory. It is characterized by several important qualities that differentiate it from other forms of political organization.
One key quality of a nation state is its sovereignty, which refers to its independence and self-governance. A nation state is not subject to the authority of any external power, and it has the right to make and enforce its own laws and policies. This sovereignty is reflected in the fact that a nation state has a monopoly on the legitimate use of force within its borders, and it is responsible for the security and well-being of its citizens.
Another quality of a nation state is its territoriality, which refers to the fact that it occupies a specific territory and is recognized as such by other states. This territory is typically defined by clear and internationally recognized borders, and it is protected by the nation state's military and other security forces.
A nation state also has a distinct culture and identity, which is shaped by its history, language, customs, and values. This culture and identity are often closely tied to the nation or ethnic group that makes up the majority of the population.
Finally, a nation state has a system of government that is responsible for managing the affairs of the state and representing the interests of its citizens. This system may be democratic, authoritarian, or somewhere in between, and it is typically characterized by a separation of powers and checks and balances to ensure accountability and transparency.
In summary, a nation state is a sovereign and independent entity that occupies a defined territory, has a distinct culture and identity, and has a system of government that manages the affairs of the state and represents the interests of its citizens. These qualities are essential to the functioning of a nation state and are key to its ability to provide security, stability, and prosperity for its citizens.