Soil is a vital component of the earth's ecosystem, as it serves as a medium for plant growth and plays a crucial role in the water cycle. One of the key functions of soil is its ability to absorb and retain water, which is essential for the survival of plants. In this essay, we will explore the process of water absorption by soil and the factors that influence this process.
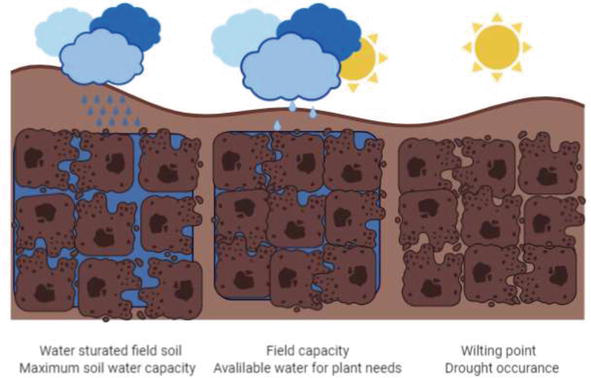
The absorption of water by soil is a complex process that involves several physical and chemical factors. The most important factor is the porosity of the soil, which refers to the amount of empty space within the soil. Soils with high porosity are able to absorb more water than soils with low porosity. The size and shape of the soil particles also play a role in water absorption. Soils with larger and more rounded particles tend to have higher porosity and are therefore better at absorbing water.
The structure of the soil also plays a role in water absorption. Soils with a well-developed structure, such as those with a high content of organic matter, are able to absorb and retain more water than soils with a poorly developed structure. The presence of soil organic matter increases the water-holding capacity of soil by providing a network of pores and channels that allow water to flow through the soil.
The chemical properties of the soil also influence its ability to absorb water. Soils with a high pH, or alkaline soils, tend to have lower water-holding capacity than acidic soils. This is because the high pH of alkaline soils can cause the soil particles to become coated with an impermeable layer of calcium carbonate, which reduces the soil's ability to absorb water.
In addition to these physical and chemical factors, the rate of water absorption by soil is also influenced by environmental conditions. The temperature of the soil, the humidity of the air, and the amount of sunlight all play a role in the absorption of water by soil. For example, warmer soils tend to absorb water more quickly than colder soils, and soils exposed to direct sunlight tend to dry out faster than soils in the shade.
Overall, the absorption of water by soil is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of physical, chemical, and environmental factors. Understanding these factors is important for effectively managing soil and ensuring that it is able to support healthy plant growth. So, proper management of soil can help to improve the water-holding capacity of soil and ensure that plants have a reliable source of water.
Water Absorption: Organ, Mechanism, Factors and Methods
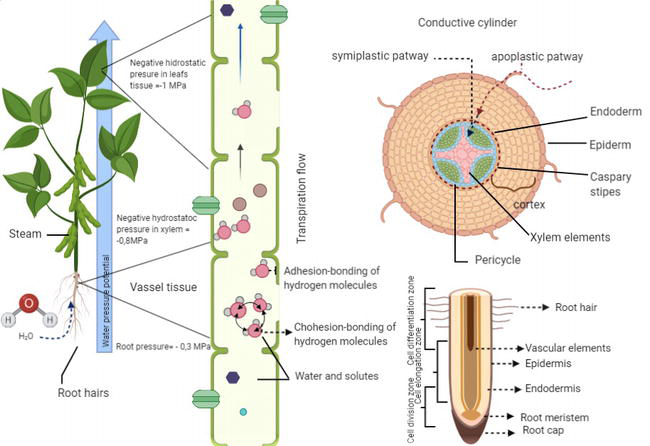
Role of Root Hairs in Water Absorption A root contains some tubular, hair-like and unicellular structures called Root hairs. For clayey soil, the adsorbed water is in the diffused double-layer form. ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make in-depth study of the organ, mechanism, factors and methods of water absorption. Cations with the same charge in an alkaline environment do not cause precipitation coagulation of colloids. Many other factors, such as permeability, infiltration rate, percolation, and more, affect the water absorption of soil also. Mineral colloids include crystalline clay minerals of kaolinite and montmorillonite groups, hydromica and amorphous compounds oxide hydrates of the R2O3 type, silicic acid, etc.
How microbes help release soil nutrients and reduce the need for ferti

Percolation studies are important for two reasons- 1 Percolating water is only source of recharge of ground water, which can be again be profitably used through springs and wells for irrigation. Chemical absorption capacity of soils is the ability of the soil to retain ions through the formation of insoluble compounds as a result of chemical reactions, or, the ability of the soil to convert anions and cations of the soil solution into insoluble substances. Some Substances Present in the Soil: Some substances, occurring in the soil, affect the absorption of water on account of their chemical nature quite apart from their osmotic properties. As a result, soil water enters into cortical cells through root hairs. Therefore, clayey and loamy soils are characterized by more mechanical absorption capacity than sandy and sandy loam soils. This type of soil is called a saturated soil.
Water Absorption by Plants : Plantlet
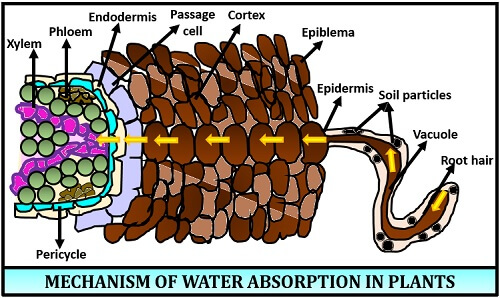
Hydrogen cation gradually destroys the SAC minerals, deteriorating the soil structure, impoverishing it with colloidal fraction and reducing the CEC, which in general negatively affects the growth, development and crop yields. Mechanism of absorption of water In higher plants, water is absorbed through root hairs which are in contact with soil water and form a root hair zone a little behind the root tips. Soils with high content of highly dispersed particles have high absorption capacity; clayey soils have higher absorption capacity than sandy soils. Teruo Higa, a Japanese Agricultural Scientist. The total water content in the soil is called holard. Peat soil is acidic and inhibits decomposition, which means it contains a high proportion of organic matter. The microbes provide the nutrients that plants need to grow and also help with nutrient absorption, water absorption, root size, and other physical functions of the plant.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/process-of-using-water-by-trees-1343505_final_edit_LR-922375b4399c4613b38c0973c50b5089.jpg)

