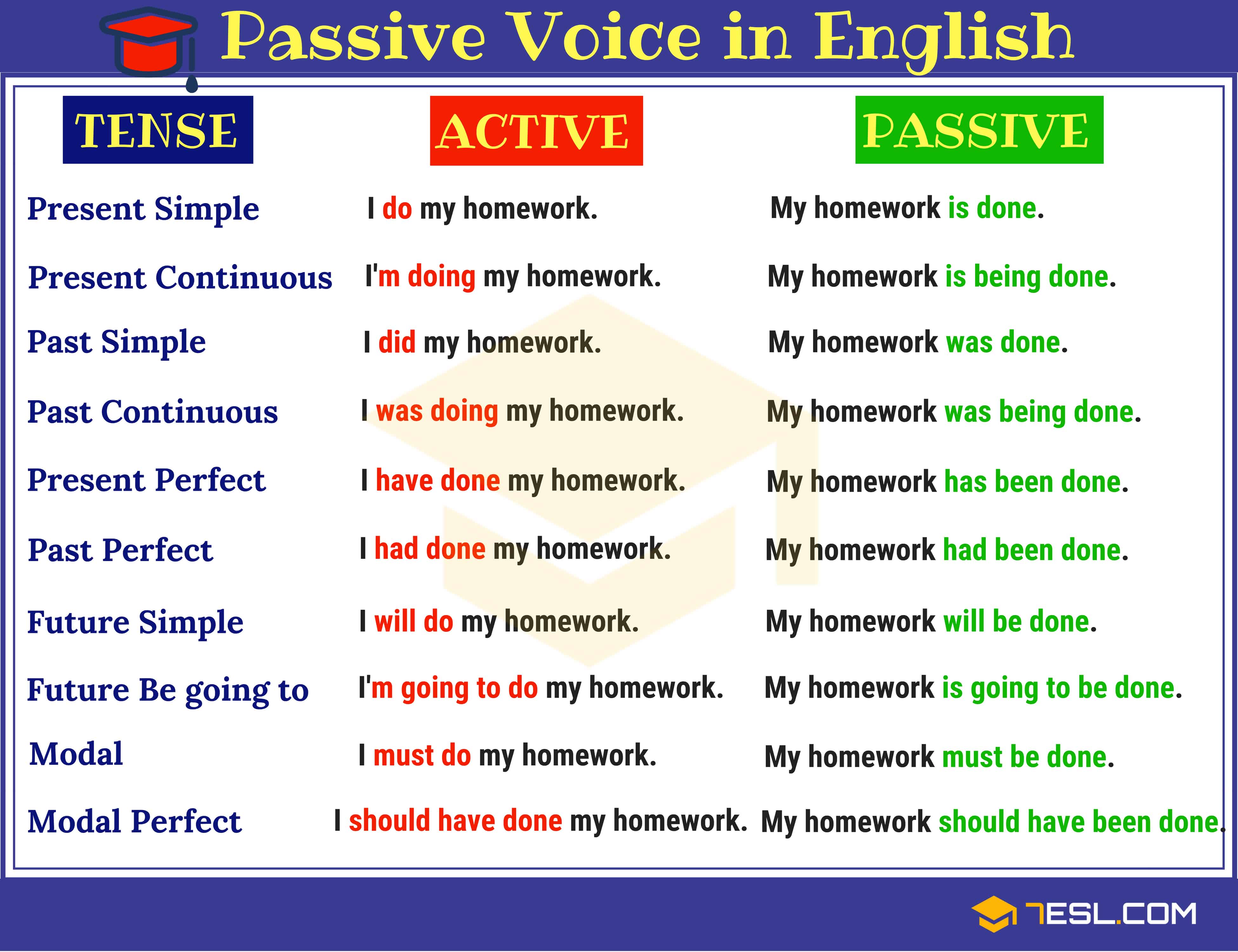
In written and spoken language, the active voice refers to a sentence construction in which the subject performs the action stated by the verb. In contrast, the passive voice is a sentence construction in which the subject is acted upon by the verb.
Using the active voice can make writing and speaking more direct, clear, and concise. It can also make the subject of the sentence more prominent and give the sentence more emphasis. For example, consider the following two sentences:
Active voice: "The teacher graded the exams." Passive voice: "The exams were graded by the teacher."
In the active voice sentence, the subject "the teacher" is performing the action of grading. In the passive voice sentence, the subject "the exams" is being acted upon by the verb "graded." The passive voice sentence is longer and less direct than the active voice sentence.
There are times when it is appropriate to use the passive voice, such as when the focus of the sentence is on the object rather than the subject. For example: "The cake was eaten by the dog." In this sentence, the focus is on the cake that was eaten, rather than the dog that did the eating.
However, in general, it is recommended to use the active voice as it can make writing and speaking more clear, concise, and engaging. To use the active voice, identify the subject of the sentence and make sure that it is performing the action stated by the verb.
In summary, the active voice is a sentence construction in which the subject performs the action stated by the verb. It can make writing and speaking more direct, clear, and concise, and is generally preferred over the passive voice. By identifying the subject and ensuring that it is performing the action stated by the verb, writers and speakers can effectively use the active voice in their language.



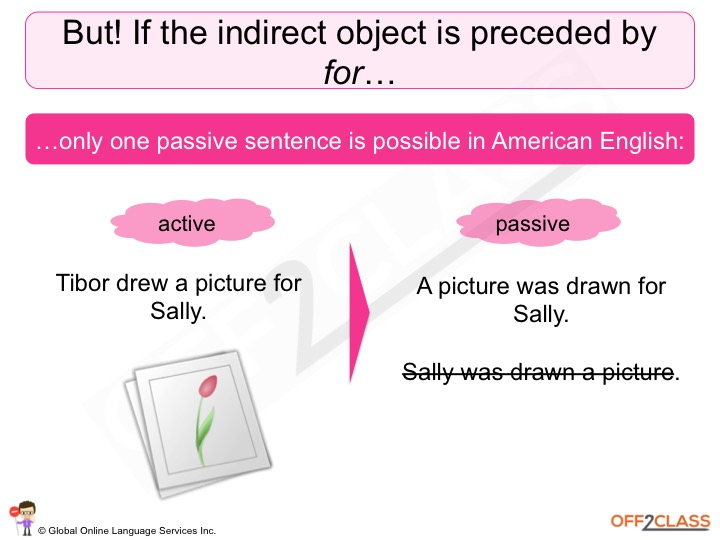




/files/img/2015-12-13_1601.png)