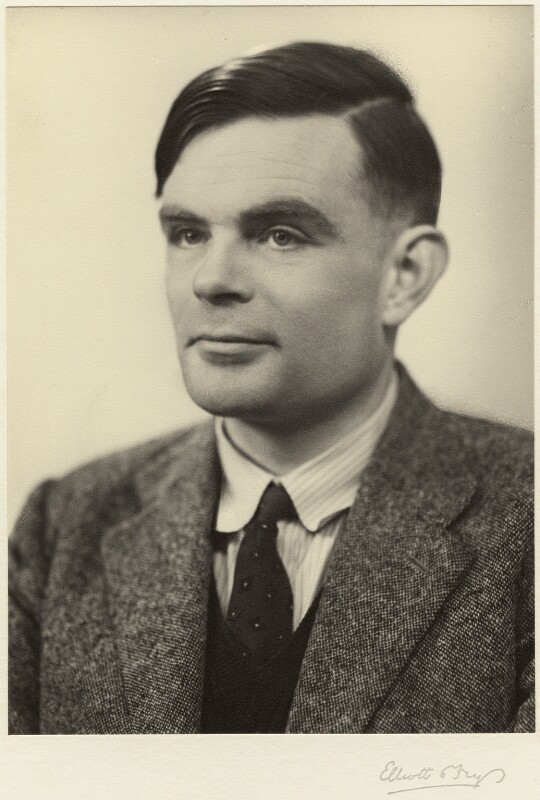
Alan Turing was a British mathematician, computer scientist, and war hero who made significant contributions to the fields of computer science and artificial intelligence. In 1950, he gave a historic speech at the London Mathematical Society in which he outlined his theory of computation and the concept of a universal machine, which later became known as the Turing machine.
Turing's speech, entitled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," was the first to propose the idea of a machine that could perform any computation that a human could. In his speech, Turing argued that it was possible to build a machine that could think and reason like a human, and that this would eventually lead to the creation of artificial intelligence.
Turing's ideas were revolutionary at the time, and they laid the foundation for the development of modern computers and artificial intelligence. In the speech, Turing outlined the concept of the Turing machine, a hypothetical device that could read and write symbols on a tape, and perform a set of predetermined actions based on the symbols it encountered.
Turing's speech had a huge impact on the field of computer science, and it is still considered one of the most important works in the history of artificial intelligence. The concept of the Turing machine has been used as the basis for many of the computers and algorithms that we use today, and it has played a critical role in the development of modern computing.
Despite the significant contributions that Turing made to the field of computer science and artificial intelligence, he is perhaps best known for his work as a codebreaker during World War II. As part of the British government's codebreaking team, Turing played a crucial role in breaking the Enigma code, which was used by the Germans to encrypt their military communications. Turing's work helped to shorten the war by several years and save countless lives.
Alan Turing was a brilliant and innovative thinker who changed the course of history with his groundbreaking ideas and discoveries. His speech at the London Mathematical Society laid the foundation for the development of modern computers and artificial intelligence, and his contributions to the field of codebreaking during World War II will be remembered for generations to come.