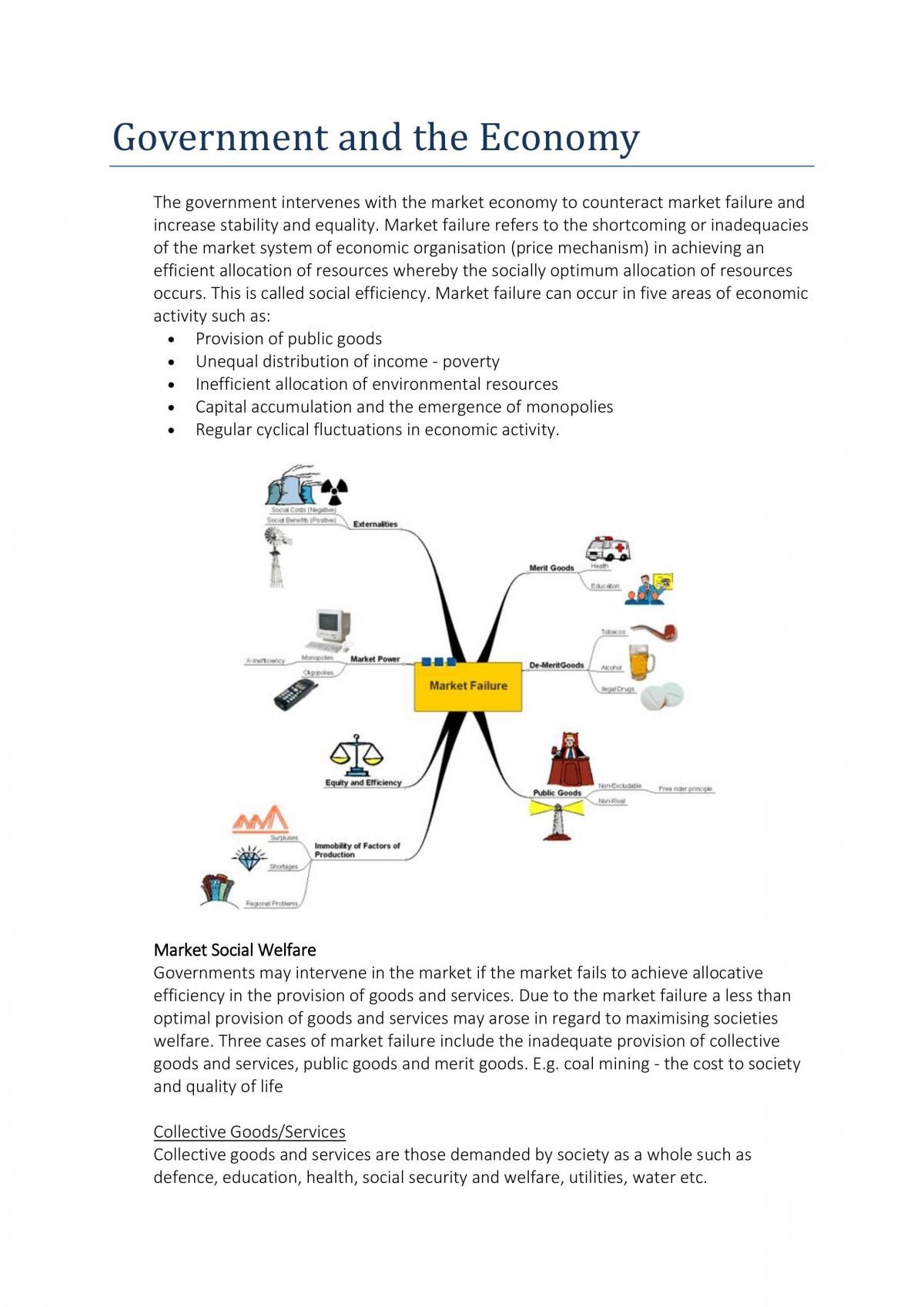
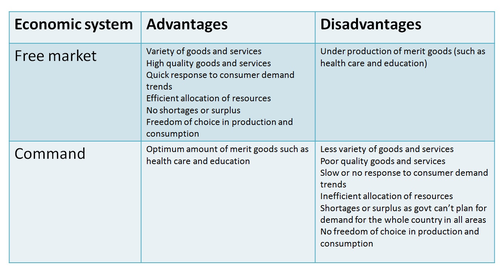
In a market economy, resources are allocated through the interaction of supply and demand in the market. This allocation of resources is guided by the profit motive, as firms seek to produce and sell goods and services in order to make a profit.
One of the key principles of a market economy is the concept of opportunity cost. This refers to the cost of forgoing the next best alternative when a decision is made. For example, if a firm decides to use its resources to produce one product, it is forgoing the opportunity to produce another product. The opportunity cost of producing one product is the value of the next best alternative that could have been produced.
In a market economy, firms must take into account the opportunity cost of using their resources in order to make the most profitable decisions. If the price of a good or service is higher than the cost of producing it, including the opportunity cost of using the resources, the firm will choose to produce it. If the price is lower than the cost, the firm will choose not to produce it. This decision-making process helps to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
There are also external factors that can influence the allocation of resources in a market economy. Government policies and regulations, such as taxes and subsidies, can affect the supply and demand of goods and services and therefore the allocation of resources. Natural disasters, technological innovations, and changes in consumer preferences can also impact the market and the allocation of resources.
Despite its benefits, the market economy has its limitations in terms of resource allocation. One criticism is that it may not always allocate resources in a way that is best for society as a whole. For example, the market may not adequately provide for the basic needs of certain individuals or groups, such as the poor or the elderly. In addition, the market may not always allocate resources efficiently, leading to overproduction or underproduction of certain goods and services.
Overall, the allocation of resources in a market economy is driven by the profit motive and guided by the principle of opportunity cost. While it has its limitations, the market economy has proven to be a successful system for allocating resources and promoting economic growth.