Ancient greek kouros. What does kouros mean in Greek? 2023-01-04
Ancient greek kouros
Rating:
7,4/10
526
reviews
The ancient Greek kouros is a type of sculpture that represents a young male figure, typically standing in a stiff, upright pose with the arms at the sides and the legs together. These sculptures were created during the Archaic period of ancient Greece, which lasted from the 8th to the 6th centuries BCE. The kouros served as a funerary monument, a votive offering, or a dedication to a god or hero.
The kouros was an important artistic and cultural expression of the ancient Greeks, and it played a significant role in their society. The kouros represented the idealized form of the male body, and it was meant to convey the strength and beauty of youth. These sculptures were often depicted in the nude, and they were designed to be viewed from all angles.
The first kouros sculptures appeared in the late 8th century BCE, and they were typically made of marble or bronze. The most famous kouros is the one known as the "Kritios Boy," which was created around 480 BCE and is now housed in the Acropolis Museum in Athens. This sculpture is considered to be a transition piece between the Archaic and Classical styles of Greek art, and it is notable for its more relaxed and naturalistic pose.
The kouros was an important artistic tradition in ancient Greece, and it continued to be popular throughout the Archaic and Classical periods. These sculptures were highly prized for their beauty and craftsmanship, and they were often used as decorations in temples and public spaces.
Despite the popularity of the kouros, it was not without its critics. Some ancient Greeks felt that the rigid, formal pose of the kouros was not an accurate representation of the human body, and they called for a more naturalistic approach to sculpture. This led to the development of the Classical style, which featured more lifelike and realistic figures.
Overall, the ancient Greek kouros was an important cultural expression of the ancient Greeks, and it played a significant role in their society. These sculptures continue to be admired for their beauty and craftsmanship, and they serve as a reminder of the artistic traditions of ancient Greece.
Kouros (The J. Paul Getty Museum Collection)

Richter, Korai: archaic Greek maidens: a study of the development of the Kore type in Greek sculpture London: Phaidon, 1968. Many books call these statues " " Ἀπόλλων but it is not certain whether this is so, except in limited instances where it can be demonstrated. Their female counterparts, korai singular: kore , wear richly painted robes and accessories made of expensive metals. Sackler Museum, Harvard Art Museums. Eyes are not so large as before and more rounded. This kore and others like her might instead represent actual young women who served the goddess as attendants. Guide to the Collections: Ancient and Oriental Art--Egyptian, Mesopotamian, Greek and Roman Far Eastern, Near Eastern Oriental Armor, Vol.
Next
Kouros

When did the kouros sculpture develop? What was the female version of the kouros? The youths are portrayed in perfect physical condition, if not overtly muscular. The characteristics of this style are as follows. Whereas early korai are extremely modest and show almost no indication of their bodies beneath their robes, Egyptian statues of women tend to show more of their form. A 5m tall statue of Poseidon used to stand inside the temple, but today only a part of it survives and it is displayed in the Archaeological Museum of Athens. Shoulder blades are now separate raised planes. Klǽovis and Víton were the sons of Kydíppi Cydippe, Κυδίππη , the priestess of Hera, Ήρα at Árgos Ἄργος. The arms have been cut by the stonemasons as rudimentary rectangles and the shaping of the feet had been begun; they are located on a 50cm high plinth.
Next
What does kouros mean in Greek?
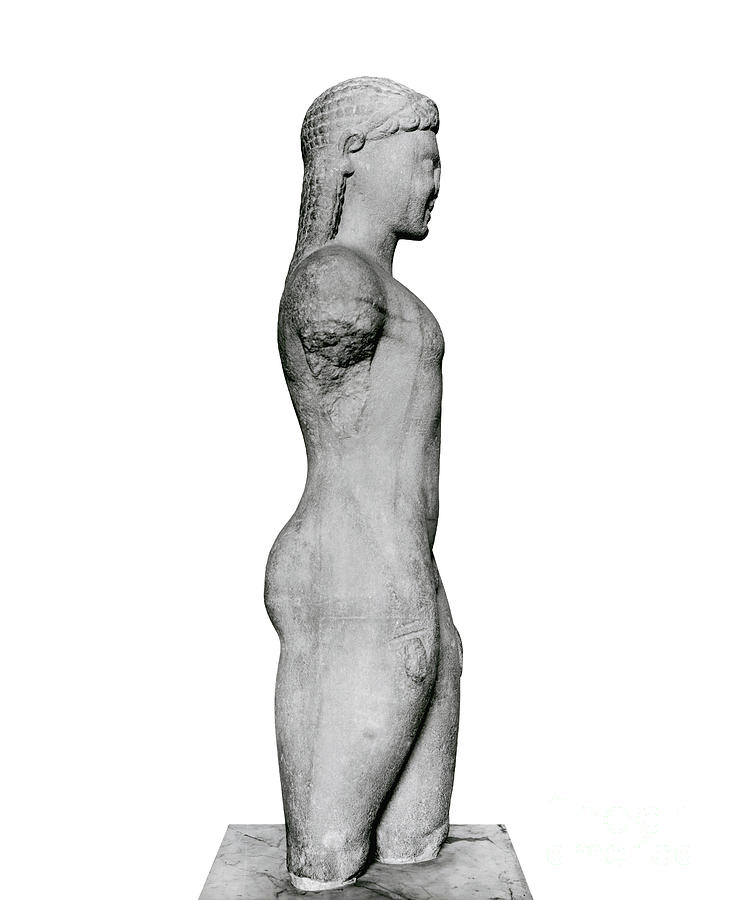
Gardner's Art through the Ages: The Western Perspective. Another subject, which is vehemently correlated to the personal outlook, is the dominating existence of sexuality in the Greek culture Lloyd and Calame 200. Antenor Kore, 525—500 B. Attic, Archaic , Naxian marble, 194. The lachrymal caruncle is sometimes indicated. As such, it can be concluded that through different periods of Greek history, female and male representation in art was solely based on their societal roles and moral principles within various time frames but that female nude representation remained more restrictive than those of males.
Next
New York Kouros

FOTO: Public Domain: commons. Catalogue of Greek Sculptures. The Sculpture and Sculptors of the Greeks, 3rd edn. Standing more than 15 feet tall, this statue has a fleshy body with no indication of individually defined muscles or bones. Athens, Kouros from Merenda.
Next
blog.sigma-systems.com

This is one of the earliest marble statues of a human figure carved in Attica. Richter, Kouroi: archaic Greek youths: a study of the development of the Kouros type in Greek sculpture London: Phaidon, 1970. Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 2004. The unfinished kouros lies in a rough stone slope. Heidelberg, DE: Verlag Archäologie und Geschichte. Greek Sculpture: An Exploration. Firstly, it has to be mentioned that Kouros implies the portrayal of young boys or adolescents Pache 72.
Next
Marble statue of a kouros (youth)

Kouroi and korai are highly idealized images. Statue of a woman Lady of Auxerre , c. These elite individuals conflated bodily beauty with moral excellence, so from their viewpoint, the idealized statues of young men and women that they commissioned displayed both inner and outer greatness. Barringer, Francois Lissarrague, and Edinburgh University Press. One was located in the quarry of Apollonas until Ludwig Ross transferred it to the Museum at Athens in 1834. The upper limit of this group may be fixed by the sculpture of the temple of Apollo, Delphi. Stewart, Greek Sculpture: An Exploration New Haven: Yale University Press, 1990.
Next
Kouros of Apollonas
.jpg/1200px-Statue_of_a_kouros_(c._530_BCE_or_modern%2C_Getty_Villa_Collection).jpg)
Roman Portraits: Sculptures in Stone and Bronze in the Collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Metropolitan Museum of Art. Metropolitan Museum of Art. It actively portrays the values and respect for the male body and sexuality in Ancient Greece. Kenneth Lapatin, Nicholaus Dietrich, Judith M.
Next
The Kouros Greek Statue: Facts and Analysis
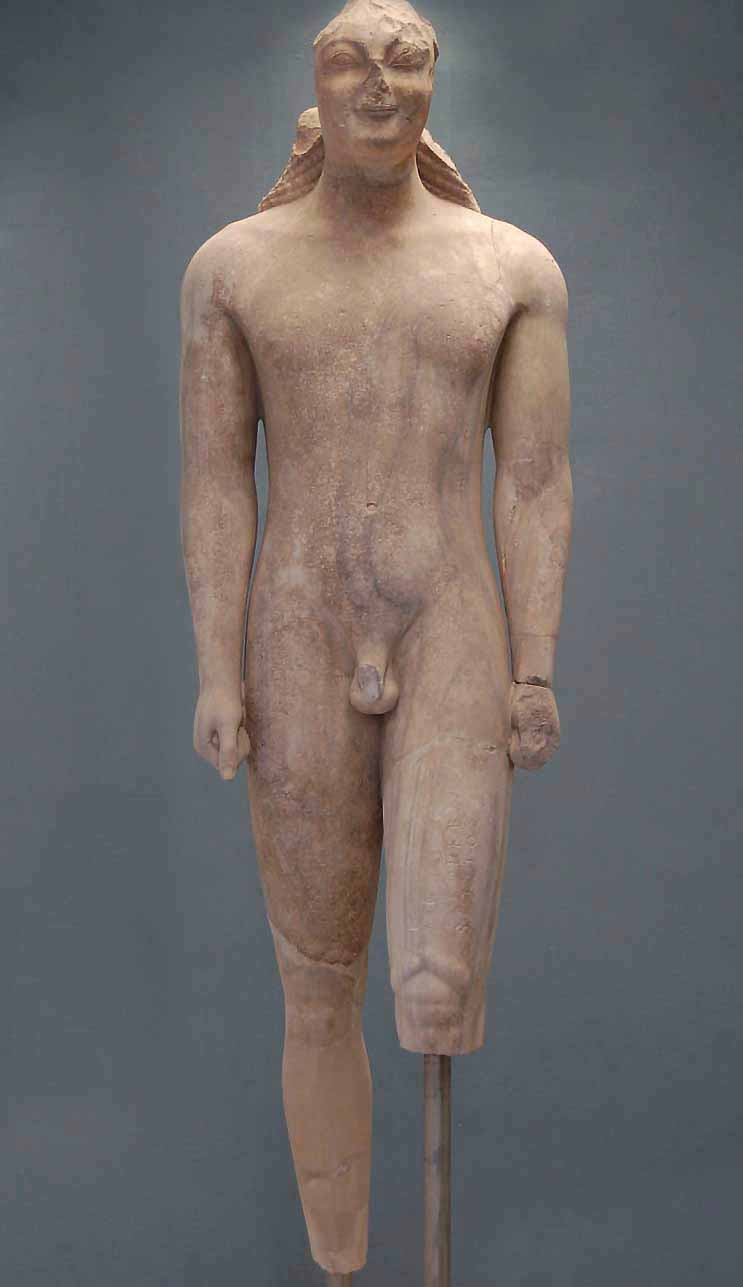

It is named for its current location, at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City. Unlike the Egyptian sculptures, the kouroi had no explicit religious purpose, serving, for example, as tombstones and commemorative markers. Which is characteristic of kouros sculptures? The texture of the statue is rather smooth. The image represents this idea: Earth divisible substance and the Sky continuous substance are the two kozmogonic substances. This group is named after the best preserved example of the era. The posture of these sculptures is decidedly erect with the left the active foot forward.
Next
What does the kouros sculpture represent?

It was identified in Paris in 1937 in the possession of the art dealer M. Artwork Details Title: Marble statue of a kouros youth Period: Archaic Date: ca. Furthermore, the ability of the sculptor to use different levels of depth to emphasize the particular features contributes to the game of shadows and the light. BCE during which statues of young men Kouros and women Kore were created, and are seen as the first foray of Greek artists into exploring the human form in stone. As for the size, the figure remains rather tall and massive in a standing position with the arms hanging down.
Next
kore

They probably began to sculpt the block into a kouros before it was sent to its final destination to reduce its weight, allowing for easier transport. However, some of the damages can be noticed. Additional resources: William R. An approach was developed to enable the student to easily approximate the Greek words. Kouros is derived from Kóri. Brinkmann, Vinzenz, Ulrike Koch-Brinkmann, Oliver Primavesi, and Jan Stubbe Østergaard. Baby and Child Heroes in Ancient Greece.
Next






.jpg/1200px-Statue_of_a_kouros_(c._530_BCE_or_modern%2C_Getty_Villa_Collection).jpg)

