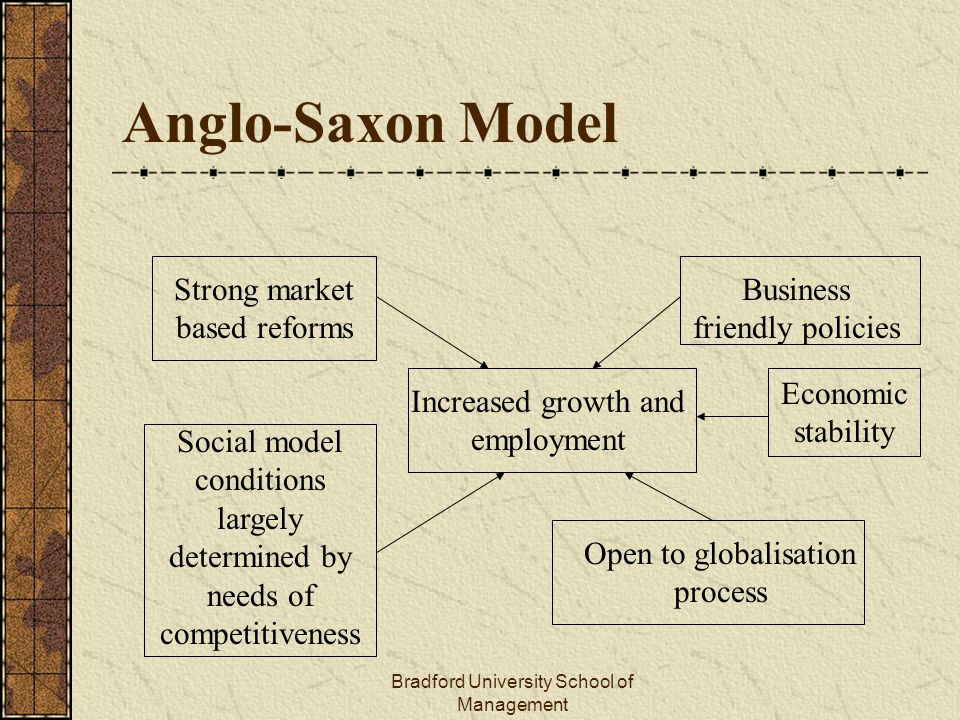
The Anglo-Saxon society was a group of tribes that inhabited England from the 5th to the 11th centuries. These tribes, which included the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, had a complex social structure that was based on a combination of Germanic and Celtic traditions.
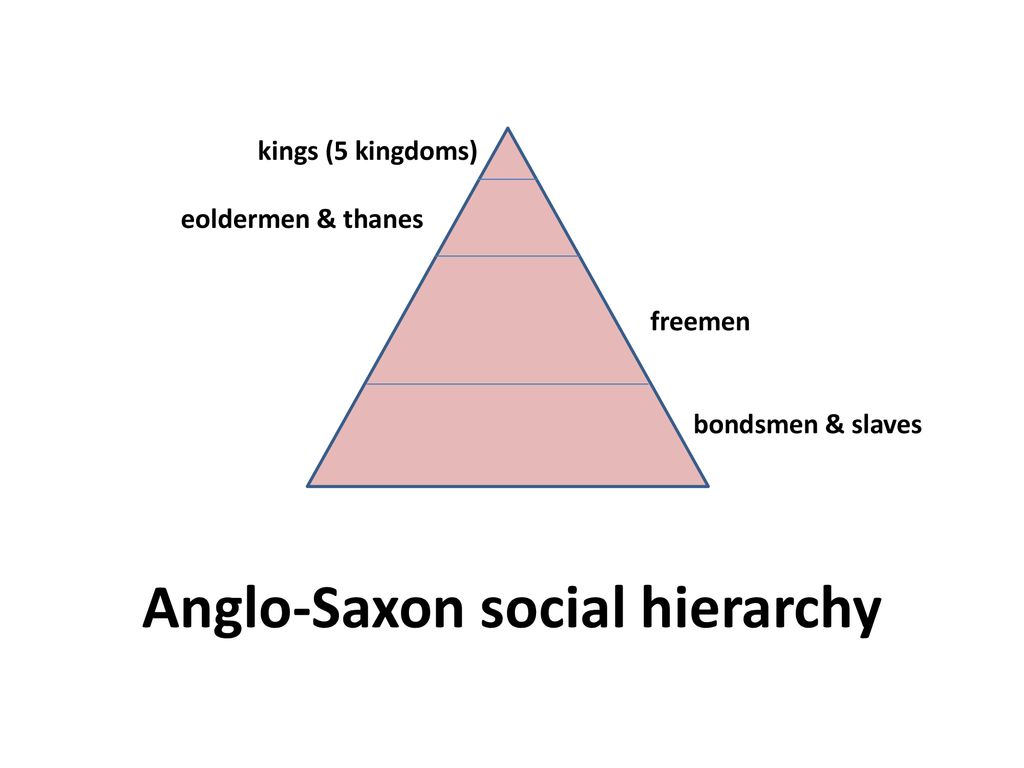
At the top of the Anglo-Saxon social hierarchy were the kings and nobles, who held a great deal of power and influence. Below them were the freemen, who were free to own land and participate in trade and commerce. The lowest class in Anglo-Saxon society was made up of slaves, who were owned by the wealthy and had few rights or freedoms.
Anglo-Saxon society was also divided by gender, with men holding a higher status than women. Women were expected to be submissive to their husbands and were not allowed to hold positions of power or authority. However, some women did play important roles in society, such as being healers or midwives.
The Anglo-Saxons were a warrior society, with a strong emphasis on military prowess. They believed in the importance of defending their land and people, and many young men were trained in the art of combat from a young age. The Anglo-Saxons also believed in the importance of loyalty and honor, and they had a code of conduct known as the "comitatus," which governed the relationships between lords and their followers.
Anglo-Saxon society was also shaped by its strong religious beliefs. The Anglo-Saxons were pagans who worshipped a variety of gods and goddesses, and they believed in the power of magic and the supernatural. They also had a strong oral tradition, and many of their stories and legends were passed down through the generations by bards and minstrels.
In conclusion, the Anglo-Saxon society was a complex and diverse culture that was shaped by its social hierarchy, military traditions, and religious beliefs. While it was a society that was heavily influenced by male dominance, it also had important roles for women and valued loyalty, honor, and the protection of its people.
Anglo Saxon Society Hierarchy
Ðegns were primarily warriors whose duty was to carry out the 'common burdens' of service in the fyrd, overseeing fortress work and bridge building. Women in Anglo-Saxon England. And if a ceorl prospered, that he possessed fully five hides of his own, a church and kitchen, bell-house and burh-gate, a seat and a special office in the king's hall, then he was entitled to the rights of a ðegn. Thus the conversion of the Anglo-Saxons was not just their switching from one practice to another, but making something fresh out of their old inheritance and their new beliefs and learning. This led to a phase of Viking partial-settlement in Anglo-Saxon England and catalyzed a period of great social and political change among the Anglo-Saxons. Farmers in Anglo Saxon England The vast majority of Anglo-Saxons made their living from farming.
Women in Anglo

Carol Pasternack; Lisa M. Earls had a lot of economic, military and legal power, but their position was dependent on the king and their thegns. In addition to his success on the battlefield, Alfred the Great was also known as a gracious and merciful man, who improved the quality of life for his people. Also in many estates further land duties arise by order of the king, such as servicing the deer-fence at the king's residence, and equipping a guard ship and guarding the coast, and attendance on his superior, and supplying a military guard, almsgiving and church dues and many other different things. There was no real concept of patriotism or loyalty to a cause. And he is to pay his hearth penny. By Tim Lambert Society in Anglo-Saxon England Everyday life in Anglo-Saxon England was hard and rough even for the rich.
Who Were the Anglo

These, then, are their means of support: land to live on, gifts, weapons, food, ale, clothing and whatever else is necessary for each of the three classes of men. At first, Anglo-Saxon society was relatively free. If possible people travelled by water along the coast or along rivers. King Ine founded Southampton at the end of the 7th Century. In the evenings apart from feasting, they enjoyed storytelling, riddles, and games like chess.