Article 15 of the Indian Constitution is a fundamental right that prohibits discrimination on the grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth. It states that "the State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them." This article is an important part of the Indian Constitution because it ensures that all citizens are treated equally and with dignity, regardless of their background or identity.
Article 15 is a crucial provision that helps to promote equality and justice in India. It protects the rights of marginalized communities, such as Dalits (formerly known as "untouchables") and women, who have historically faced discrimination and abuse in Indian society. By prohibiting discrimination on the basis of religion, race, caste, sex, and place of birth, Article 15 ensures that all citizens have the opportunity to participate fully in society and to enjoy the same rights and privileges as others.
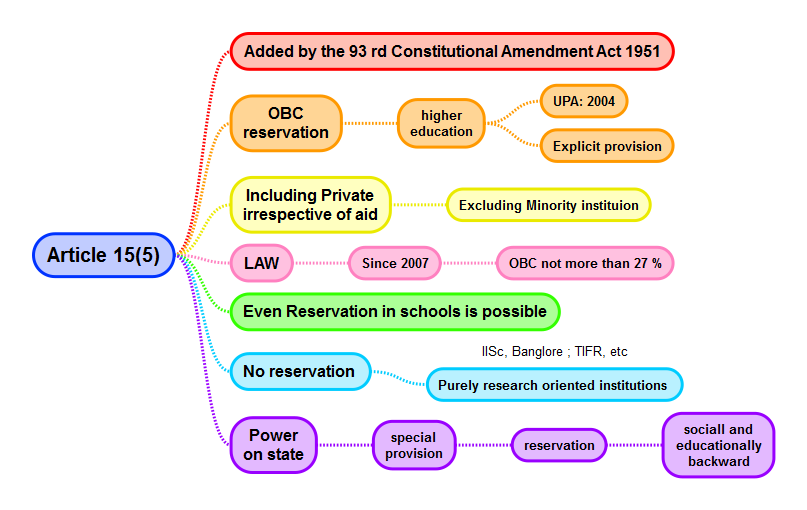
The Article also allows the State to take affirmative action to ensure that disadvantaged groups have equal access to education, employment, and other opportunities. For example, the Indian government has implemented quotas for certain reserved categories, such as Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, in education and employment, to ensure that these groups have equal access to these opportunities.
However, while Article 15 is a powerful tool for promoting equality and justice in India, it has its limitations. For example, it does not address issues of discrimination based on factors such as sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability. Moreover, the implementation of affirmative action policies has often been controversial, with some arguing that they perpetuate a system of discrimination rather than promoting true equality.
In conclusion, Article 15 of the Indian Constitution is a vital provision that ensures that all citizens are treated equally and with dignity, regardless of their background or identity. It is an important tool for promoting equality and justice in India, although it has its limitations. It is crucial that the government and society continue to work towards ensuring that all citizens have equal access to opportunities and are treated with respect and dignity.