Memory and storage are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different things in the context of computers and other electronic devices. Understanding the difference between memory and storage can be helpful for understanding how computers work and for troubleshooting issues with your device.
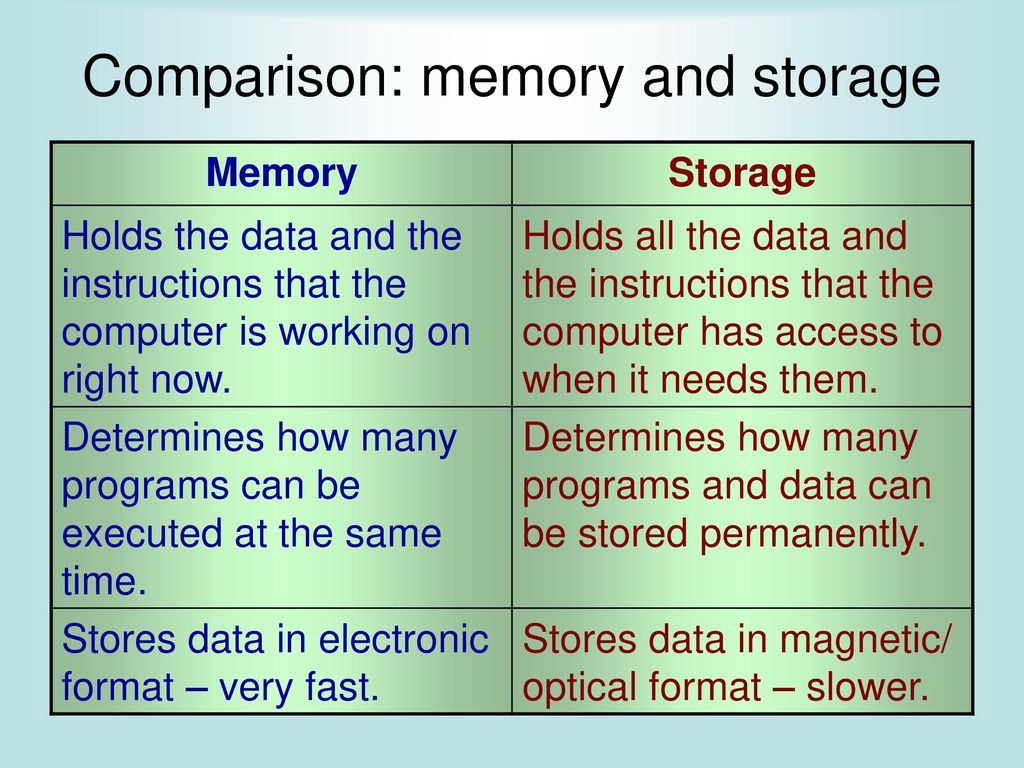
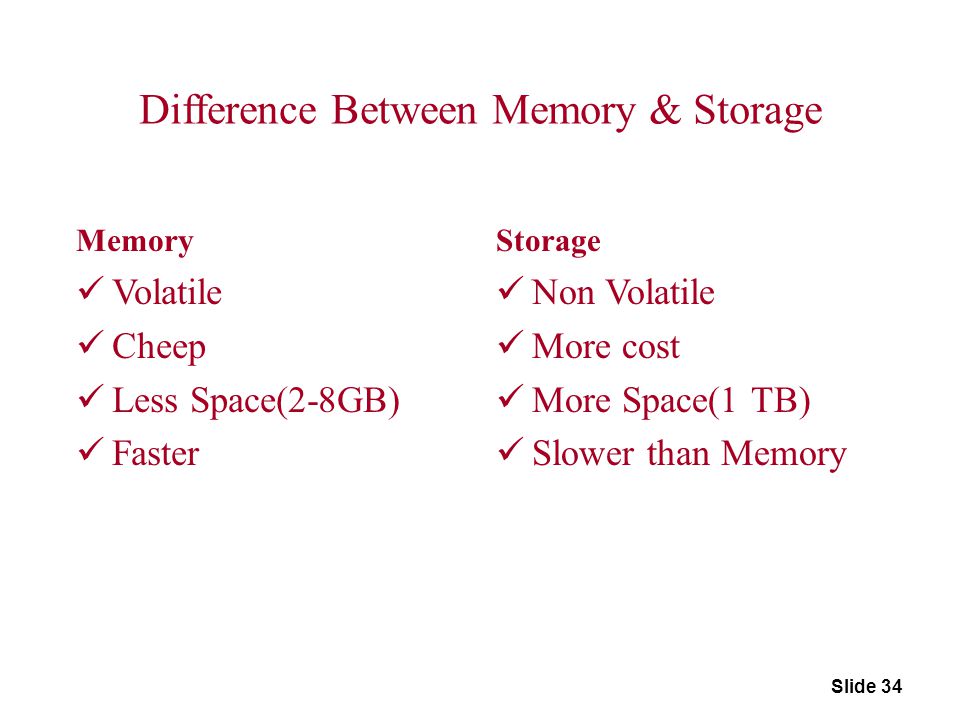
Memory, also known as RAM (random access memory), is a type of computer hardware that is used to store data that is being actively used or processed by the computer's central processing unit (CPU). When you open a program or perform a task on your computer, the data for that task is loaded into memory so that the CPU can access it quickly. Memory is volatile, which means that it is only temporary and is wiped clean when the computer is turned off.
Storage, on the other hand, is a type of computer hardware that is used to store data permanently. There are several types of storage devices, including hard drives, solid state drives, and USB drives. These devices are used to store files, documents, and other types of data that you want to keep even when the computer is turned off. Storage is non-volatile, which means that it retains data even when the power is turned off.
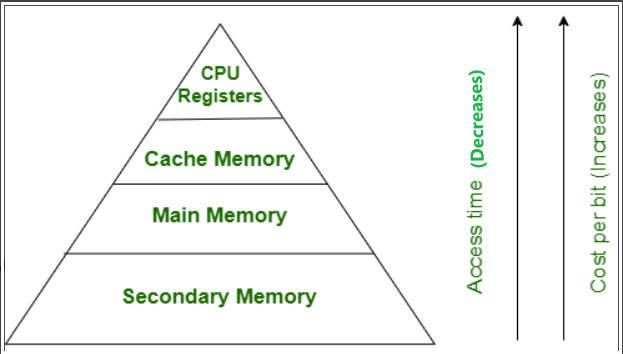
One key difference between memory and storage is speed. Memory is much faster than storage because it is accessed directly by the CPU, whereas storage requires the computer to access the data through input/output (I/O) channels. This means that tasks that require a lot of data processing, such as video editing or 3D rendering, may be slower if you have a limited amount of memory.
Another difference between memory and storage is capacity. Memory is typically limited to a few gigabytes, while storage can range from a few hundred gigabytes to several terabytes. This means that storage is better suited for storing large amounts of data, such as photos, videos, and music collections.
In summary, memory and storage are two important components of a computer that serve different purposes. Memory is used to store data that is being actively used by the CPU, while storage is used to store data permanently. Understanding the difference between these two types of hardware can be helpful for optimizing your computer's performance and for making informed decisions about upgrading your device.