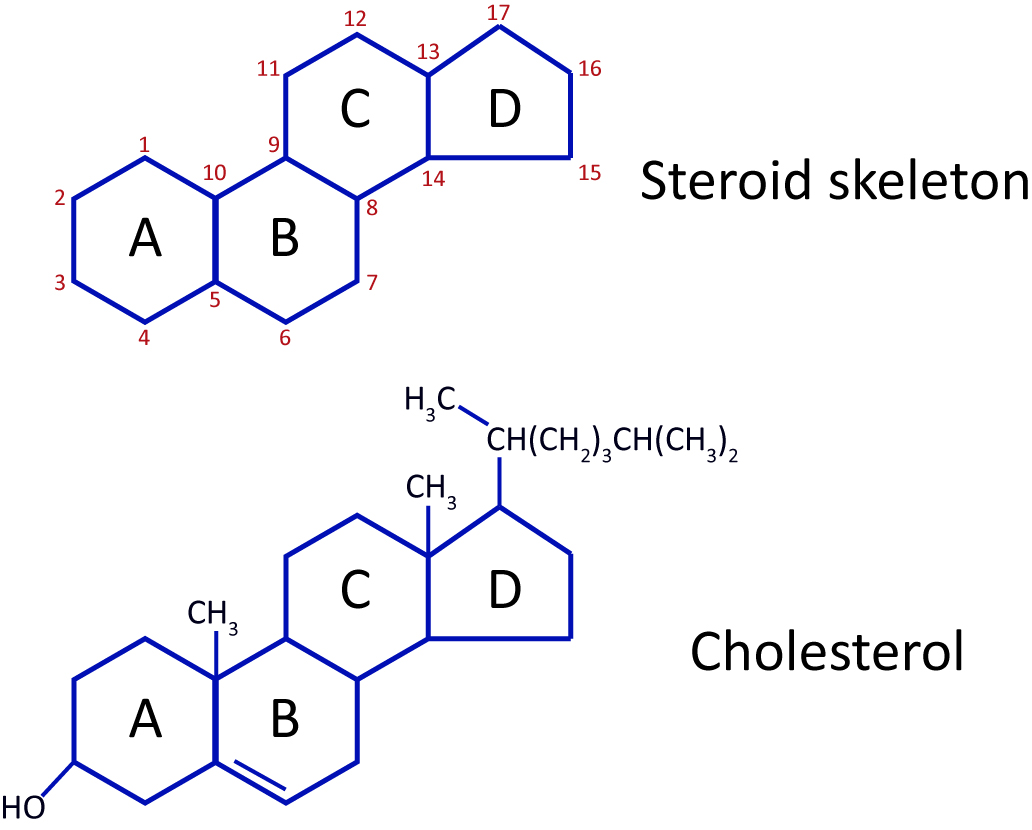
Lipids are a diverse group of biomolecules that play a variety of important roles in living organisms. They are essential components of cell membranes, energy storage molecules, signaling molecules, and precursors for the synthesis of hormones and other biologically active molecules. In this essay, we will explore the biological significance of lipids and how they contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms.
One of the most important roles of lipids is in the formation and maintenance of cell membranes. Cell membranes are thin, semipermeable barriers that enclose the interior of cells and separate them from the external environment. They are composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is made up of two layers of phospholipids arranged in a head-to-tail fashion. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face inward, while the hydrophilic heads face outward. This arrangement creates a barrier that is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while preventing the passage of others.
Lipids are also important energy storage molecules in living organisms. The most well-known lipid energy storage molecule is triacylglycerol, also known as triglyceride. Triglycerides are composed of three fatty acid molecules bonded to a glycerol molecule. They are stored in specialized cells called adipocytes, which are found in adipose tissue such as fat deposits in the body. When energy is needed, the body can hydrolyze the triglycerides to release the energy stored within them.
Lipids also serve as signaling molecules in the body. Many hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen, are synthesized from lipids. They are also involved in the signaling pathways that control various physiological processes, such as inflammation, blood clotting, and immune responses.
In addition to their roles in cell membranes, energy storage, and signaling, lipids also have other important biological functions. They are important components of the protective layer of the skin and are essential for maintaining the integrity and moisture balance of the skin. Lipids are also important for the absorption and transport of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K.
In conclusion, lipids are an essential class of biomolecules that play a variety of important roles in living organisms. They are involved in the formation and maintenance of cell membranes, energy storage, signaling, and other biological functions. Understanding the biological significance of lipids is important for understanding the overall functioning of living organisms and for developing treatments for diseases that involve lipid metabolism.