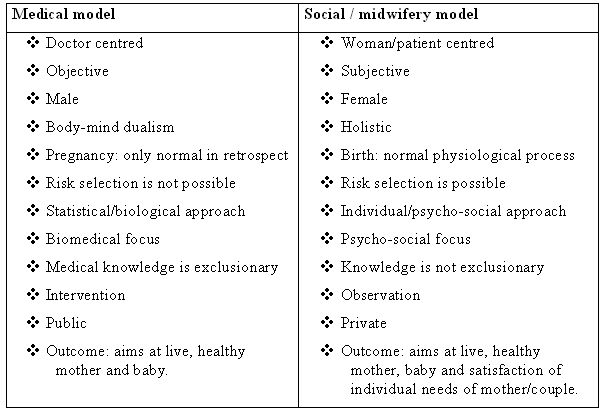
The biomedical model of health and illness is a dominant approach in modern Western medicine that focuses on identifying and treating the biological causes of disease and disability. This model is based on the belief that illness is caused by specific pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses, or by abnormal functioning of the body's physiological processes.
According to the biomedical model, health is defined as the absence of disease or abnormal functioning of the body's systems. This approach emphasizes the use of scientific and medical technologies, such as pharmaceuticals, surgery, and diagnostic tests, to identify and treat medical conditions.
One of the strengths of the biomedical model is its ability to effectively diagnose and treat many acute and infectious diseases. It has led to the development of many life-saving treatments and has greatly improved the health and lifespan of many people around the world.
However, the biomedical model has some limitations. It often focuses solely on the physical aspects of illness and ignores the social, psychological, and environmental factors that can also contribute to the development and management of disease. Additionally, the biomedical model tends to prioritize the treatment of symptoms over addressing the root causes of illness, leading to a focus on short-term solutions rather than long-term prevention.
The biomedical model has also been criticized for its tendency to pathologize and medicalize certain conditions, such as mental health disorders and social issues, rather than addressing the underlying social, economic, and political factors that contribute to these conditions.
Overall, the biomedical model of health and illness has been a powerful and effective approach in modern medicine, but it is important to recognize its limitations and the need to consider other factors that can impact health and well-being. Alternative approaches, such as the biopsychosocial model, which takes into account the interconnected nature of biological, psychological, and social factors in health and illness, may be more holistic and effective in addressing the complex and multifactorial nature of health and disease.
What Is The Biomedical Definition Of Health?

Business Bliss Consultants FZE, 'Evaluation of Biomedical and Holistic Models of Health' nursinganswers. What Does Biomedical Mean? Due to not seeing any physical evidence or symptoms of illness such as blood and vomiting, they automatically assume they are healthy. For example, there are medical issues that are caused by environmental factors, such as air pollution. A biomedical and social models of health is a way of thinking about health that is based on the understanding that health is a product of a complex web of relationships among people, the environment, and their own health. The advantage of this model is that it educates people to not get the disease and there are government support agencies, for example for vaccinations and it is also less costly to prevent the disease before it happens. Basically, if you were to explain illness to your little kid sister, you'd tell her that illness is when a person is sick, and a person is far more than a collection of body parts.
Understanding the Biomedical Model

The relationship between health and illness There is no difference between health and illness if you look at it from the biopsychosocial perspective. Biology is said to be a branch of knowledge that deals with living organisms and vital processes and 'medicine' is the science of health and the prevention, alleviation, or cure of disease. Findlay, 1973 The main objective of the biomedical model is to focus on the human body solely and treat the illness and diseases sperate from the mind. It is a method that tries to tackle the wider effects on health social, cultural, environmental and economic factors rather than disease and injury. Thus, the biomedical model focusses more on testing and diagnosis of disease and the treatment of the pathogens to cure the disease, rather than looking for extenuating factors. Good Thinking , 2018 also unrealistic area to keep funding without outside investment. You can call medical model of health or biomechanical model of health at times.
Evaluation of Biomedical and Holistic Models of Health

If any pure mental disorder, for that matter, is just a weak-man's excuse for life's difficulties? This essay will also discuss and analyse how both models relate to lay perspectives on health and illness. In today's world, you'd tell me I am crazy, no pun intended. The holistic model presents many disadvantages, if you have a serious medical illness such as aids or cancer the time spent looking for other treatments can cause the diseases to spread which could lead the disease to become untreatable and the patient having a shorter life. By the 1870s Pasteur was able to demonstrate that germs were the cause rather the product of disease. In this mechanistic view, the body is perceived to function like a machine,.