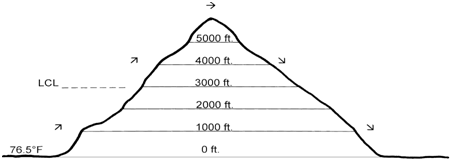
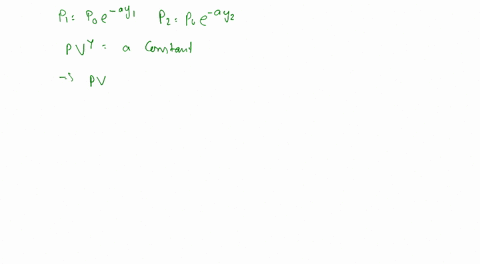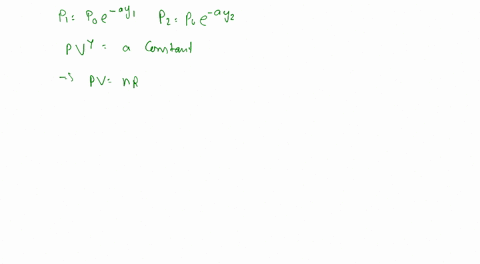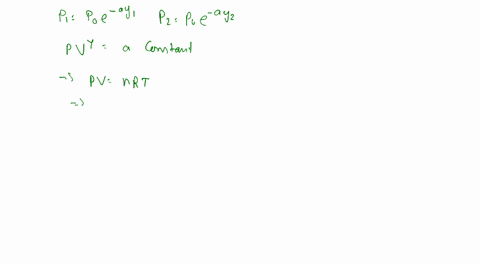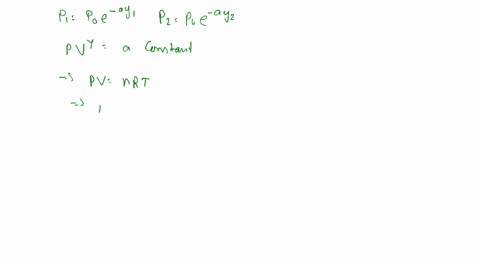Calculating the temperature of a parcel of air at different elevations can be a useful tool in understanding and predicting weather patterns. There are several factors that can affect the temperature of a parcel of air as it rises or falls in elevation, including the amount of moisture it contains, the amount of heat it absorbs or radiates, and the rate at which it expands or contracts.
One important factor to consider when calculating the temperature of a parcel at different elevations is the process of adiabatic heating or cooling. This refers to the change in temperature that occurs as a parcel of air expands or contracts due to changes in pressure. As a parcel of air rises, the pressure on it decreases, causing it to expand and cool. Conversely, as a parcel of air falls, the pressure on it increases, causing it to contract and heat up.
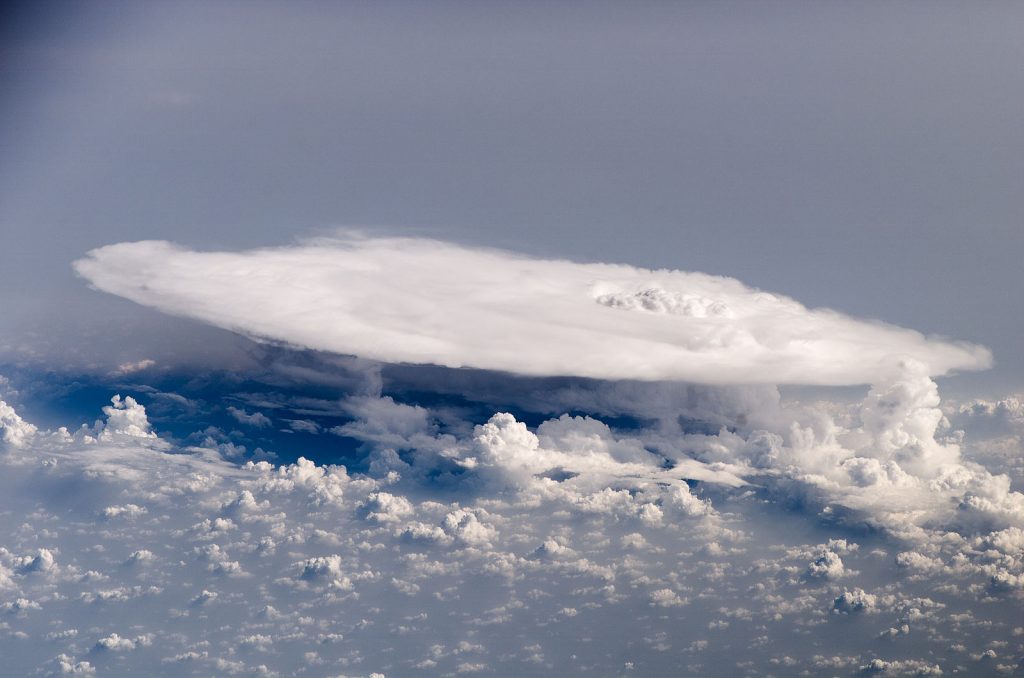
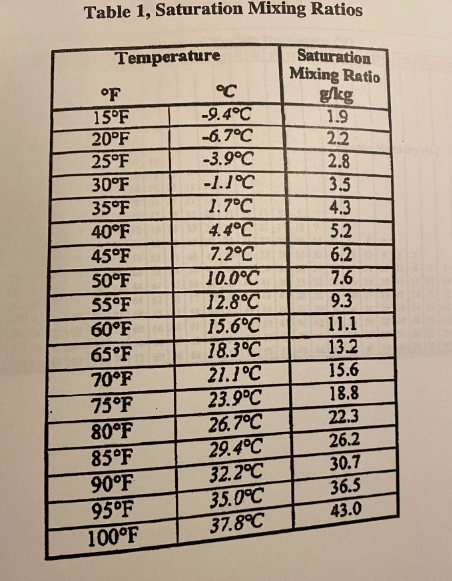
Another factor to consider is the amount of moisture contained within the parcel. Moist air has a lower temperature than dry air at the same pressure, due to the latent heat of vaporization required to change water from a liquid to a gas. As a parcel of moist air rises, the air pressure decreases, allowing the water vapor to condense into clouds. This releases latent heat, which can offset the cooling that would normally occur due to adiabatic expansion.
The amount of heat absorbed or radiated by a parcel of air can also affect its temperature. For example, a parcel of air that is heated by the sun will be warmer than a parcel of air that is not exposed to direct sunlight. Similarly, a parcel of air that is cooled by radiating heat to the ground or to the surrounding atmosphere will be cooler than a parcel that is not losing heat in this way.
To calculate the temperature of a parcel at different elevations, we can use the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are directly proportional to one another. By measuring the pressure and volume of the parcel at different elevations, we can calculate its temperature using the following equation:
PV = nRT
Where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in kelvins.
By taking into account the factors discussed above and using the ideal gas law, we can accurately calculate the temperature of a parcel of air at different elevations. This can help us better understand and predict weather patterns and the movements of air masses.