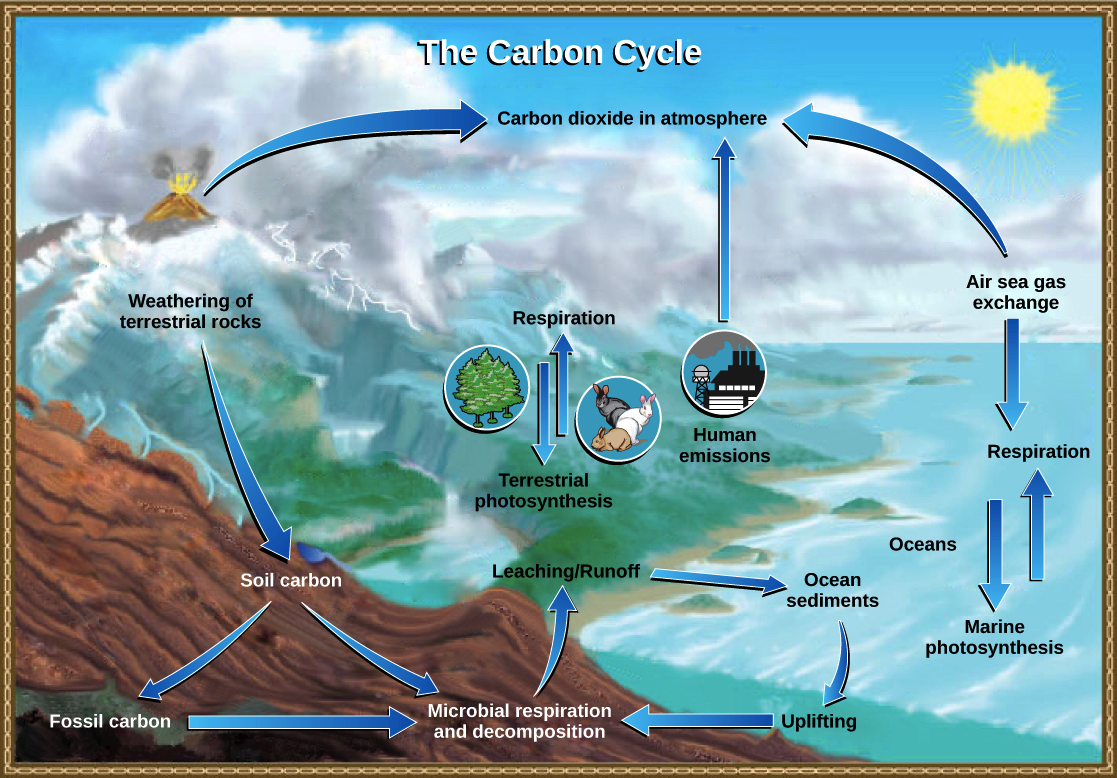
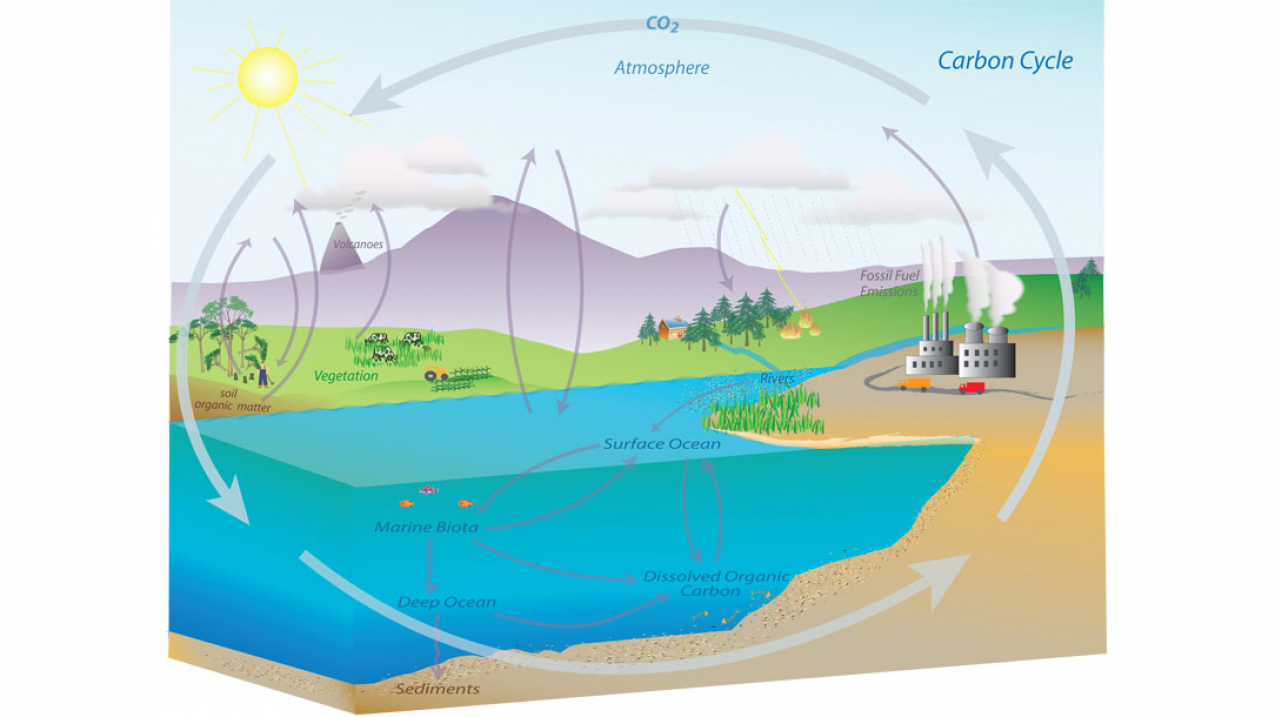
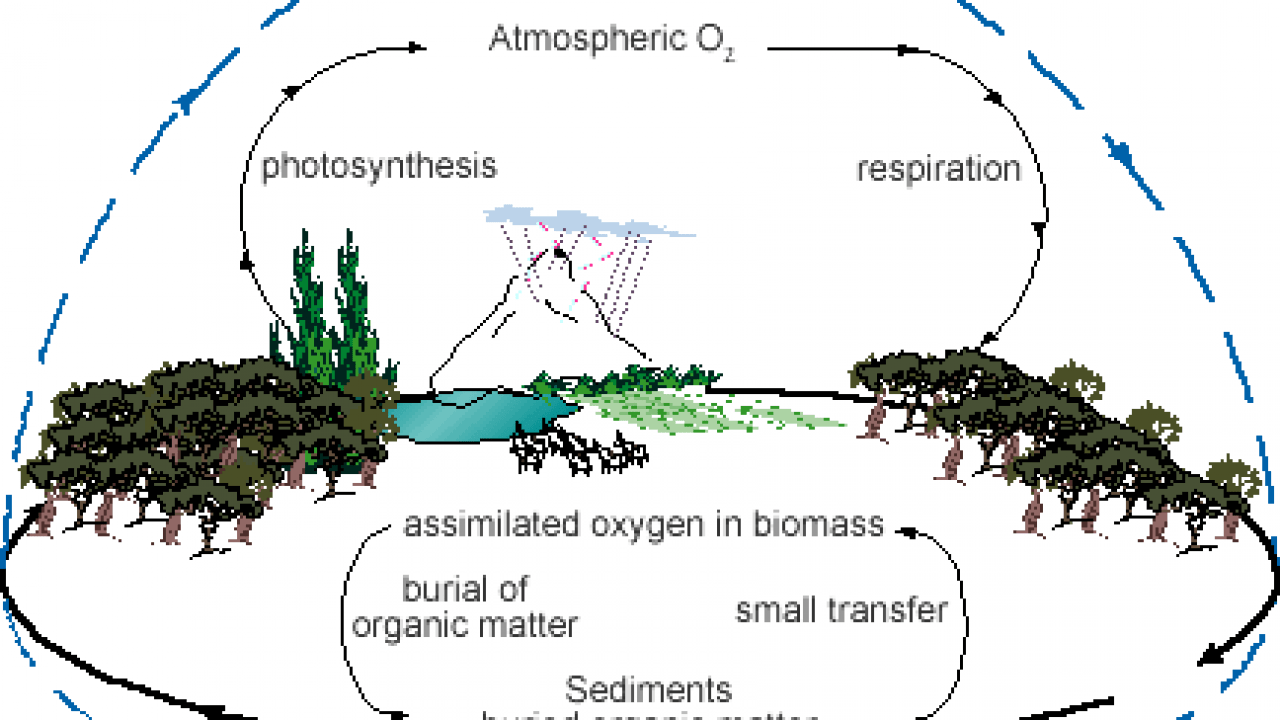
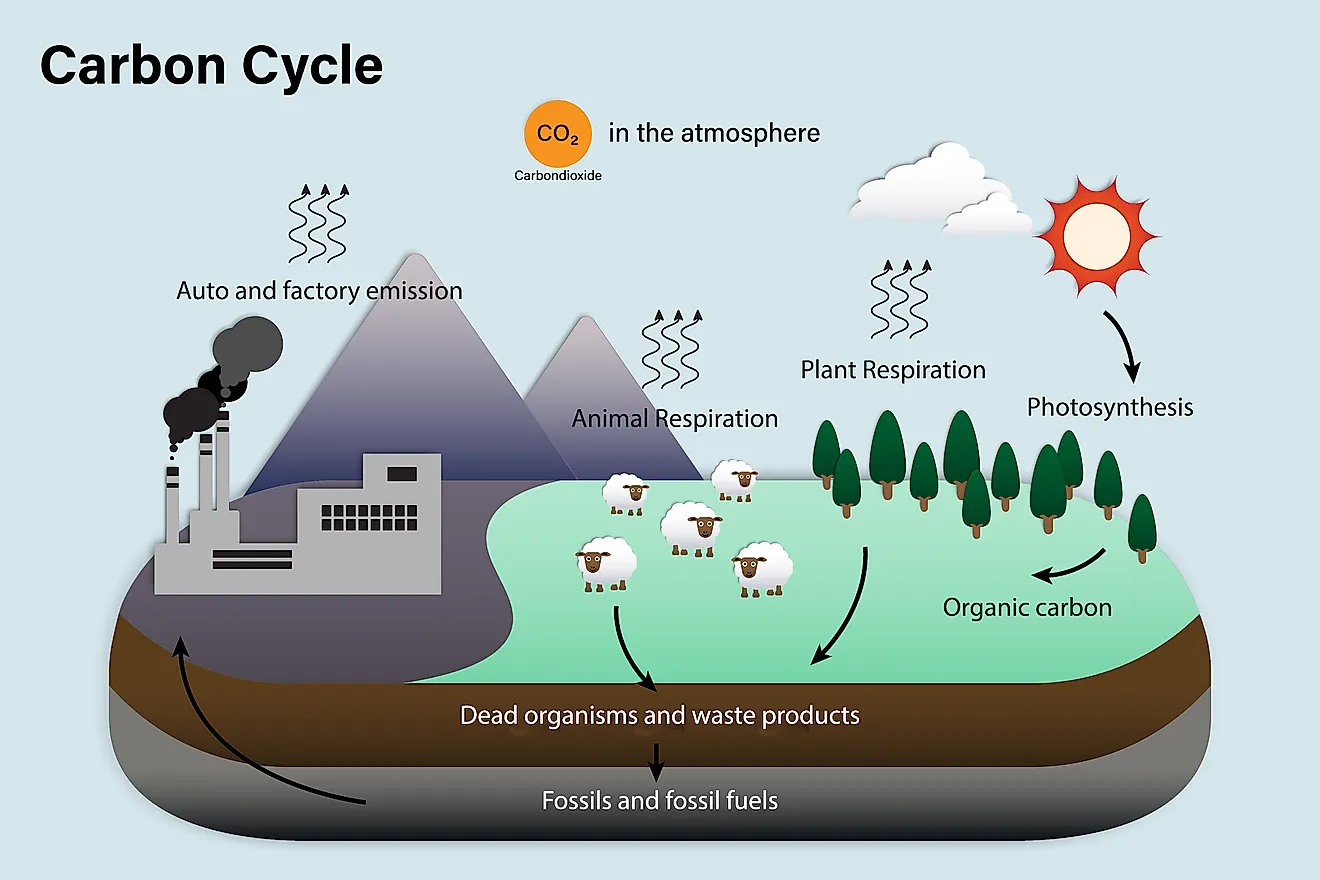
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land. It plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate and supporting life on the planet.
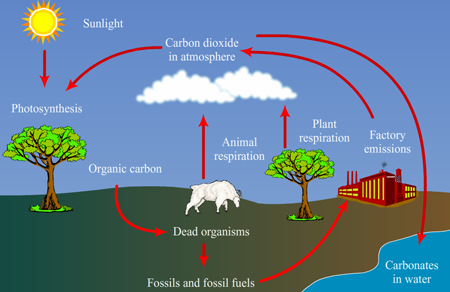
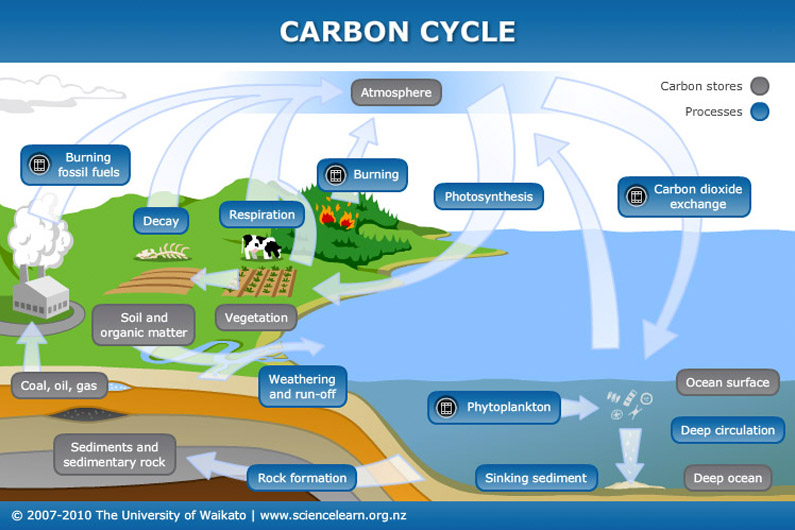
The carbon cycle begins with the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere through natural processes such as respiration, decomposition, and volcanic eruptions. Plants and other photosynthesizing organisms absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter through photosynthesis. This process removes CO2 from the atmosphere and stores it in the form of plant biomass.
When plants die and decompose, the carbon stored in their biomass is released back into the atmosphere as CO2. This process is called decomposition. In addition, carbon can be released into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, and through deforestation and land use changes.
The oceans also play a significant role in the carbon cycle. They absorb a large amount of CO2 from the atmosphere, and tiny marine organisms, such as phytoplankton, convert it into organic matter. When these organisms die, their carbon-rich bodies sink to the bottom of the ocean, where it can be stored for hundreds of years.
The carbon cycle is not a simple one-way process, however. There are also processes that remove CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in the oceans and on land. For example, forests absorb CO2 through photosynthesis and store it in the form of wood and other plant matter.
Overall, the carbon cycle helps to regulate the amount of CO2 in the Earth's atmosphere and plays a vital role in maintaining the planet's climate. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, are disrupting the natural balance of the carbon cycle, leading to an increase in atmospheric CO2 and contributing to climate change.
Carbon cycle

Changes to fluxes in the carbon cycle that humans are responsible for include: increased contribution of CO 2 and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere through the combustion of fossil fuels and biomass; increased contribution of CO 2 to the atmosphere due to land-use changes; increased CO 2 dissolving into the ocean through ocean-atmosphere exchange; and increased terrestrial photosynthesis. For example, the metamorphic reactions that occur under heat and pressure can release carbon dioxide. Why or why not? Resources Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory: Carbon Cycle Science Page 11 Sass, Ronald. Biomass, which is biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms, is a much smaller reservoir of carbon. Photosynthesis takes place in organelles called chloroplasts, shown in Figure 7.
Climate Change: The Carbon Cycle
All plants, animals including humans! Carbon is environmentally friendly because it traps the heat of the sun. Diamonds are also a form of Carbon, as is Coal! Everything — carbohydrates, sugars, our DNA, our cells, all have Carbon. As the world accelerated in the production and transportation of manufactured goods, the production and consumption of fossil fuels grew. Nitrogen and Air Pollution An unsightly haze of smog, visible from NCAR's Mesa Laboratory, rests over Boulder Valley. This is the process which breaks down Carbon dioxide into compounds that can be used as nutrition by the plants. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to oxygen in a gas called carbon dioxide CO 2. It is so named because carbon flows through the various carbon reservoirs in a matter of days, months, or years.
Biogeochemical Cycles
They use energy from the sun to combine the carbon dioxide and water to form carbohydrates. Locate the carbon cycle icon and identify other Earth system processes and phenomena that cause changes to, or are affected by, the cycling of carbon. Do you think this correlation is more likely due to personal biomass fires for activities such as cooking, or due to slash-and-burn agriculture? The number of herbivores will increase when the plant supply increases and then the herbivores are left without a food source when the plants die. The first two impacts, both contributing excess CO2 to the atmosphere at a rate of 4 Gt of carbon per year have, by far, the largest impact on our planet. Ergo, we would all perish! Certain actions of humans are causing changes to the nitrogen cycle and the amount of nitrogen that is stored in reservoirs.