"Echo" is a poem written by Christina Rossetti, a Victorian poet known for her religious and devotional works. The poem explores the theme of loss and the enduring power of memory through the metaphor of an echo.
In the opening lines of the poem, Rossetti introduces the idea of an echo as a voice that repeats the words of others, but "dies away" when the sound that caused it has ceased. This serves as a metaphor for the way that memories and emotions can linger long after the events or people that sparked them are gone.
The speaker of the poem laments the loss of a loved one, saying that their absence feels like a "silent desert" and a "vacant nest." They wonder if their loved one can still hear them, even though they are no longer physically present. This longing for connection and the fear of being forgotten is a common theme in Rossetti's poetry, and it is evident in the speaker's words.
As the poem progresses, the speaker reflects on the way that echoes can be both comforting and unsettling. On the one hand, hearing an echo can feel like a reassuring presence, a reminder that someone or something has been there before. On the other hand, an echo can also be a source of loneliness and longing, as it is a reminder of what is no longer present.
In the final stanza, the speaker speaks directly to the echo, asking it to "whisper low" the words of their loved one, as if they were still there. This serves as a poignant reminder of the enduring power of memory and the ways in which it can continue to shape our thoughts and feelings long after the people and events that inspired them are gone.
Overall, "Echo" is a beautifully crafted poem that explores the theme of loss and the enduring power of memory through the metaphor of an echo. Rossetti's use of language and imagery is evocative and moving, and the poem speaks to the universal human experience of loss and the desire to hold onto the people and memories that we hold dear.
Calvin Cycle Model

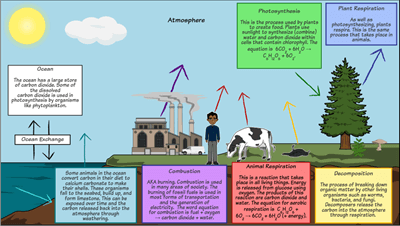
Credit: IPCC, 2007 Other potential positive carbon cycle feedbacks that are even more uncertain, but could be quite sizeable in magnitude, are methane feedbacks, related to the possible release of frozen methane currently trapped in thawing Arctic permafrost, and so-called "clathrate"—a crystalline form of methane that is found in abundance along the continental shelves of the oceans, which could be destablized by modest ocean warming. These build up on the seafloor, where they are eventually broken down by the waves and compacted under extreme pressure, resulting in limestone. However, each turn forms 2 molecules of G3Ps so in total 6 molecules of the compound are formed. Question 4: Why is the carbon cycle important? Once in their suits, astronauts breathe pure oxygen for a few hours. Glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes, produces two equivalents of NADH and four equivalents of ATP. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to FAD to produce FADH 2.
Carbon Cycle Feedbacks

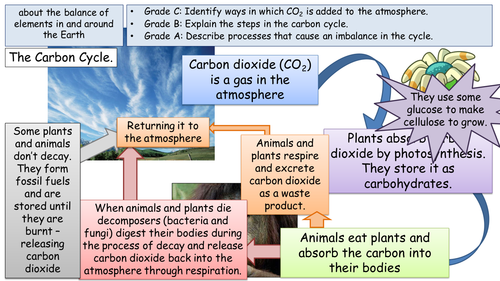
Brian Gaudet, Assistant Research Professor, Department of Meteorology, College of Earth and Mineral Sciences, The Pennsylvania State University. There are six main processes in the carbon cycle: photosynthesis, respiration, exchange, sedimentation, extraction, and combustion. Accessed June 20, 2017. Because it is nonmetallic and tetravalent, it may form covalent chemical connections with four electrons. Heterotrophs, carnivores, and omnivores cannot take in carbon dioxide directly in the body.
Carbon Cycle in Microorganisms
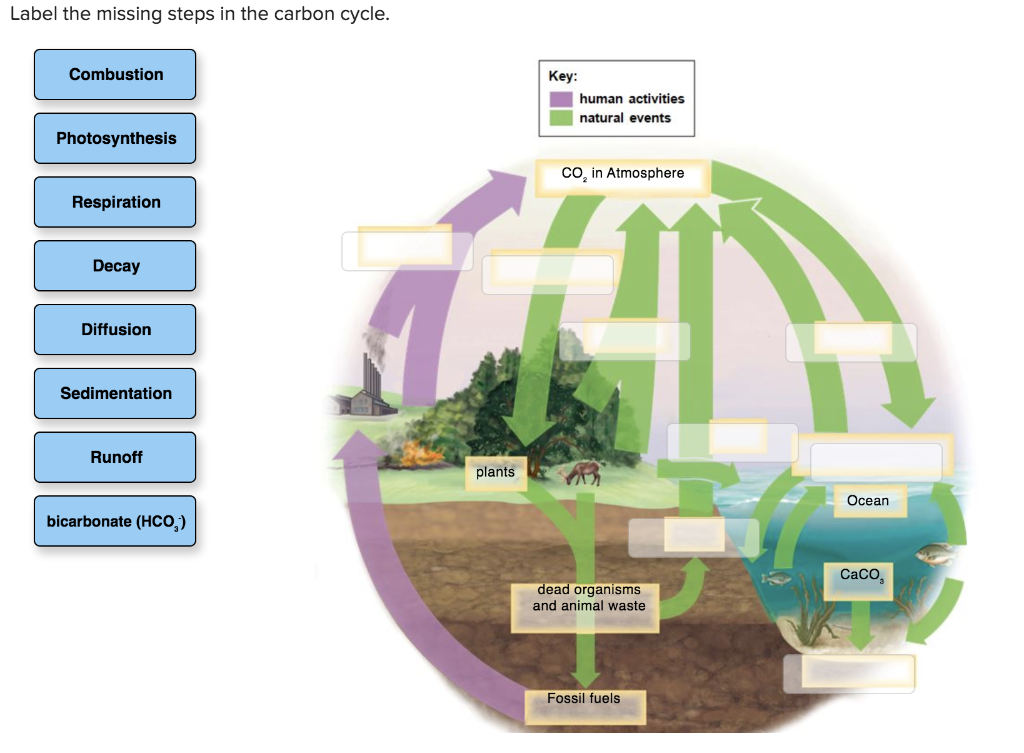
Scroll down to find out more. The reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase. Malate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction. Step 8 The oxidation of malate regenerates oxaloacetate, a four-carbon compound, and another molecule of NAD + is reduced to NADH in this step. Finally, there is the negative silicate rock weathering feedback which we know to be a very important regulator of atmospheric CO 2 levels on very long, geological timescales: a warmer climate, with its more vigorous hydrological cycle, leads to increased physical and chemical weathering the process of taking CO 2 out of the atmosphere by reacting it with rocks , through the formation of carbonic acid, which dissolves silicate rocks, producing dissolved salts that run off through river systems, eventually reaching the oceans. Cellular respiration is a four-stage process. A major component of the Calvin cycle is the enzyme ribulose-1, 5- biphosphate carboxylase also known as RUBISCO.