Cell organelles are small structures within cells that perform specific functions necessary for the cell to survive and function properly. There are several different types of cell organelles, each with its own unique function.
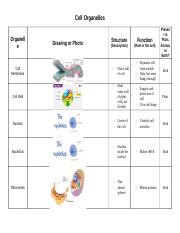
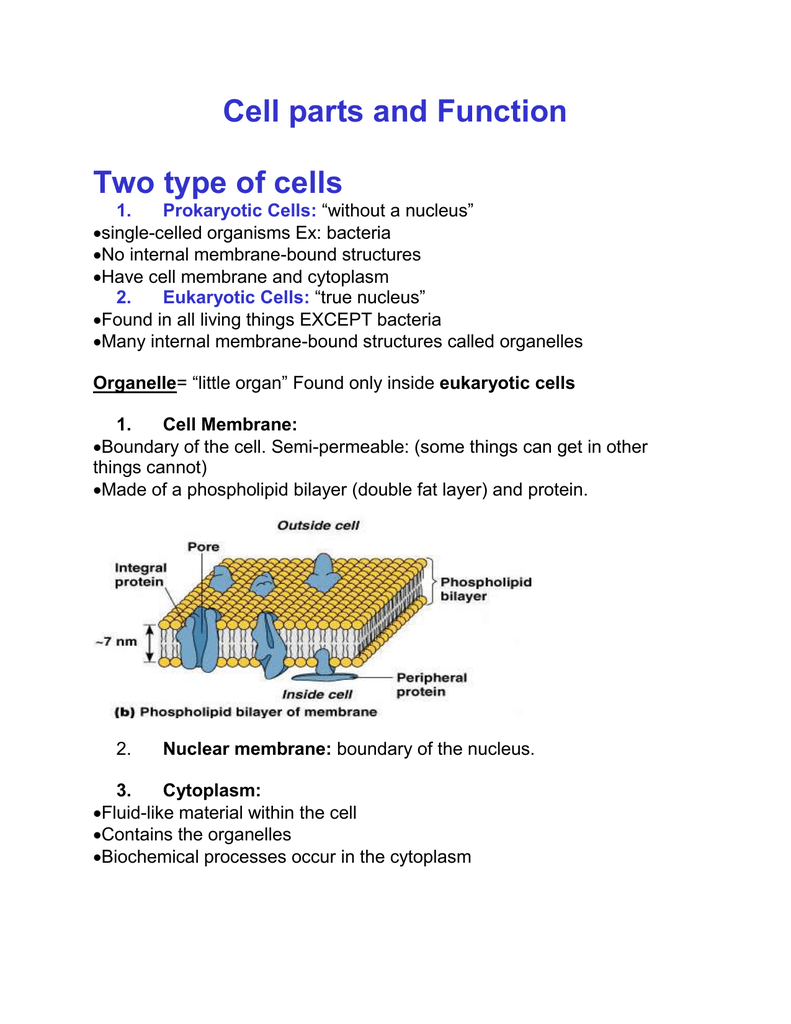
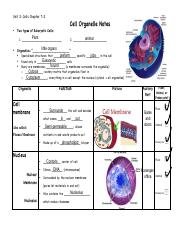
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside from the outside environment. It is made up of lipids and proteins and helps to protect the cell and maintain its shape. The cell membrane is also responsible for regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell's genetic material, or DNA. It is separated from the rest of the cell by the nuclear envelope, which is a double membrane that encloses the nucleus. The nucleus is responsible for controlling the cell's activities and directing the synthesis of proteins.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of flattened tubes and sacs that is involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids. There are two types of ER: the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The SER is involved in the synthesis of lipids and steroids, while the RER is involved in the synthesis and modification of proteins.
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs that is involved in the modification, sorting, and delivery of proteins and lipids. Proteins and lipids enter the Golgi at one end and are modified and sorted as they move through the stack. The modified proteins and lipids are then shipped out of the Golgi in vesicles to their final destination within the cell or to other cells.
The lysosomes are small, spherical organelles that contain enzymes that can break down and recycle various substances within the cell. They are formed from vesicles that bud off from the Golgi apparatus and contain enzymes that can digest proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
The mitochondria are rod-shaped organelles that are the primary site of energy production in the cell. They contain enzymes that convert nutrients into ATP, the primary source of energy for the cell. The mitochondria also play a role in the synthesis of lipids and the regulation of cell death.
The peroxisomes are small, spherical organelles that contain enzymes that can break down various toxic substances and byproducts within the cell. They are similar to lysosomes in that they contain enzymes that can digest a variety of substances, but they are not formed from vesicles that bud off from the Golgi apparatus.
The vacuoles are large, fluid-filled sacs that function in storage, waste removal, and support for the cell. Plant cells often have a single large central vacuole that takes up most of the cell and helps to support the cell's structure. Animal cells may have smaller vacuoles that function in waste removal and storage.
In summary, cell organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions necessary for the cell to survive and function properly. Each organelle has a unique function, and the interactions between organelles are critical for the overall function of the cell.