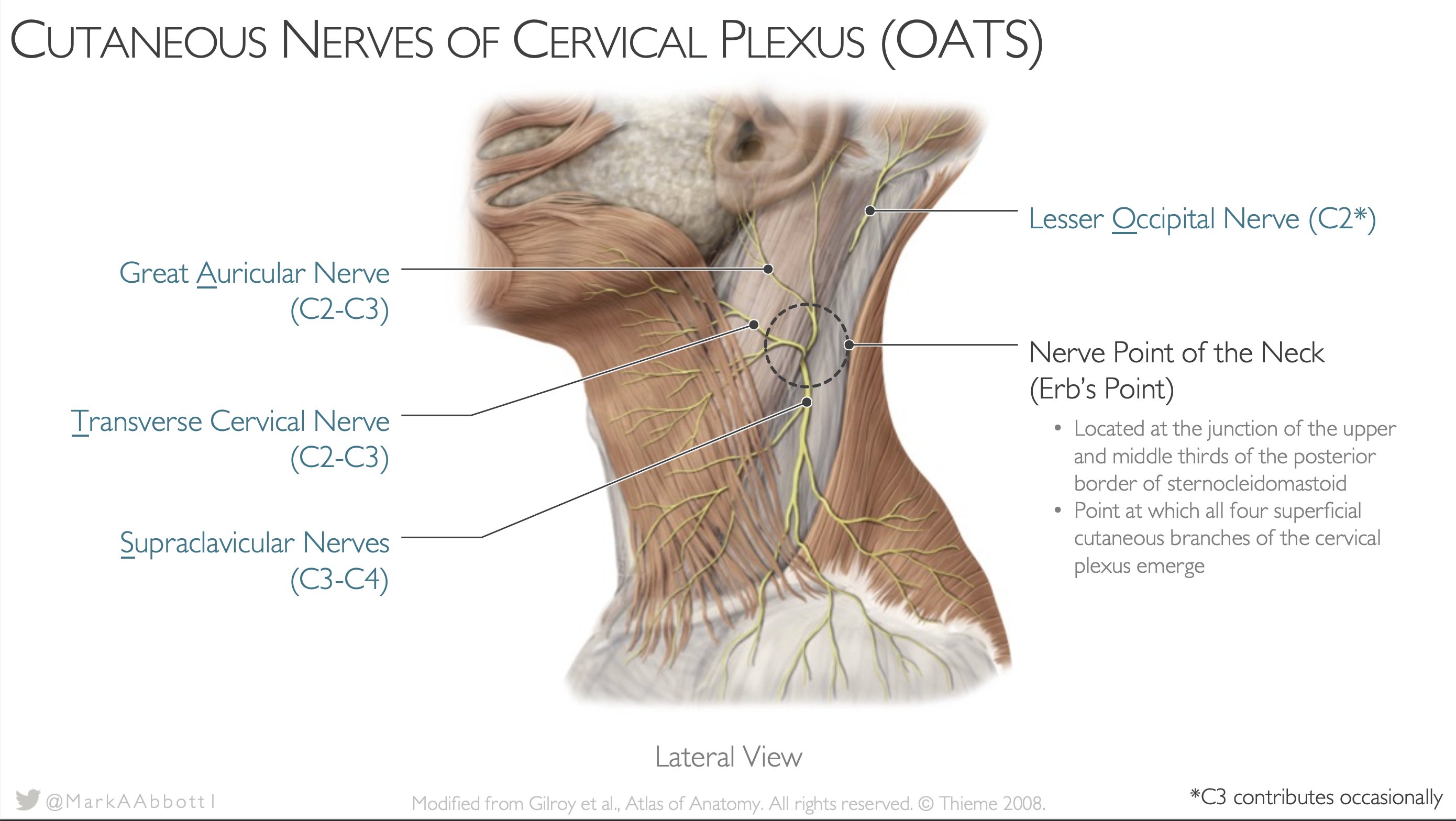
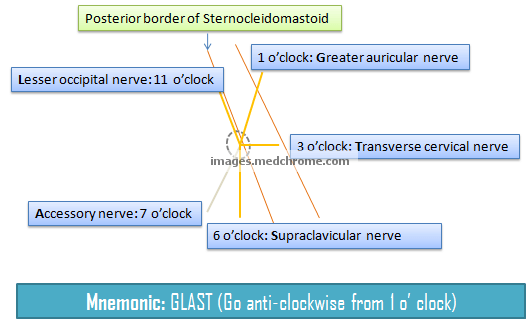
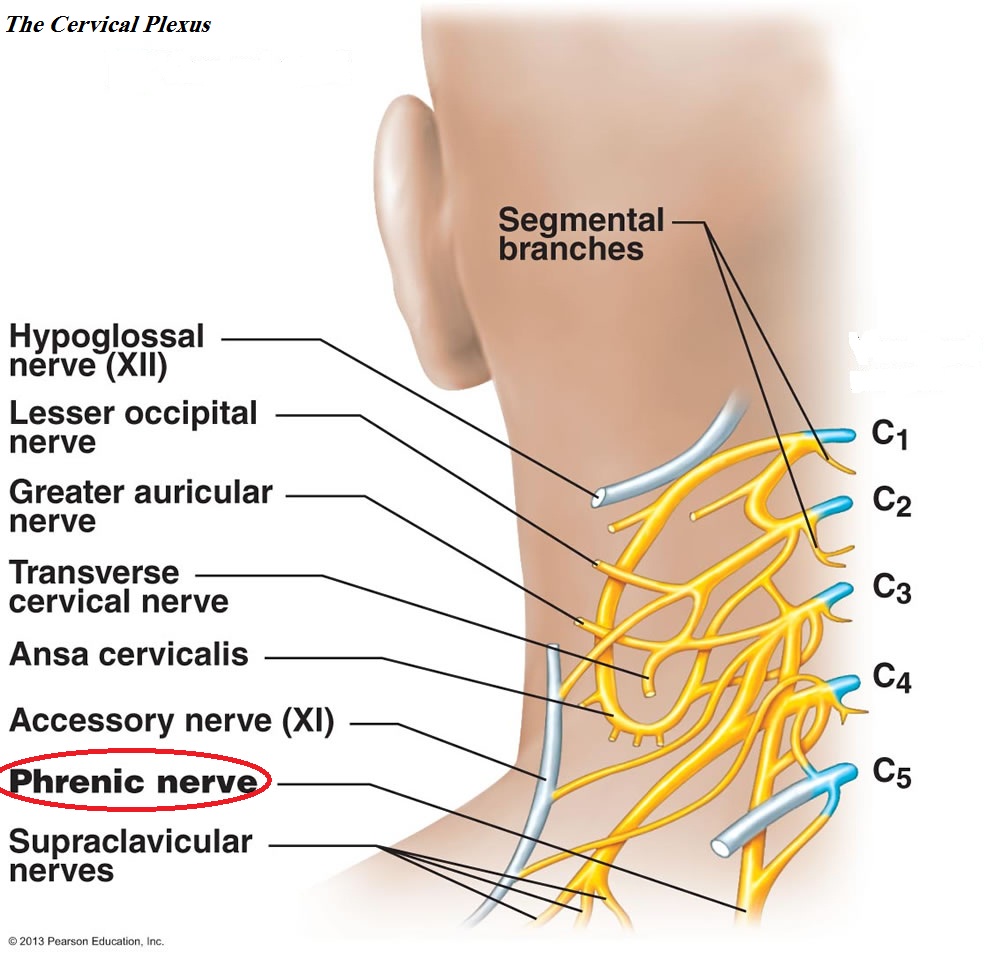
The cervical plexus is a network of nerves located in the neck region of the human body. It is made up of a group of nerve fibers that originate from the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical spinal nerves, and it innervates various muscles and structures in the neck and upper shoulder area. The cervical plexus is an important component of the peripheral nervous system, and it plays a vital role in controlling movement and sensation in the neck and upper limb.
The cervical plexus is formed by the merging of the ventral rami of the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical nerves. These nerves emerge from the spinal cord and pass through the intervertebral foramen, or openings between the vertebrae in the spine. Once they reach the neck region, the nerves divide into smaller branches, which innervate specific muscles and structures in the neck and upper shoulder area.
The cervical plexus has several important functions in the body. It is responsible for controlling the movement of the neck and upper limb, as well as providing sensation to these areas. The cervical plexus also plays a role in regulating blood flow to the head and neck region, and it helps to control the reflexes that are necessary for maintaining balance and coordination.
There are several muscles and structures in the neck and upper shoulder area that are innervated by the cervical plexus. These include the muscles of the neck and upper back, as well as the trapezius muscle, which is responsible for moving the shoulder blade. The cervical plexus also innervates the muscles of the upper limb, including the biceps, triceps, and forearm muscles.
Injury to the cervical plexus can have serious consequences, as it can result in muscle weakness, paralysis, and loss of sensation in the neck and upper limb. This type of injury is most commonly caused by trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, but it can also be caused by surgical procedures or certain medical conditions. Treatment for cervical plexus injuries may include physical therapy, medications, and surgery, depending on the severity of the injury.
In conclusion, the cervical plexus is an important network of nerves that plays a vital role in controlling movement and sensation in the neck and upper limb. It is formed by the merging of the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical nerves and innervates various muscles and structures in the neck and upper shoulder area. Injury to the cervical plexus can have serious consequences, and treatment may include physical therapy, medications, and surgery.


:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ansa-cervicalis-2/dr48EAOEovmtDqgdLcAoQ_Ansa_cervicalis.png)