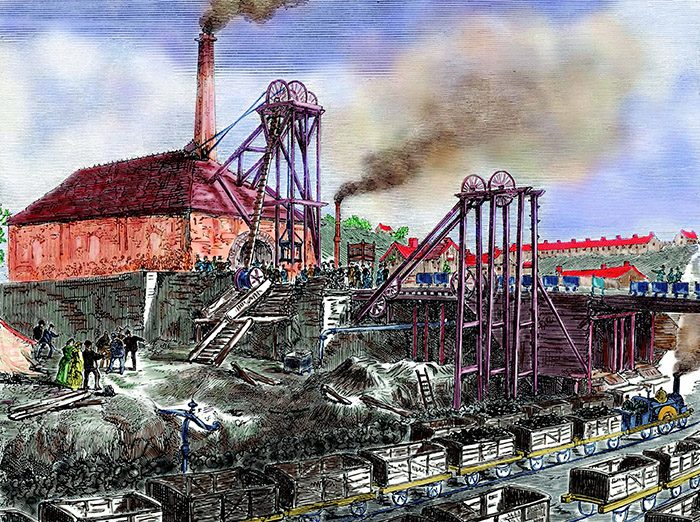
Industrialization in Manchester, a city in the northwest of England, played a pivotal role in the development of the Industrial Revolution. Located at the confluence of the Rivers Irwell and Medlock, Manchester was ideally situated to take advantage of the abundance of coal, iron, and water power available in the surrounding region. As a result, the city became a hub of manufacturing and trade, and its population exploded as people flocked to the city seeking work.
One of the key drivers of industrialization in Manchester was the growth of the textile industry. The city was home to a number of cotton mills, which were powered by steam engines and used newly invented machines such as the spinning jenny and the power loom to produce cotton goods at an unprecedented rate. These mills employed large numbers of workers, many of whom were women and children who worked long hours in dangerous and unhealthy conditions.
The rapid industrialization of Manchester also had significant social and economic consequences. As the population of the city grew, housing became scarce and working-class families were forced to live in crowded, poorly-ventilated tenements. Pollution from the factories also had a negative impact on the environment and the health of the city's residents. Despite these challenges, Manchester emerged as a major industrial center and was a driving force behind the Industrial Revolution in the United Kingdom.
In addition to its textile industry, Manchester was also home to a number of other important industries, including engineering, chemical production, and printing. The city's industries were supported by a network of transportation infrastructure, including canals and railways, which enabled goods to be easily transported to other parts of the country and beyond.
Despite the many challenges and difficulties associated with industrialization, Manchester's rapid economic growth had a profound impact on the city and the region. The city became a center of innovation and progress, and its success inspired other cities and regions to follow suit. Today, Manchester remains a thriving center of industry and commerce, and its legacy as a key player in the Industrial Revolution continues to be felt around the world.