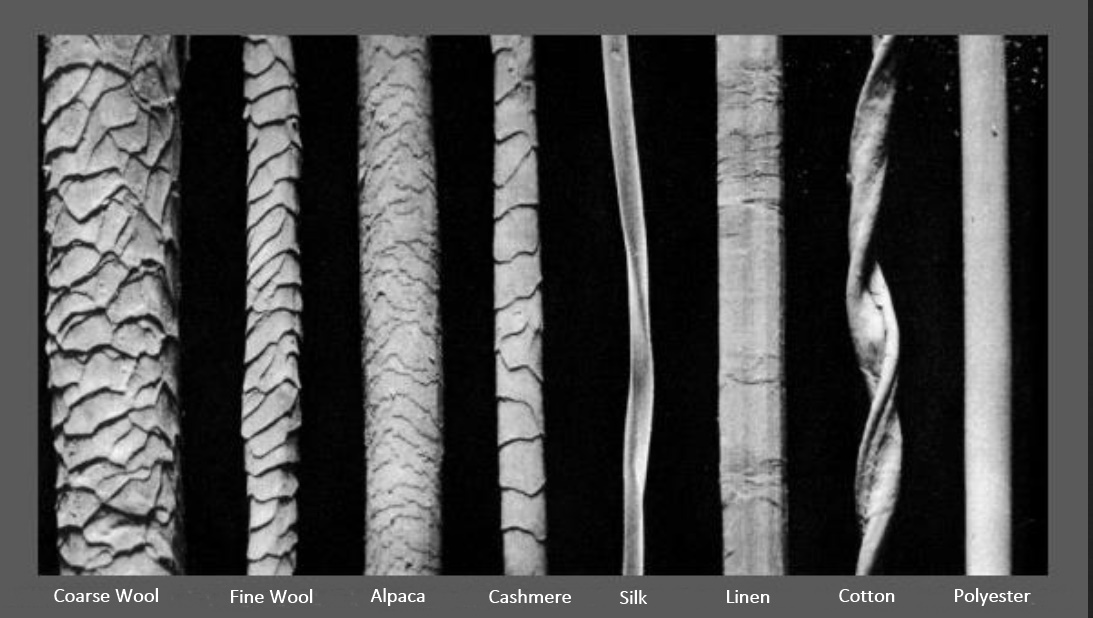
Silk is a natural protein fiber that is produced by certain insects and spiders. It is highly prized for its strength, softness, and shimmering appearance, and has been used for centuries to make clothing, bedding, and other textile products.
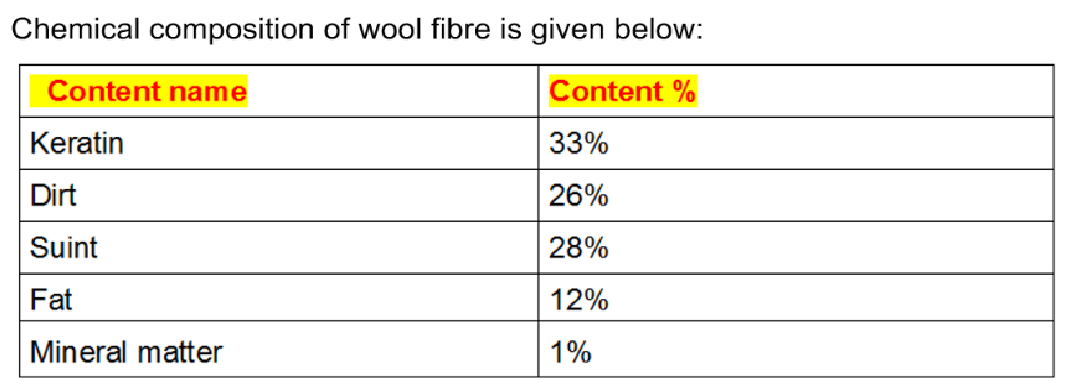
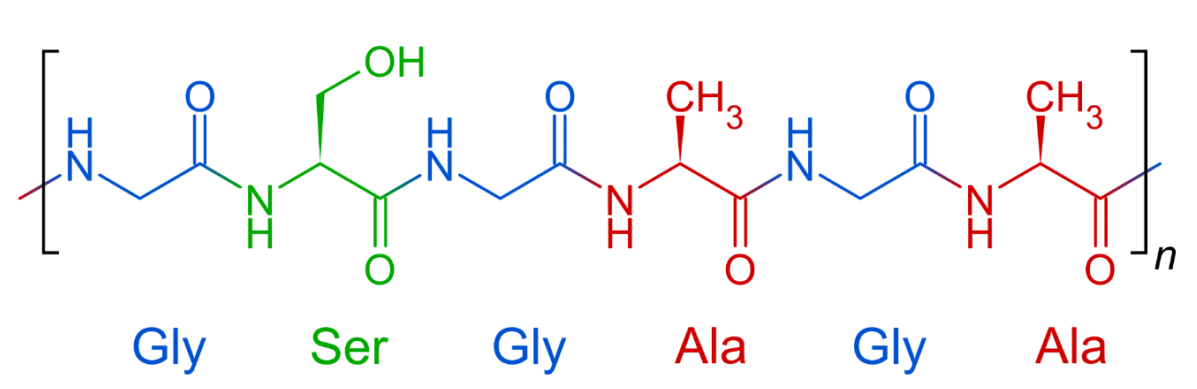
The chemical composition of silk is primarily made up of proteins, specifically a group of proteins called fibroin and a small amount of sericin. Fibroin is a long, linear protein that is responsible for the strength and elasticity of silk, while sericin is a sticky, glue-like protein that helps to hold the fibers together.
Fibroin is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. There are twenty different amino acids that can be found in fibroin, but the most common ones are glycine, alanine, and serine. These amino acids are arranged in a specific pattern to give silk its unique properties.
In addition to proteins, silk also contains small amounts of other substances such as lipids, pigments, and minerals. Lipids are fats that are found in the outer layers of the silk fiber and help to protect the fiber from damage. Pigments give silk its characteristic colors, and minerals help to give the fiber its strength and rigidity.
Silk is produced by certain insects and spiders through a process called spinning. During this process, the insects or spiders secrete a liquid protein from glands in their bodies, which hardens into the silk fibers once it comes into contact with the air. The insects or spiders then spin the fibers into a cocoon or web, which they use for protection while they undergo metamorphosis.
Once the silk fibers have been collected, they can be processed into a variety of different textile products. The fibers are first cleaned and degummed to remove any impurities or contaminants, and then they are spun into yarn. The yarn can then be woven or knitted into fabrics, or it can be used to create other products such as ribbons or cordage.
In conclusion, the chemical composition of silk is primarily made up of proteins, specifically fibroin and sericin. These proteins give silk its unique properties, such as its strength, softness, and shimmering appearance. Other substances found in silk, such as lipids, pigments, and minerals, also contribute to its characteristics.