The chemistry of carbohydrates lab is a fascinating exploration of the properties and reactions of these important biomolecules. Carbohydrates are a class of organic compounds that include sugars, starches, and cellulose, and they play a vital role in the biology of all living organisms. In this lab, students will have the opportunity to investigate the physical and chemical properties of carbohydrates, as well as learn about the various methods used to analyze and characterize them.
One of the key properties of carbohydrates is their ability to form crystalline structures. In the lab, students can observe this property by examining the crystal structure of sucrose, a common sugar found in many plants. By using a polarizing microscope, students can observe the regular, repeating patterns of the sucrose crystals and learn about the different types of crystal structures that can form.
Another important aspect of the chemistry of carbohydrates is their ability to undergo chemical reactions. One common reaction that students may explore in the lab is the hydrolysis of starch, which is a process in which the starch molecule is broken down into its component glucose units. This reaction can be observed by adding a starch solution to iodine, which will turn blue-black in the presence of starch. By monitoring the color change, students can learn about the kinetics of the hydrolysis reaction and how it can be influenced by factors such as temperature and pH.
In addition to these hands-on experiments, students in a carbohydrate chemistry lab may also have the opportunity to learn about the various techniques used to analyze and characterize carbohydrates. These techniques may include spectroscopic methods such as infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, as well as chromatographic techniques such as thin-layer chromatography and gas chromatography. These methods allow scientists to identify the specific types of carbohydrates present in a sample and determine their relative proportions.
Overall, the chemistry of carbohydrates lab is a valuable opportunity for students to learn about the properties and reactions of these important biomolecules. Through hands-on experimentation and the use of analytical techniques, students can gain a deeper understanding of the role that carbohydrates play in the biology of living organisms and the many ways in which they can be studied and characterized.
Chemistry 230 Lab

Experiment to perform colour tests for carbohydrates reducing sugars : What are carbohydrates Reducing sugars? As is generally true for most acetals, glycoside formation involves the loss of an equivalent of water. I also gained knowledge about the Iodine-starch test. The group size limited the amount of subjects to four, of which one half ate light bread and the other half dark. The Tollens' test is commonly used to detect aldehyde functions; and because of the facile interconversion of ketoses and aldoses under the basic conditions of this test, ketoses such as fructose also react and are classified as reducing sugars. VWR Revolutionary Data Logging Thermometer The VWR Traceable Logger-Trac Temperature Datalogger is perfect for monitoring material during storage, handling, and transportation.
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates

On the other hand, amylopectin is a form of starch in which the glucose molecules are in branched chains. When it was time to choose a college, she decided on the University of Wisconsin at Madison. What was the color of the initial iodine test on the starch solution? A simple solution to this dilemma is achieved by converting the open aldehyde structure for glucose into a cyclic hemiacetal, called a glucopyranose, as shown in the following diagram. However, intake of saccharin too much can lead to type 2 diabetes or even obesity. By clicking on the diagram, the consequences of such an exchange will be displayed. Ketoses If a monosaccharide has a carbonyl function on one of the inner atoms of the carbon chain it is classified as a ketose. Tetroses: composed of 4 carbon atoms, CH2O 4, include threose, erythrose, and ketose.
Introduction to Carbohydrates
A regular swimming pool is used. They provide us energy and thus form an important part of our food. The most important compounds in this class, cellulose, starch and glycogen are all polymers of glucose. Excessive inhalation may cause minor respiratory irritation. Note that despite the very low concentration of the open chain aldehyde in this mixture, typical chemical reactions of aldehydes take place rapidly. In the experiment tube there is amylase, Carb Cutter, TRIS, and starch. It is prepared by reaction of cellulose with acetic anhydride and an acid catalyst.
Ward's® Chemistry of Carbohydrates Lab Activity
By converting an aldose to its corresponding aldaric acid derivative, the ends of the chain become identical this could also be accomplished by reducing the aldehyde to CH 2OH, as noted below. If you do not wish to agree to these Terms of Use, do not access or use any part of the Web Site. The chemical reaction is given below. A summary of these redox reactions, and derivative nomenclature is given in the following table. Disaccharides When the alcohol component of a glycoside is provided by a hydroxyl function on another monosaccharide, the compound is called a disaccharide. The insoluble part is known as fiber, which is mostly cellulose.
Carbohydrates Chemistry Lab Report

Models of representative aldoses may be examined by clicking on the Fischer formulas for glyceraldehyde, erythrose, threose, ribose, arabinose, allose, altrose, glucose or mannose in the above diagram. The formation of red precipitate confirms the presence of reducing sugars. From this, we produced a standard curve for the phenol sulfuric acid assay. Metallic ions are reduced in this process. Hydrolysis of Disaccharides and Polysaccharides a.





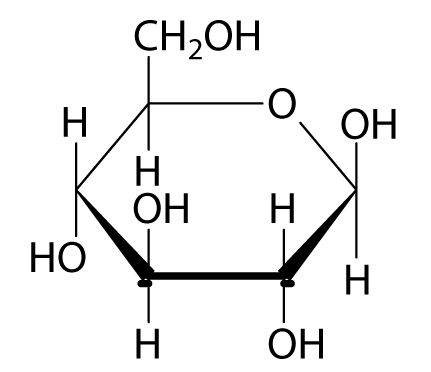
(105).jpg)
