A narrative essay is a type of essay that tells a story, usually from the writer's personal perspective. Narrative essays can be about a wide range of topics, as long as they have a clear plot and a central theme. Here are some ideas for things to write a narrative essay about:
An important event or experience from your life: This could be something that had a big impact on you, like a trip you took, a challenge you faced, or a moment of realization.
A person who has had a significant influence on you: This could be a family member, a friend, a teacher, or anyone else who has made a difference in your life.
A place that holds special meaning for you: This could be a place you've visited, a place you've lived, or a place you've always dreamed of going.
A time when you faced a difficult decision: This could be a decision that affected your life in a big way, like choosing a career path or moving to a new city.
A memorable moment or experience with a friend or loved one: This could be a time when you laughed, cried, or learned something new together.
Remember, a narrative essay should have a clear plot, with a beginning, middle, and end, and it should have a central theme or message that ties everything together. As you brainstorm ideas, think about what you want to say and what you hope your readers will take away from your essay.
What are the magnifying parts of microscope and their functions?
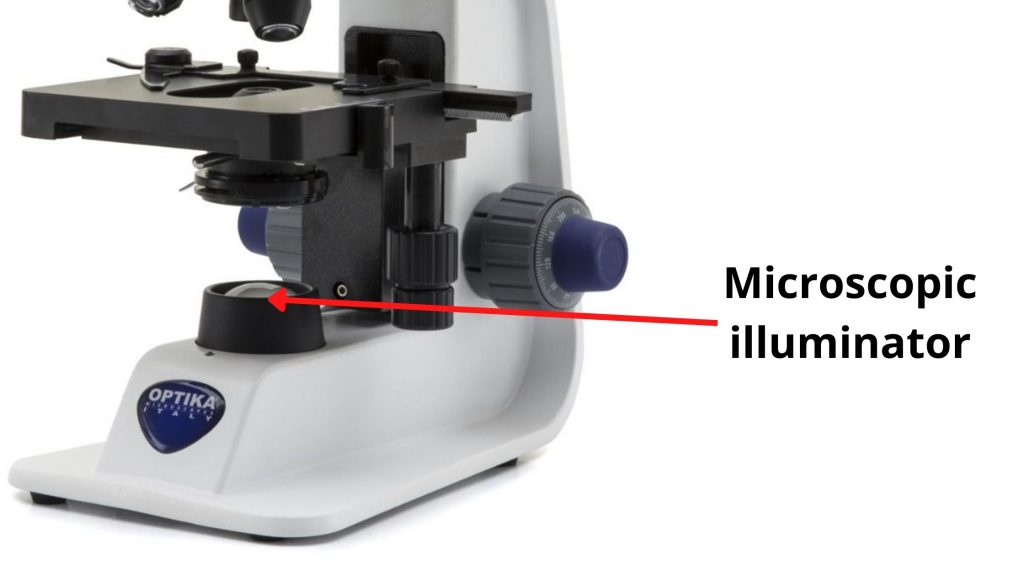
Abbe condensers are useful when the magnification is higher than 400X and the numerical aperture of the condenser lens is the same as or greater than the numerical aperture of the objective lens. The invention of the How does a microscope work? Objective Lenses : Usually you will find 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope. If you have a mechanical stage, the clips act more like a vice where you adjust the clips to clamp the slide in place. Most compound microscopes are parfocal. Also, it connects the eyepieces to the objective lenses.
Microscope Optical Components

Focus : The ability to achieve a clear image, typically achieved by moving either the eyepiece tubes or the stage. It is used with the high power objective to bring the specimen into better focus Stage The test specimen is placed over it for viewing. Holds the object lenses above the stage and rotates so that all lenses may be used. The head part supports the upper portion of the optical parts. The microscope parts work together in hospitals and in forensic labs, for scientists and students, bacteriologists and biologists so that they may view bacteria, plant and animal cells and tissues, and various microorganisms the world over. Each of these components plays an important role in producing high-resolution images of the sample being studied.
What are the function of the microscope Labelled?
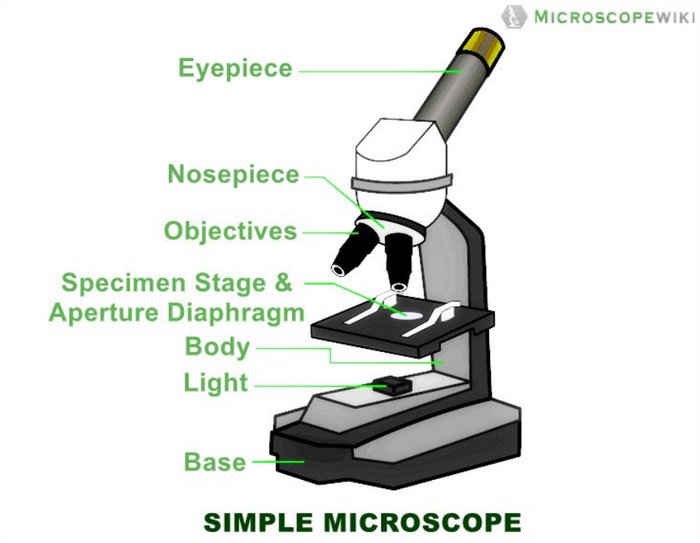
It corrects the defects of the objective. In addition, to get the greatest clarity at high levels of magnification, you will need a microscope with an Abbe condenser. Immersion oil comes in two main types: Type A and Type B. Inverted Microscope : A microscope designed with the objectives under the stage and the light source above. The image produced at the intermediate plane is further magnified by a factor of 25 centimeters called the near distance to the eye divided by the focal length of the eyepiece. The intensity of illumination and orientation of light pathways throughout the microscope can be controlled with strategically placed diaphragms, mirrors, prisms, beamsplitters, and other optical elements to achieve the desired degree of brightness and contrast in the specimen. This locks the focus knob in place and prevents it from being moved too far down.
What Are Parts Of Microscope And Their Function?
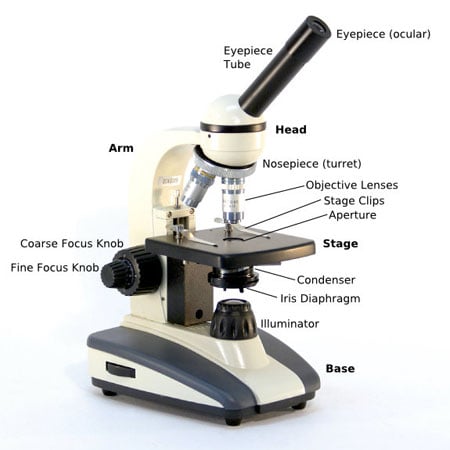
Magnifies the thing by 10. One of these linear functions is the objective function. Note the infinity "afocal" space that is defined by parallel light beams in every azimuth between the objective and the tube lens. The principal focal points are F' and F, the front and rear focal points, respectively. The eyepiece then magnifies the primary image into the final one that is seen by the observer. Even without the addition of specific devices to condition illumination and filter image-forming waves, some degree of natural filtering occurs with even the most basic microscope configuration. Objectives are available with magnifications ranging from 2X — 200X.
7 Types of Microscope and Their Functions
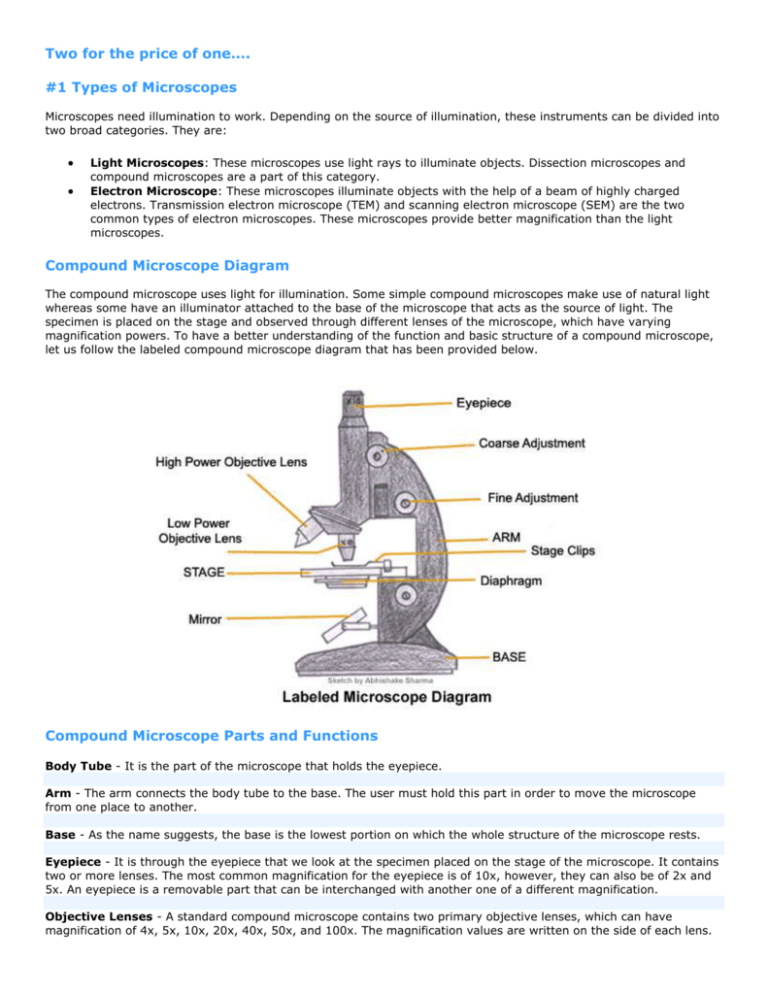
The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens. Achromatic Lens : A lens that helps to correct the misalignment of light that occurs when it is refracted through a prism or lens. Rack Stop : This feature determines how far up the stage can go. They are often used in general-purpose microscopes and are well-suited for viewing most types of specimens. Used in commercial applications that involve inspection. They support the entire microscope and provides the base to it. Objectives designed to be used with a microscope having a tube length of 160 millimeters are inscribed with this value on the barrel.
Microscope Parts and Functions
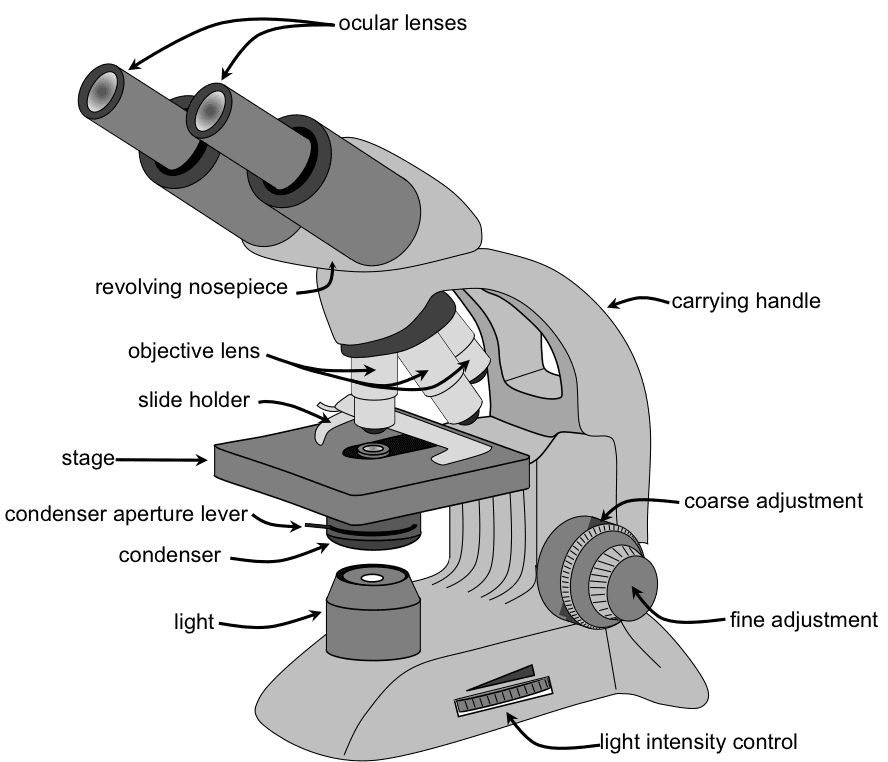
Illuminating part It is seen below the stage and made up of a system of convex lenses which focus light from illuminating sources and is used to condense light towards the object. What are the kind of microscope and its function? What are the two main parts of microscope? Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed. The objective lens is a lens that is located near the eye to see, this lens is mounted on a rotating wheel or rotating handle on the microscope that you can rotate according to the magnification you want. In the laboratory, Microscopes are used to visualize minute objects, for example; plant cell, animal cell, bacteria, fungi, etc. Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus. C-Mount : This is an adapter with a standard thread for mounting a lens to a camera. Paraxial light rays are those traveling very close to the optical axis, resulting in incident and refraction angles that are very small, which when measured in radians, can be considered as equal to their sine values.
What are the characteristics and functions of light microscopes?
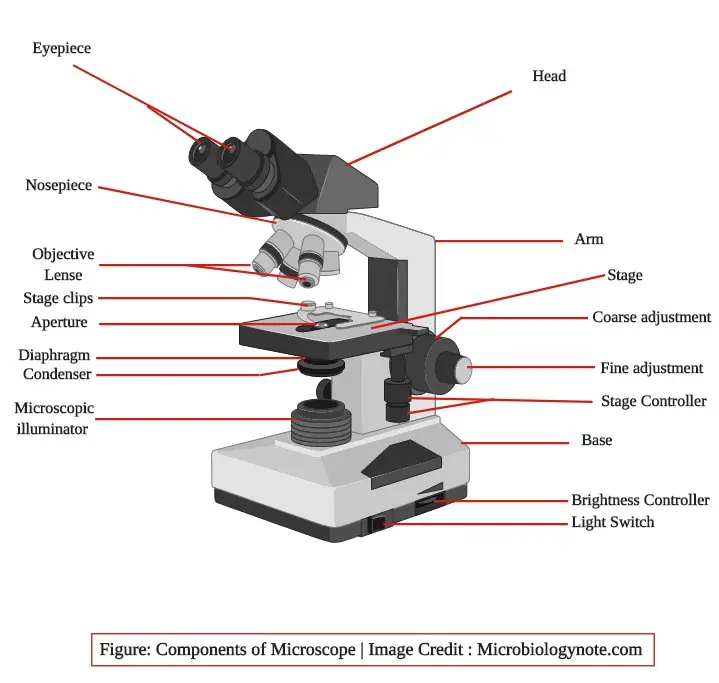
The cost of this action was often an increase in magnification and reduced light intensities in resulting images. Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen. All of the imaging components in the optical microscope are governed by the basic geometrical relationships described above. The magnified image of the specimen is first produced by the objective. Diaphragm: Diaphragm is used to vary the intensity and size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide.
What are the 14 parts of a microscope and their functions?
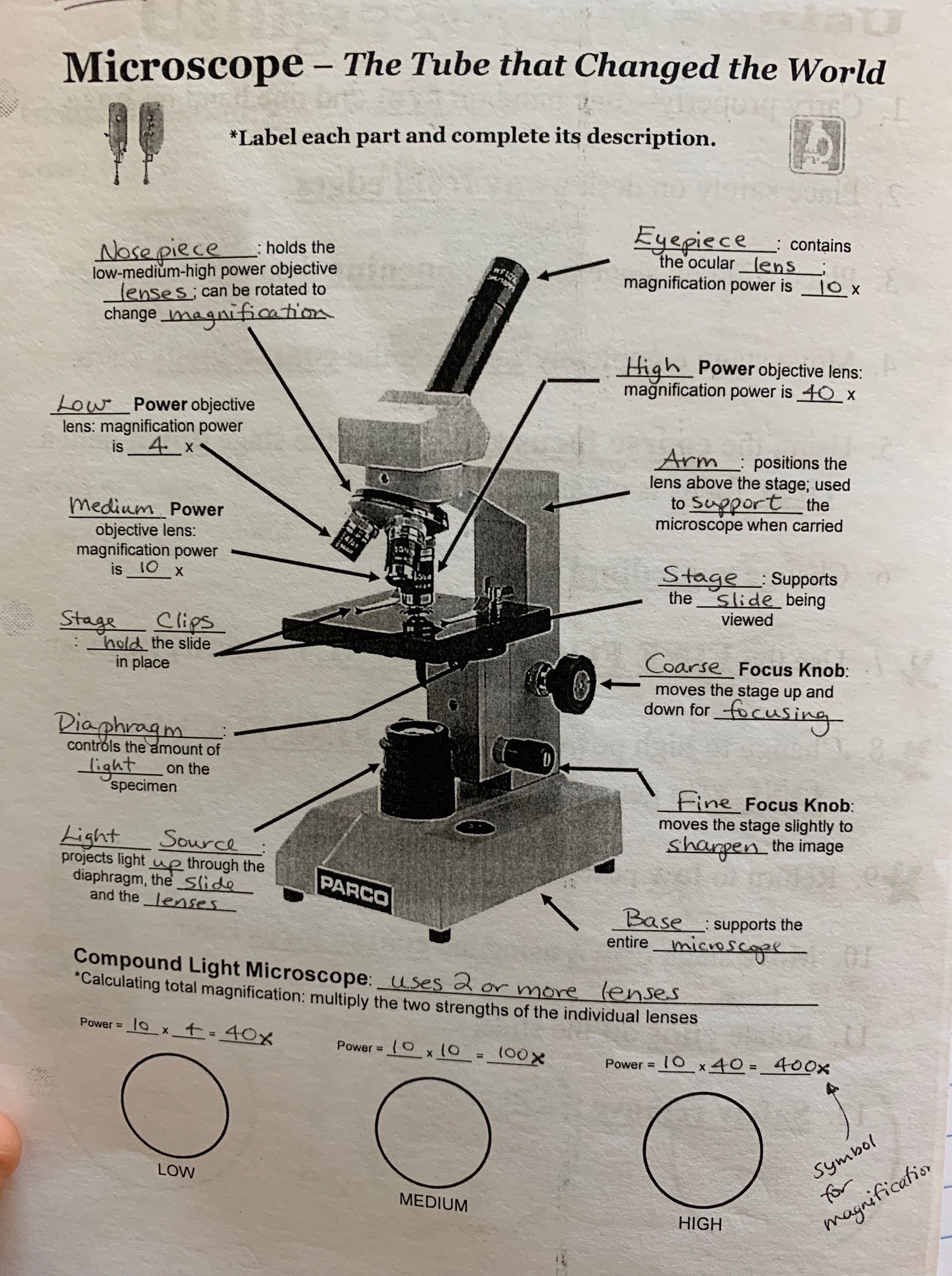
What is an advantage of using a compound light microscope over an electron microscope? It should be noted that a conventional film camera system can also be employed in place of a video or CCD sensor, in which case the image plane coincides with the plane of the chemical emulsion layered onto the film base. Condenser Lens : Condenser lenses focus the light that shines up through the slide and are useful for attaining sharp images at magnifications of 400X and above. What are the 3 lenses on a microscope? Its magnification capacity ranges between… 2. Image planes 2, 3, 3', and 4 Figures 7-11 are related to each other geometrically as illustrated in Figure 12. Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes. Look at the Compound Microscope.







