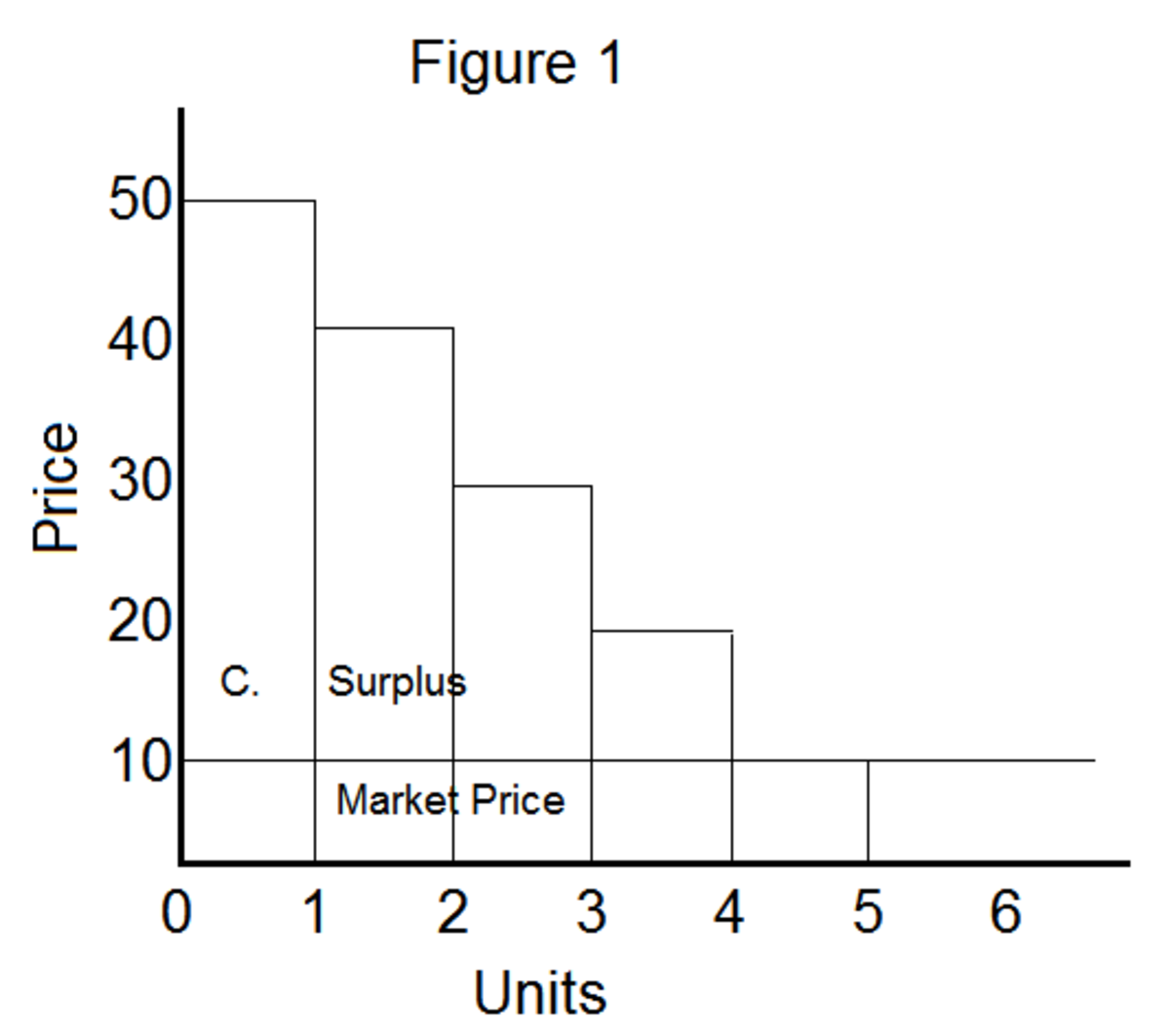
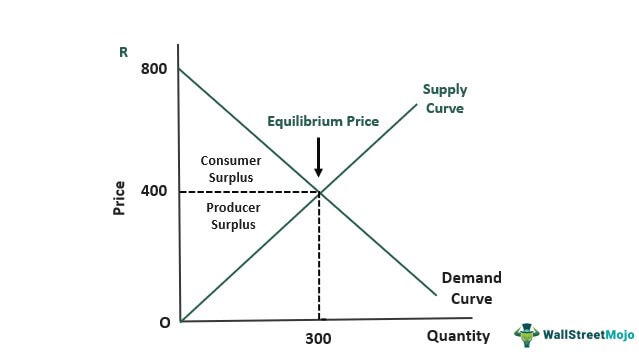
The concept of consumer surplus refers to the difference between the amount a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and the amount they actually pay. It represents the additional benefit or satisfaction that a consumer derives from purchasing a product or service.
Consumer surplus is a key concept in economics, as it helps to understand the relationship between the demand for a good or service and its price. When the price of a good or service is lower than the maximum amount a consumer is willing to pay, they experience a consumer surplus. This surplus can be thought of as a measure of the value that a consumer derives from the good or service.
There are several factors that can affect the size of a consumer's surplus. One of the most significant factors is the elasticity of demand for the good or service. If the demand for a good or service is elastic, it means that consumers are sensitive to changes in price, and they may be willing to switch to a substitute if the price increases. In this case, the consumer surplus will be relatively large, as the price is lower than the maximum amount the consumer is willing to pay. On the other hand, if the demand for a good or service is inelastic, it means that consumers are less sensitive to changes in price, and they are willing to pay a higher price for the good or service. In this case, the consumer surplus will be relatively small.
Another factor that can affect the size of a consumer's surplus is the availability of substitutes for the good or service. If there are many substitutes available, it means that consumers have more options and are less likely to pay a high price for the good or service. In this case, the consumer surplus will be relatively large. On the other hand, if there are few substitutes available, it means that consumers have limited options and may be willing to pay a higher price for the good or service. In this case, the consumer surplus will be relatively small.
In addition to the factors mentioned above, the consumer surplus can also be affected by a variety of other factors, such as the consumer's income, the price of other goods and services, and the consumer's preferences and tastes.
Overall, the concept of consumer surplus is an important one, as it helps to understand the relationship between the demand for a good or service and its price, and it can help to inform decisions about pricing and marketing strategies.