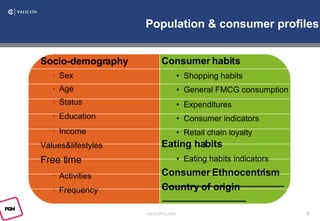
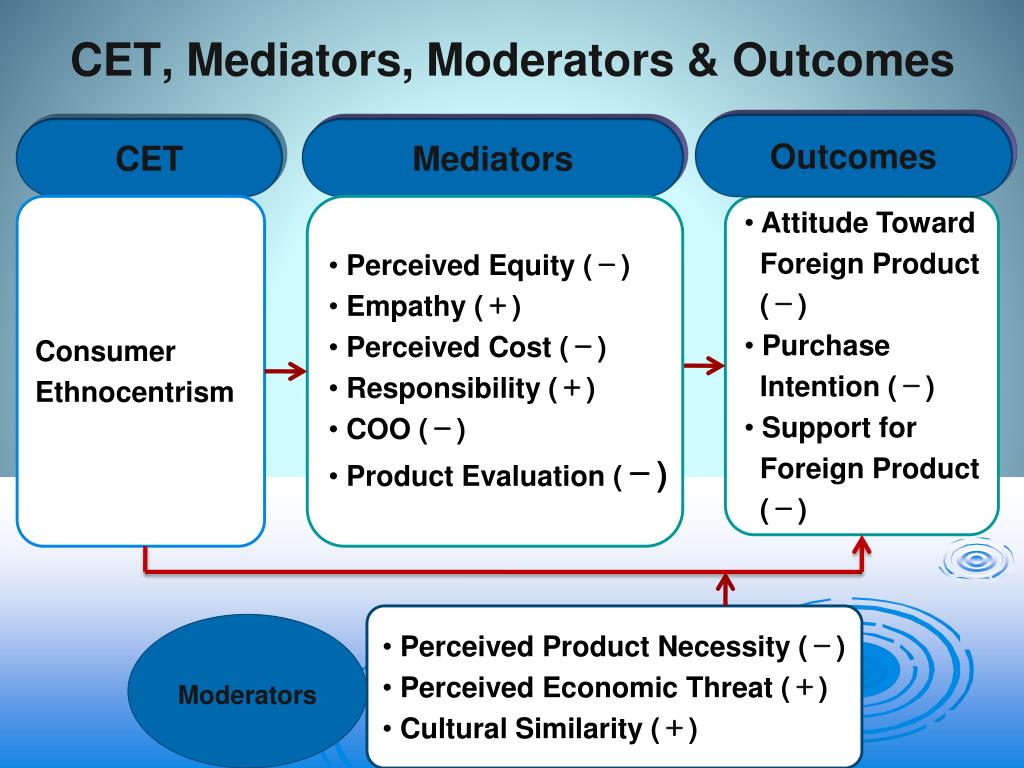
Consumer ethnocentrism is a concept that refers to the tendency of individuals to favor products and services from their own country over those from other countries. It is based on the belief that one's own culture and nation are superior to others, and that buying domestically produced goods supports the nation's economy and its people.
There are several factors that contribute to consumer ethnocentrism. One of the main factors is nationalism, which is the belief in the superiority of one's own nation and the desire to protect its interests. Nationalism can be fueled by various events and circumstances, such as war, economic recession, or perceived threats to national security.
Another factor that contributes to consumer ethnocentrism is the perception of quality. Consumers may believe that products and services produced in their own country are of higher quality than those produced in other countries. This belief can be reinforced by marketing campaigns that emphasize the quality and reliability of domestic products.
Cultural values and traditions can also play a role in consumer ethnocentrism. For example, some cultures place a strong emphasis on buying locally produced goods as a way of supporting their communities and preserving their cultural traditions. In these cases, consumers may be more likely to favor domestic products over foreign ones.
There are several consequences of consumer ethnocentrism. On the one hand, it can lead to increased sales and profits for domestic companies, as consumers are more likely to buy their products. This can contribute to the growth and development of the domestic economy.
On the other hand, consumer ethnocentrism can also have negative consequences for international trade and relations. If consumers consistently favor domestic products over foreign ones, it can create barriers to trade and lead to tensions between countries. In extreme cases, it can even lead to trade wars and other conflicts.
Overall, consumer ethnocentrism is a complex phenomenon that is influenced by a variety of factors, including nationalism, perceptions of quality, cultural values, and other factors. While it can have positive effects on domestic economies, it can also lead to negative consequences for international trade and relations.