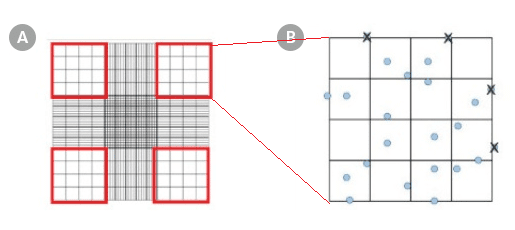
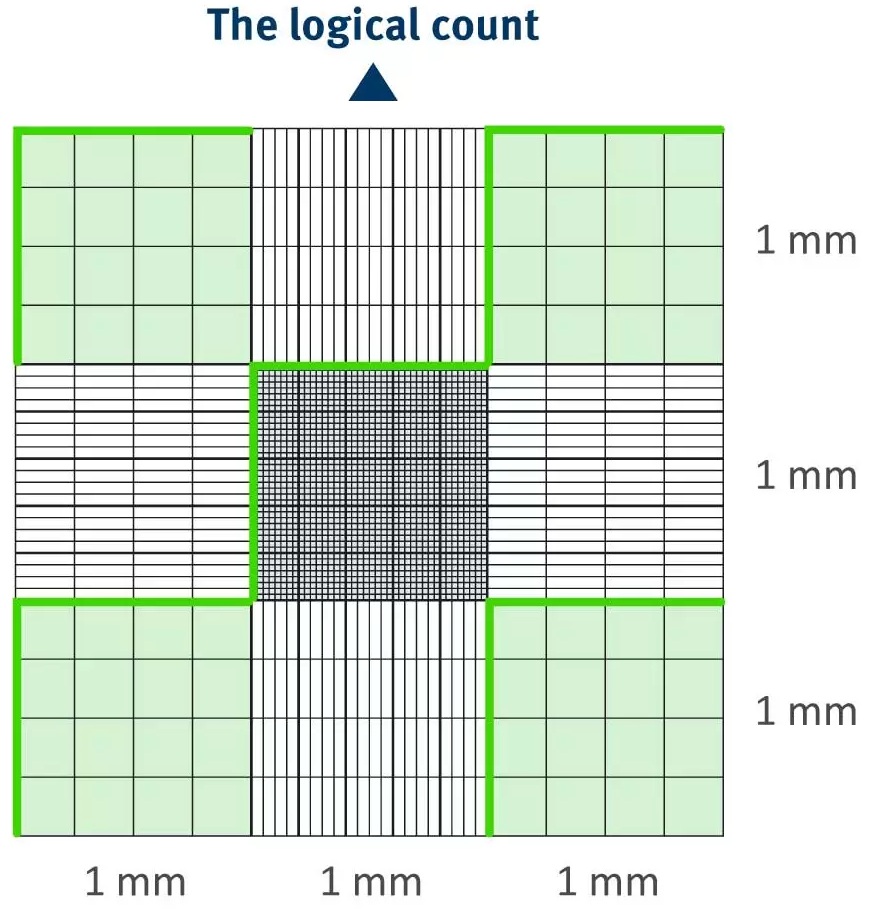
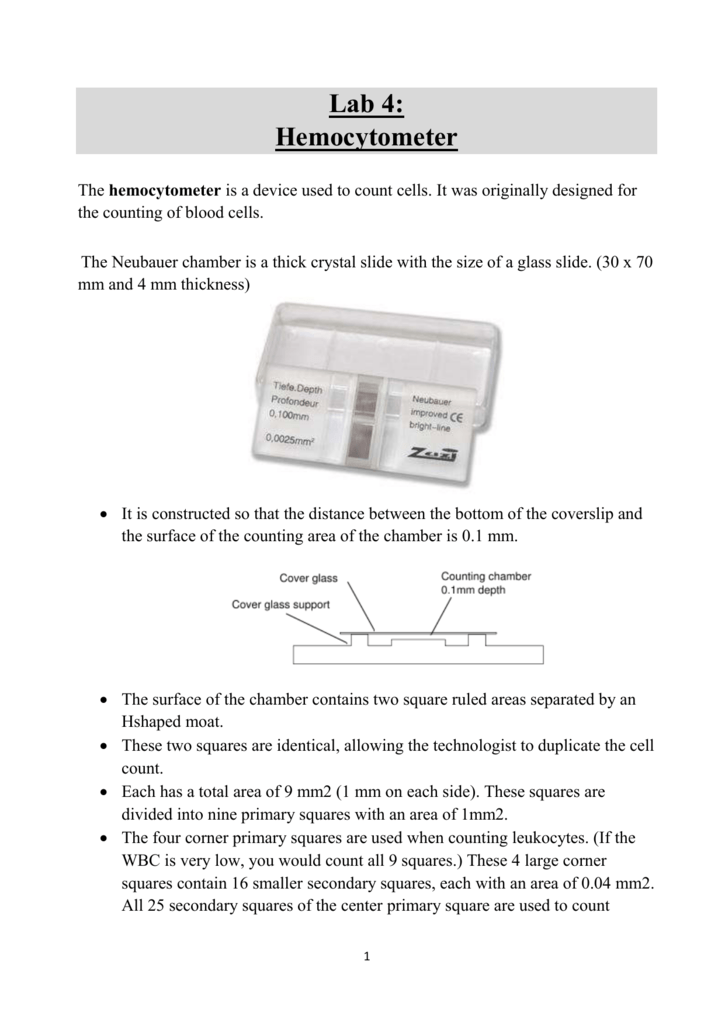
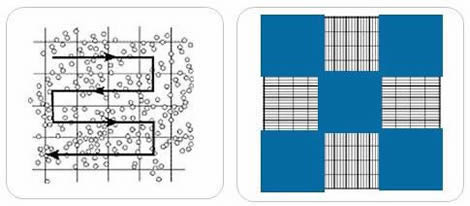
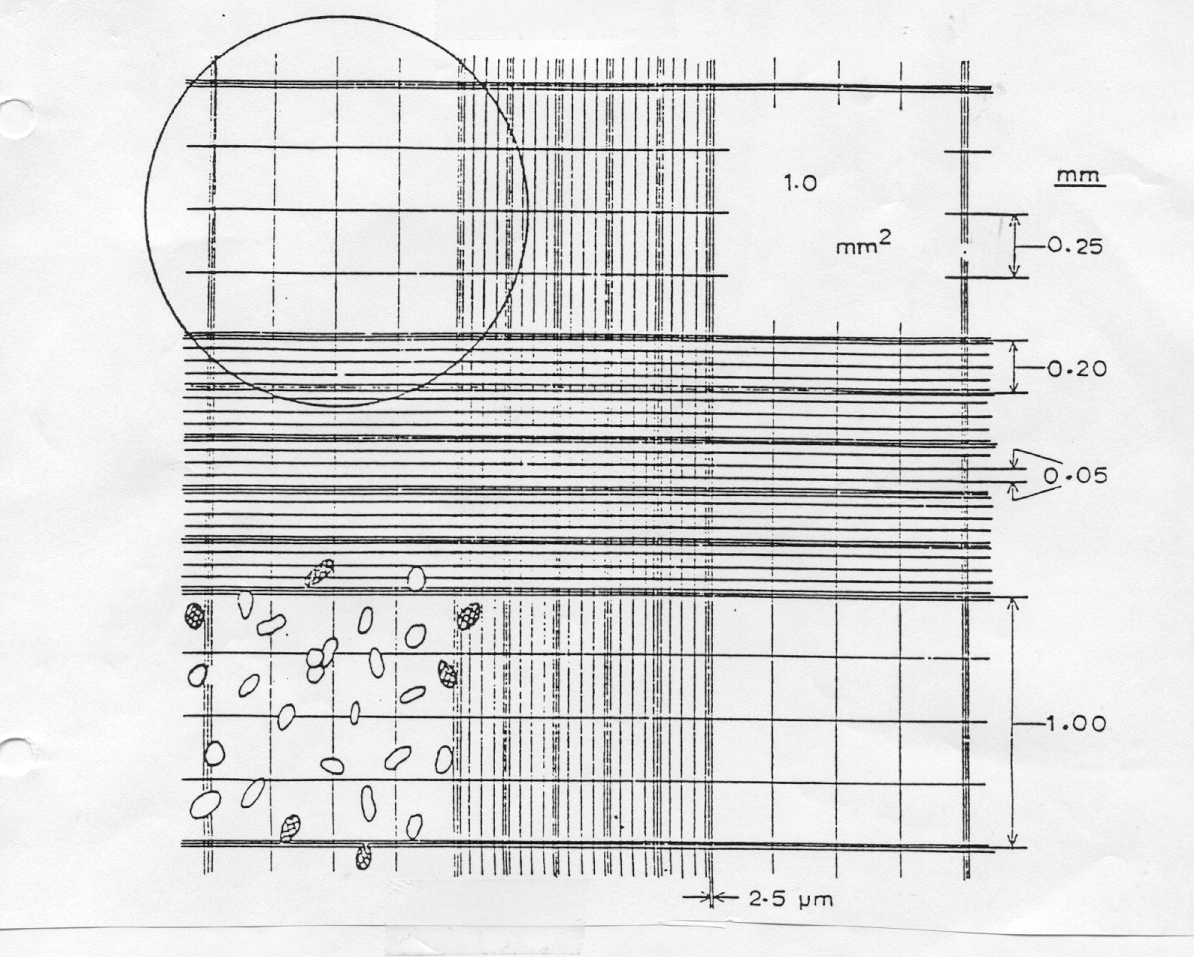
A counting chamber, also known as a hemocytometer, is a laboratory instrument used to count cells in a liquid sample. It consists of a transparent chamber with a grid of lines etched onto its surface, allowing for precise counting of cells within a known volume of fluid. There are several formulas that are used in conjunction with a counting chamber to accurately determine the number of cells present in a sample.
One of the most commonly used formulas for counting cells with a counting chamber is the formula for calculating the cell concentration, which is expressed in terms of cells per milliliter (cells/mL). To use this formula, the number of cells counted within a specific grid area on the counting chamber is divided by the volume of fluid in that grid area, which is typically 0.1 mL. For example, if 50 cells are counted within a grid area of 0.1 mL, the cell concentration would be calculated as 50 cells/0.1 mL = 500 cells/mL.
Another important formula used in conjunction with a counting chamber is the formula for calculating the total number of cells in a sample. This formula involves multiplying the cell concentration (expressed in cells/mL) by the total volume of the sample. For example, if a sample has a cell concentration of 500 cells/mL and a total volume of 10 mL, the total number of cells in the sample can be calculated as 500 cells/mL x 10 mL = 5000 cells.
In addition to these formulas, there are also correction factors that can be applied to the cell count to account for various factors that may affect the accuracy of the count. For example, the dilution factor is used to correct for samples that are too concentrated to accurately count using a counting chamber. The viability factor is used to correct for cells that are not viable or are not in a healthy state, as these cells may not be counted accurately using a counting chamber.
In conclusion, the counting chamber is a valuable tool for accurately counting cells in a liquid sample. The use of formulas such as the cell concentration formula and the total number of cells formula, as well as correction factors, allows for accurate and reliable cell counts to be obtained. These cell counts are important for a variety of applications, including the diagnosis of certain medical conditions, the production of vaccines and other biological products, and the monitoring of cell cultures in research and industry.