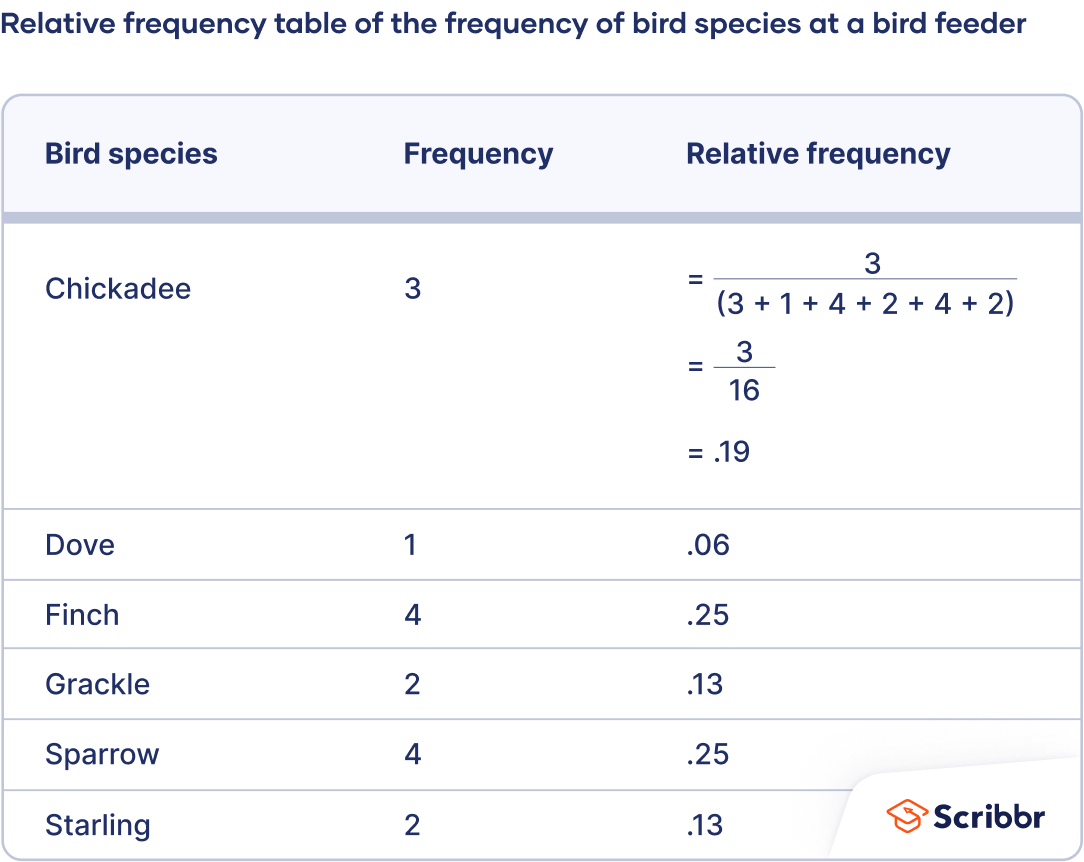
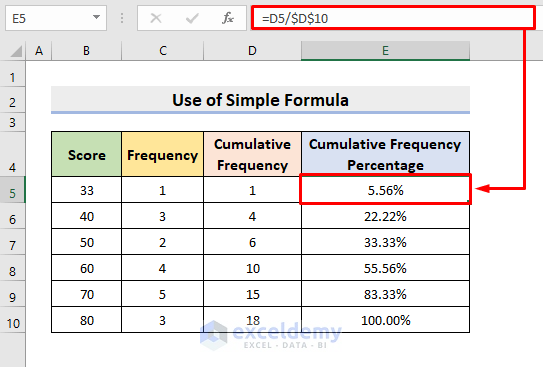
A cumulative frequency distribution is a type of frequency distribution that shows the total number of observations that fall below each value in a set of data. It is often used to visualize the distribution of a continuous variable, such as height or weight, and can be helpful in understanding the underlying patterns in the data.
One example of a cumulative frequency distribution is a graph showing the distribution of heights among a group of individuals. To create this graph, we would first measure the height of each person in the group and then sort the data from lowest to highest. Next, we would plot the heights on the x-axis and the cumulative frequency on the y-axis. The cumulative frequency is calculated by adding up the frequencies of each value as we move from left to right on the x-axis.
For example, let's say we have a group of 10 people with the following heights:
5'3", 5'4", 5'5", 5'6", 5'7", 5'8", 5'9", 5'10", 5'11", 6'0"
We would first sort the data from lowest to highest:
5'3", 5'4", 5'5", 5'6", 5'7", 5'8", 5'9", 5'10", 5'11", 6'0"
Then, we would plot the heights on the x-axis and the cumulative frequency on the y-axis. The cumulative frequency for each height is calculated by adding up the frequencies of all the previous heights. For example, the cumulative frequency for 5'7" would be the sum of the frequencies of 5'3", 5'4", 5'5", and 5'6".
Here is what the cumulative frequency distribution graph would look like:
| Height (x-axis) | Cumulative Frequency (y-axis) |
|---|---|
| 5'3" | 1 |
| 5'4" | 2 |
| 5'5" | 3 |
| 5'6" | 4 |
| 5'7" | 5 |
| 5'8" | 6 |
| 5'9" | 7 |
| 5'10" | 8 |
| 5'11" | 9 |
| 6'0" | 10 |
From this graph, we can see that the majority of the individuals in this group are between 5'7" and 5'11" in height. We can also see that there is a relatively small number of individuals who are shorter or taller than this range.
Cumulative frequency distributions can be useful in a variety of contexts, such as when we want to compare the distribution of a continuous variable across different groups or when we want to understand the distribution of a continuous variable within a single group. They can also be helpful in identifying outliers or unusual values in the data.
In conclusion, cumulative frequency distributions are a useful tool for visualizing the distribution of a continuous variable and understanding patterns in the data. They can be helpful in a variety of contexts and can provide valuable insights into the underlying patterns in the data.