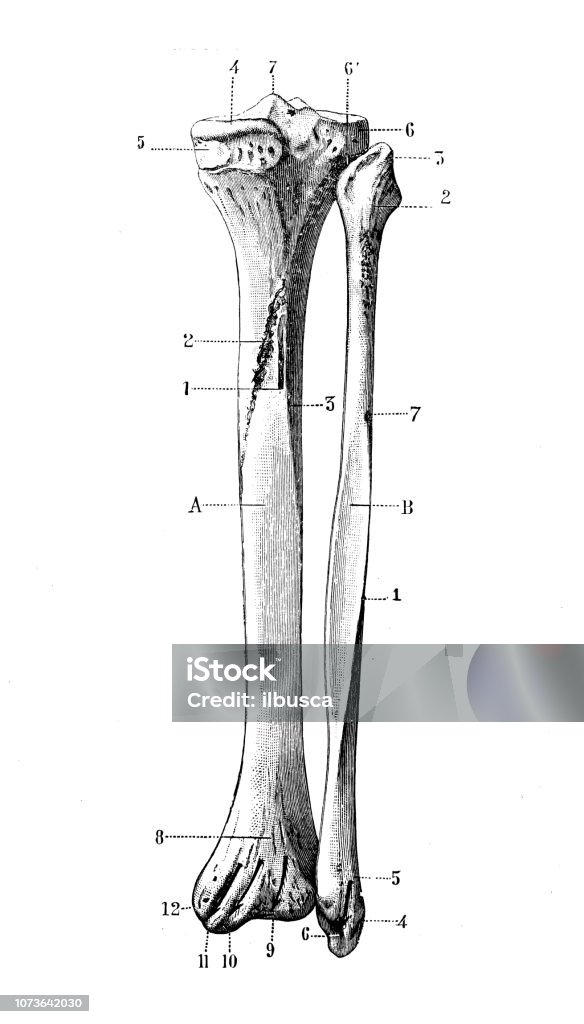
The tibia and fibula are two bones located in the lower leg. The tibia, also known as the shinbone, is the larger of the two bones and is the primary weight-bearing bone in the leg. It is the innermost bone of the lower leg, and it articulates with the femur at the knee joint and the talus at the ankle joint.
The fibula, on the other hand, is a smaller and thinner bone that runs parallel to the tibia. It is located on the outer side of the lower leg, and it articulates with the tibia at the top and bottom ends. The fibula does not bear as much weight as the tibia, but it plays a crucial role in stabilizing the ankle and supporting the muscles of the lower leg.
Both the tibia and fibula are essential for movement and support in the lower leg. They work together to allow us to walk, run, and perform other activities that involve movement of the lower body. The tibia and fibula also provide protection for the muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in the lower leg.
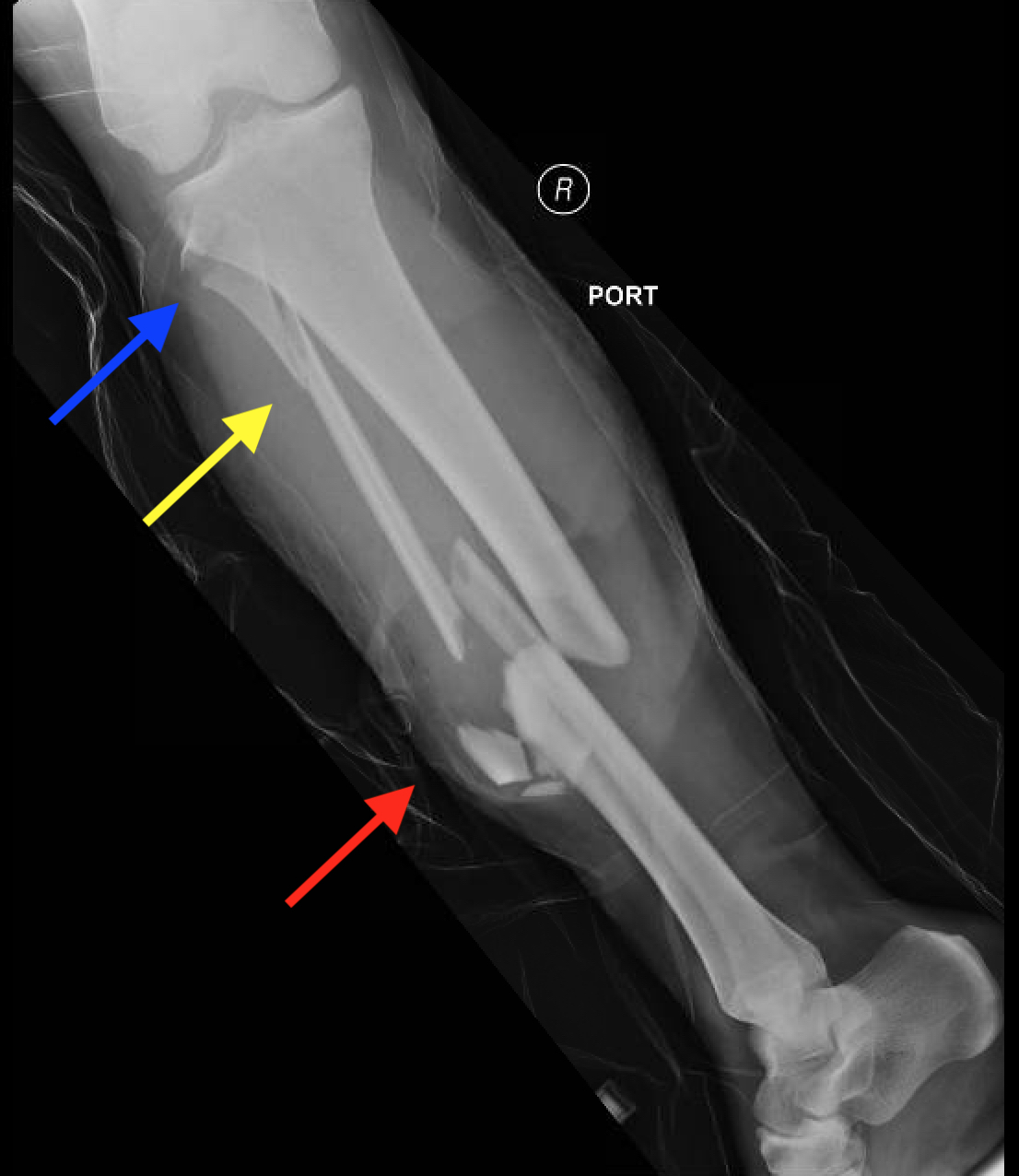
Injuries to the tibia and fibula are common, especially in sports and other physical activities. Fractures of these bones can occur due to trauma or overuse, and they can range from simple to complex. Treatment for tibia and fibula fractures may involve immobilization with a cast or surgery to repair the bone.
Overall, the tibia and fibula are vital bones in the lower leg that play important roles in movement and support. Without them, our lower bodies would not be able to function properly.
Tibia/Fibula Fracture Open Reduction and Internal Fixation

The tibia and fibula are very different bones. Reamed nailing versus unreamed nailing continues to be debated in the literature, but reamed nailing appears to be more effective in most situations, with the possible exception being very contaminated open fractures. Or, you may receive local anesthesia and a medicine to help you relax. The fibula is a non-weight-bearing bone. Treatment for a broken tibia-fibula will depend on the location, complexity, and severity of your child's fracture. Proximally make a longitudinal incision overlying the subcutaneous surface of the tibia, halfway between the anterior and posterior borders.
The Tibia and Fibula

The tibia is also known as the shinbone, and is the second largest bone in the body. To reduce the risk of thermal necrosis during the reaming of the medullary canal, do not use a tourniquet. Another possible, albeit rare, complication of ankle fractures is complex regional pain syndrome CRPS; previously known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy or RSD. IM nails give the best results in terms of rate of union, time to union, and complications. Biomechanically, these plates are on the compression side of the bone.
Tibia and fibula series

Physical Therapy after Tibia and Fibula Fractures After surgery, physical therapy will begin as soon as the surgeon decides. These views should be evaluated for the integrity of the bones as well as proper alignment between joint surfaces. Objective Evidence Patients with suspected ankle fractures should have x-rays performed: an anterior-posterior AP , lateral, and mortise view. It is important to minimize the amount of soft tissue that is stripped from bone in this approach when it is used for fracture work. Begin at the level of the tibial tubercle and extend the incision distally, ending 6 cm above the ankle. These hold bone fragments in place and help keep bones aligned as they heal.
Tibia and Fibula Bone Quiz for Anatomy

Complications of ankle fractures include malunion, non-union, stiffness, and wound breakdown. There is some evidence that the results of plating proximal-third and distal-third tibial shaft fractures are comparable to intramedullary nailing in terms of union and complications. The oval fibular articular facet is found on the head of fibula, facing anteriorly, superiorly and medially. The tibial plafond, lateral malleolus, and medial malleolus form a mortise, a socket in which the talus sits Figure 2. The capsular pattern of the tibiofibular joint is described as pain when the joint is stressed.