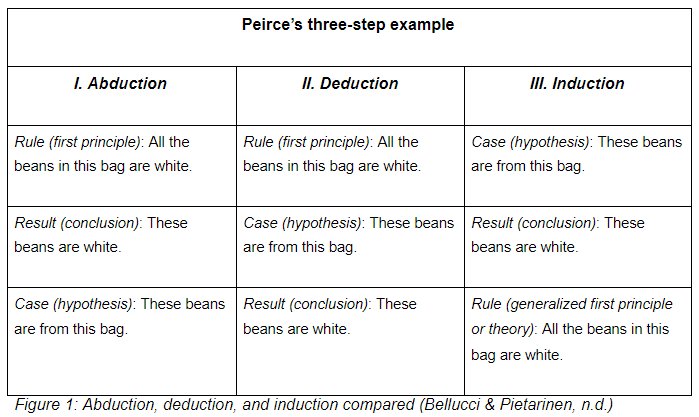
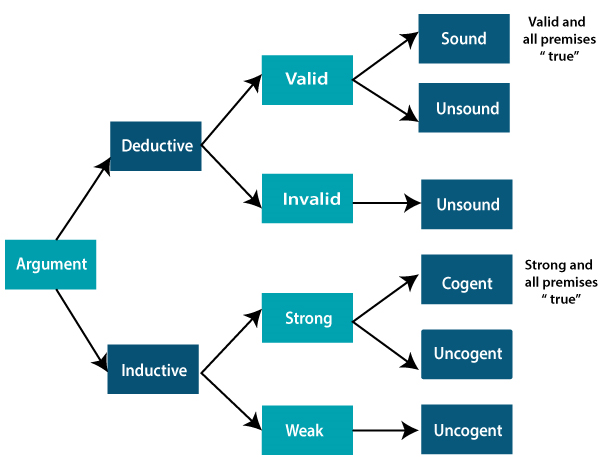
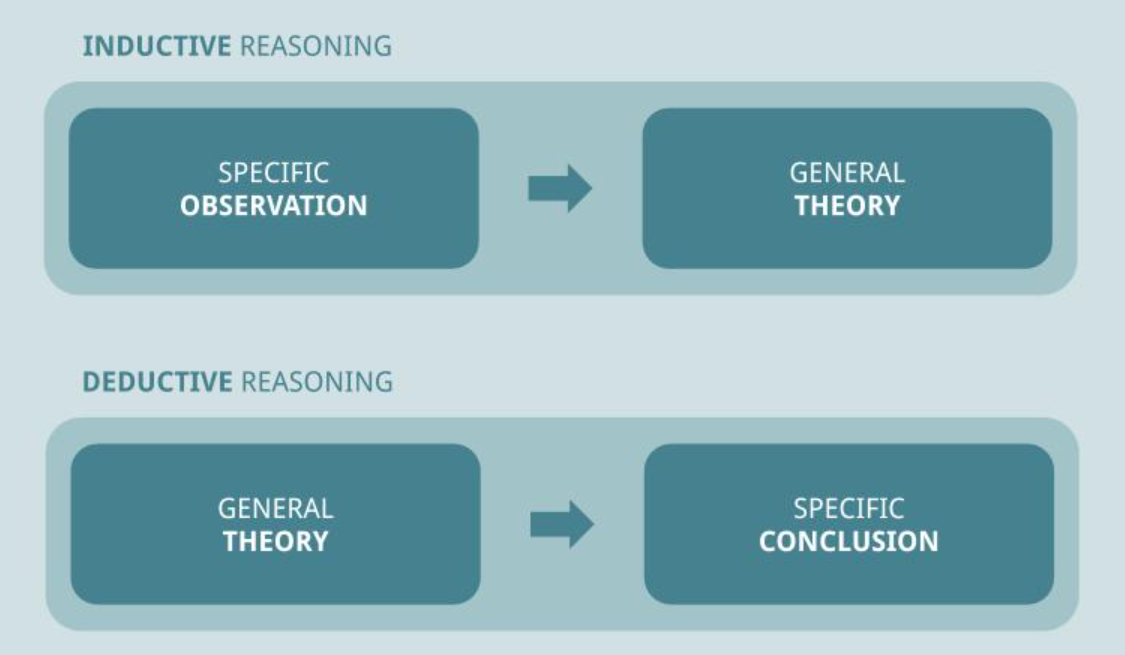
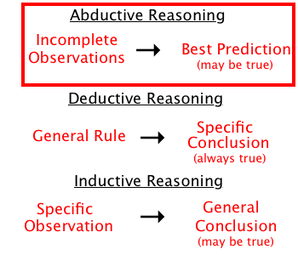
The deductive method and the inductive method are two fundamental approaches to reasoning and problem-solving that are commonly used in a variety of fields, including science, mathematics, and philosophy. While both methods can be useful in different situations, they differ in their fundamental approaches to understanding and explaining the world around us.
The deductive method involves starting with a general principle or theory and using logical reasoning to arrive at a specific conclusion. This approach is often used in mathematics, where a set of axioms and definitions are used to prove theorems and solve problems. In science, the deductive method is often used to test hypotheses and make predictions based on established laws and theories.
For example, if we start with the principle that all cats have fur, and we observe a particular animal that has fur, we can logically deduce that this animal is a cat. In this case, the general principle (all cats have fur) is used to draw a specific conclusion (the animal is a cat).
In contrast, the inductive method involves starting with specific observations or data and using these observations to form a general principle or theory. This approach is often used in scientific research, where data is collected through experiments or observations and used to develop theories or models that can explain the phenomena being studied.
For example, if we observe a large number of cats and find that they all have fur, we may conclude that all cats have fur. In this case, the specific observations (all the cats we observed have fur) are used to form a general principle (all cats have fur).
While both the deductive method and the inductive method can be useful in different situations, they have some key differences. The deductive method is generally considered to be more certain and reliable, since it relies on logical reasoning and established principles. However, it can be limited in its scope, as it can only be used to draw conclusions that are logically entailed by the starting principles.
On the other hand, the inductive method is more flexible and open-ended, as it allows for the formation of new theories and ideas based on observations. However, it can be less certain and reliable, since it is based on incomplete or limited data and may be subject to interpretation.
In conclusion, the deductive method and the inductive method are two fundamentally different approaches to reasoning and problem-solving that have their own strengths and limitations. While the deductive method is more certain and reliable, the inductive method is more flexible and open-ended. Both methods can be useful in different situations and are important tools for understanding and explaining the world around us.