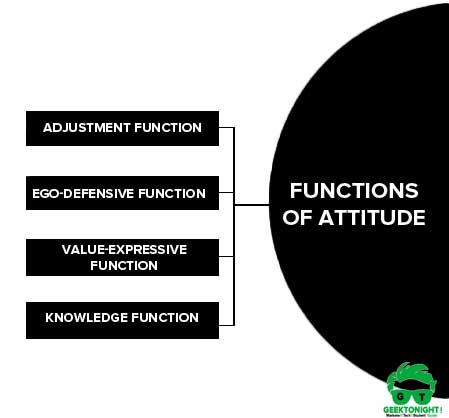
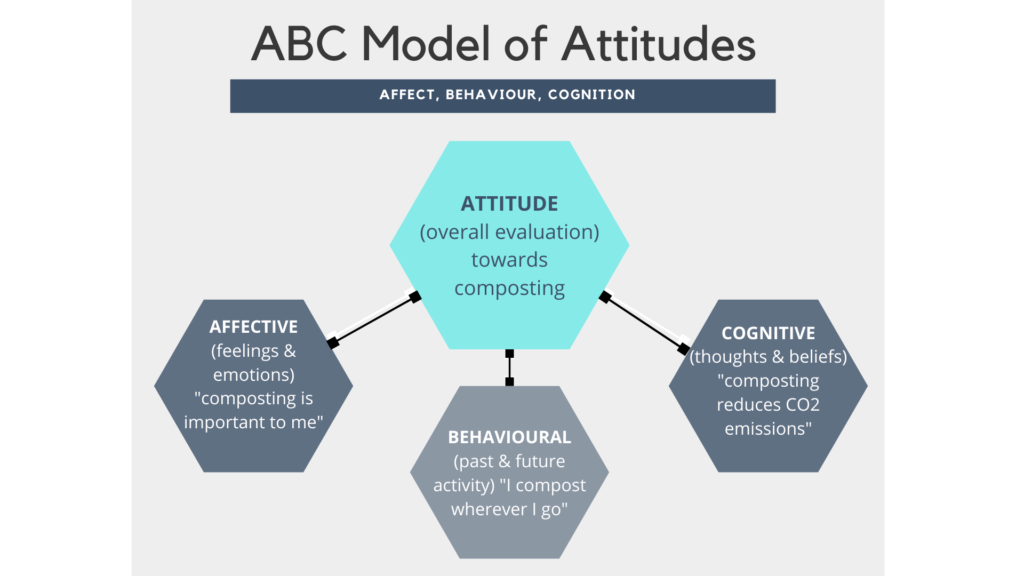
Cognitive consistency refers to the idea that people prefer to have their thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes be consistent with one another. This means that people tend to seek out information that supports their existing beliefs and attitudes, and they often avoid or reject information that conflicts with them.
There are several theories that have been proposed to explain why cognitive consistency is important to humans. One theory is that cognitive consistency helps to reduce the mental effort required to process new information. When our thoughts and beliefs are consistent, we don't have to constantly reevaluate them or try to reconcile conflicting ideas. This can make it easier to make decisions and form opinions, as we don't have to constantly weigh the pros and cons of different viewpoints.
Another theory is that cognitive consistency helps us to maintain a sense of coherence and stability in our beliefs and attitudes. When our thoughts and beliefs are consistent, we feel more confident and certain about them, which can give us a sense of security and self-esteem. In contrast, when our beliefs are inconsistent or contradictory, we may feel confused or uncertain, which can be unsettling and unsettling.
There are several ways in which people strive for cognitive consistency. One way is by selectively attending to information that supports their existing beliefs and attitudes, and ignoring or discounting information that conflicts with them. This is known as confirmation bias, and it can lead people to seek out information that supports their existing beliefs, while ignoring or dismissing information that challenges them.
Another way that people strive for cognitive consistency is by trying to reconcile conflicting beliefs or attitudes. For example, if someone believes that they should be kind and compassionate, but they also believe that they should be tough and aggressive, they may try to find ways to reconcile these conflicting beliefs, perhaps by thinking that being kind and compassionate is a sign of strength, or that being tough and aggressive is necessary to protect themselves or others.
Overall, cognitive consistency is an important aspect of human cognition, as it helps us to maintain a sense of coherence and stability in our beliefs and attitudes. While it is important to be open to new ideas and to consider multiple viewpoints, it is also important to be aware of the ways in which we may be biased towards information that confirms our existing beliefs, and to try to balance this bias with a willingness to consider opposing viewpoints.