Natural products chemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study and isolation of chemical compounds that are produced by living organisms. These compounds, also known as natural products, can be found in a variety of sources such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. Natural products chemistry is an interdisciplinary field that combines elements of organic chemistry, biochemistry, pharmacology, and botany.
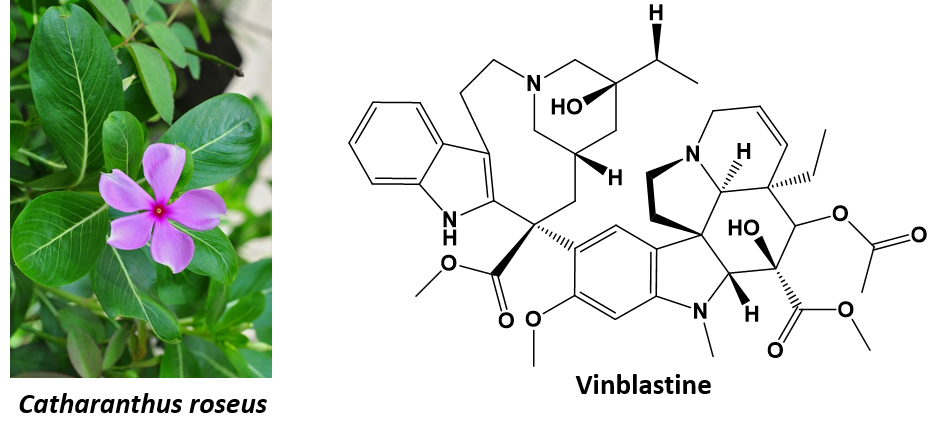
One of the main goals of natural products chemistry is to discover and characterize new natural products, which can have a wide range of applications in various fields. For example, natural products have been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat various ailments. Many natural products have been shown to have medicinal properties, and have been used to develop new drugs. In addition, natural products have also been used as flavorings and fragrances, and in the production of cosmetics and other personal care products.
The study of natural products chemistry involves the isolation and purification of natural products from their sources, followed by the identification and characterization of their chemical structures. This process often involves the use of various analytical techniques, such as spectroscopy and chromatography, to determine the structures of the compounds.
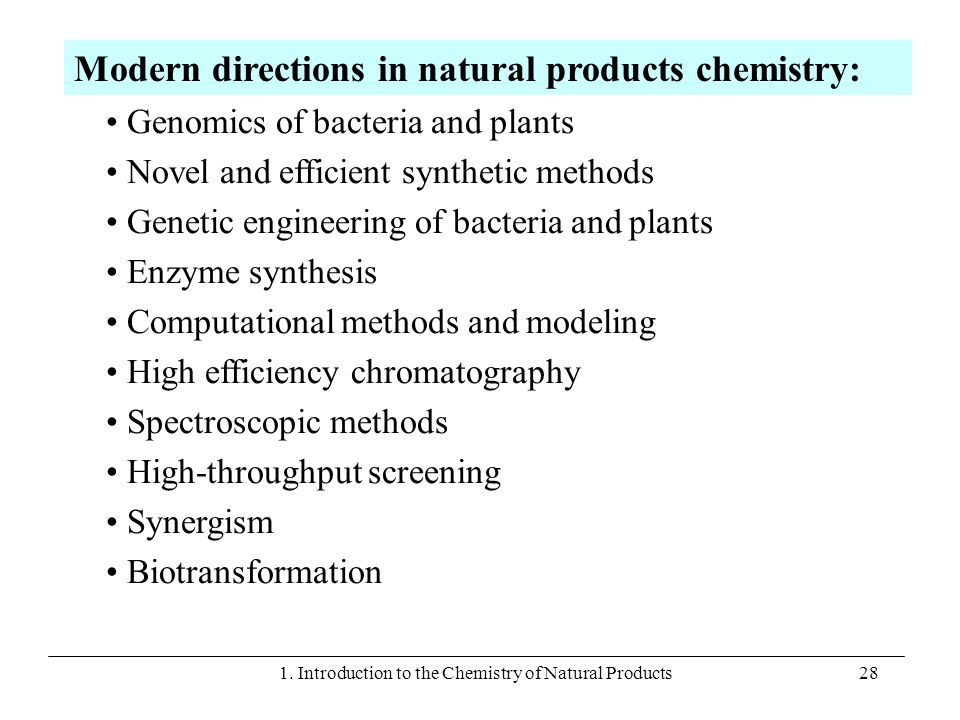
One of the major challenges in natural products chemistry is the diversity of natural products. There are thousands of different natural products, and each one has its own unique chemical structure and properties. This makes the identification and characterization of natural products a complex and time-consuming process. However, advances in technology have made it easier to isolate and identify natural products, and have led to the discovery of many new compounds.
In addition to its practical applications, natural products chemistry is also an important field of research for understanding the chemical processes that occur within living organisms. By studying natural products, scientists can gain insight into the functions of different enzymes and pathways within cells, and how these processes are regulated. This understanding can help researchers develop new drugs and therapies, and can also lead to a greater understanding of the fundamental processes of life.
Overall, natural products chemistry is a diverse and fascinating field that has the potential to improve our understanding of the natural world and to provide new solutions to various problems. Its discoveries and applications continue to make important contributions to the fields of medicine, agriculture, and industry.