Describe the modern periodic table. Modern Periodic Table of Elements 2022-12-07
Describe the modern periodic table
Rating:
6,5/10
232
reviews
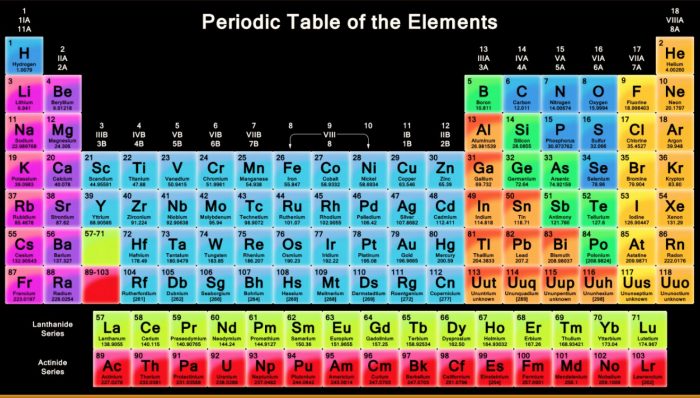
The modern periodic table is a cornerstone of chemistry and a powerful tool for organizing and understanding the elements. It is a chart that arranges all of the known chemical elements in order of their atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The table is organized into rows called periods and columns called groups.
One of the most important features of the periodic table is that it organizes the elements into families with similar chemical properties. For example, the alkali metals are a group of elements in the first column of the table and are characterized by their reactivity and tendency to form positive ions. The halogens, on the other hand, are a group of elements in the last column of the table and are known for their highly reactive nature and ability to form negative ions.
Another key feature of the periodic table is that it shows the electron configurations of the elements. Each element has a unique electron configuration, which is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus and the arrangement of its electrons. This electron configuration can be used to predict the chemical behavior of an element and how it will interact with other elements.
One of the most interesting aspects of the modern periodic table is that it has changed significantly over time as new elements have been discovered and our understanding of the atomic structure of matter has evolved. For example, the original periodic table, proposed by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, only included 63 elements. Today, the periodic table includes 118 elements, including several that were synthesized in laboratories and do not occur naturally on Earth.
In conclusion, the modern periodic table is a vital tool for organizing and understanding the chemical elements. It helps us to predict the properties and behavior of these elements and has undergone significant changes as our understanding of atomic structure has evolved. It is a testament to the power of science and the ongoing quest for knowledge about the fundamental building blocks of the universe.
The description of the modern periodic table

It makes the position of the transition elements quite clear. As the colour code is to show the metals, which are shown in purple in the above image of the periodic table. Elements of the group have one s-electron in the outer electron shell. He placed elements that had similar properties underneath each other on his periodic table. Features of Modern Periodic Table There are eighteen vertical columns known as groups in the modern periodic table which are arranged from left to right and seven horizontal rows which are known as periods. In ancient times, elements like gold and silver were easily accessible, however, the elements which Aristotle chose were Earth, In 1649 the idea of elements took a big step when Hennig Brand was the first person to discover a new element called phosphorus. For the lighter elements, the bonds in small diatomic molecules are so strong that a condensed phase is disfavoured: thus nitrogen N 2 , oxygen O 2 , white phosphorus P 4 , sulfur S 8 , and the stable halogens F 2, Cl 2, Br 2, and I 2 readily form covalent molecules with few atoms.
Next
Periodic table
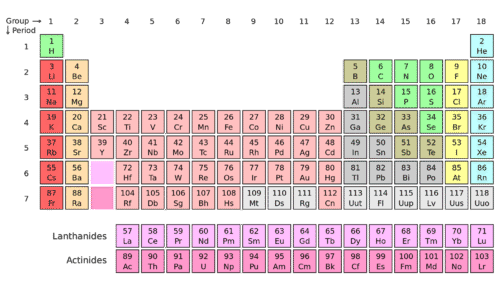
Being highly reactive, these elements always occur in combined form, these are all coloured elements as they absorb visible light. Similarly, the blue colour shows the metalloids, which have the property of metals and non-metals. The allotropes of carbon are Diamond, the hardest element in the world. There are 4 blocks s, p, d, and f. They form either small molecules like hydrogen or oxygen, whose atoms bond in pairs or giant structures stretching indefinitely like carbon or silicon. We have radioactive elements actinides present in group 3 of period seven.
Next
Describe the features of the modern periodic table. null
Modern Periodic Table And Its Significance History of the Periodic Table Earlier scientists assumed that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses. He was the first to leave room for elements that were not yet discovered. Across a period, the elements have different valencies. It is indeed true that for many of us the picture of a History of the Periodic Table The periodic table that we study today is the modern periodic table and was invented by Dmitri Mendeleev. Therefore, the bottom-left most element francium is predicted to have the lowest electronegativity and the top-right most element fluorine is predicted to have the highest electronegativity. The major contributions to the development of the periodic table were made by Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, John Newlands, Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner, Julius Lothar Meyer, Glenn T.
Next
Modern Periodic Table: Definition, Features, Trends, Advantages
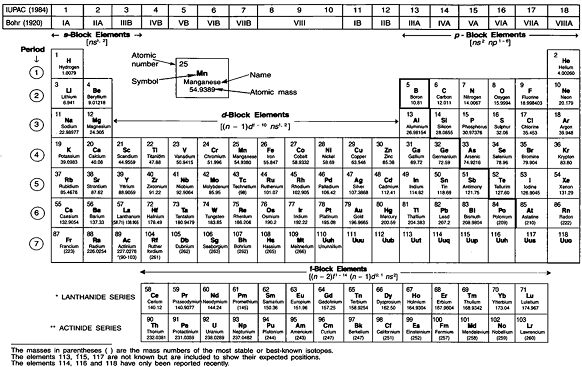
All isotopes of an element have the same atomic number and occupy the same position in the modern periodic table. At the start of the 19th century, Joseph Proust and his team were demonstrating the Law of Definite Proportions experimentally. Mendeleev classified the atoms in a table called Mendeleev's periodic table in the form of periods and groups. This makes the group somewhat exceptional. Chemists may create much heavier elements that may be more stable because of the special properties of certain combinations of proton and neutron numbers.
Next
The modern periodic table
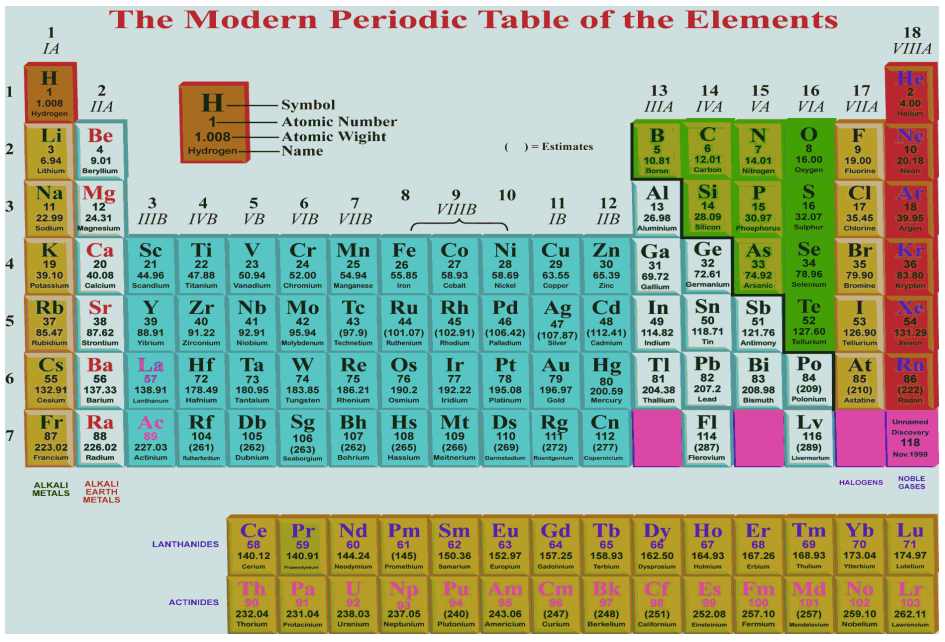
Chemical elements are arranged in a recurring pattern called the periodic law in their properties, in which elements in the same column group have similar properties. The above table shows the names and atomic numbers of the elements, and also their blocks, natural occurrences and Variations Period 1 Main article: Although the modern periodic table is standard today, the placement of the period 1 elements hydrogen and helium remains an open issue under discussion, and some variation can be found. Most non-metallic solids are brittle and are neither malleable nor ductile. Across a period, the ionization energy increases, and the ionization energy decreases down a group. All isotopes of an element have the same atomic number and occupy the same position in the modern periodic table.
Next
What Are the Parts of the Periodic Table?
Brand was an alchemist who was in search of the Philosopher's Stone, or an object which would turn any kind of ordinary metal into gold. The first shell contains only one orbital, a spherical s orbital. The scope of terms varies significantly between authors. What is the name of a modern periodic table? It is soluble in water and is heavier than air. Examples of groups of elements that are metals include alkali metals, alkaline earths, basic metals, and transition metals.
Next
How Is the Periodic Table Organized Today?

It makes the position of the transition elements quite clear. Moseley's Periodic Law Henry Moseley showed that the chemical and 'Physical and chemical properties of an element are a periodic function of its atomic number. Find out the conceptual differences of all these postulates so that you can understand how this modern periodic table developed in due course of time. Properties of the middle element also lied in the middle of both the other elements. An IUPAC project has been recently initiated to resolve the question.
Next
Chapter 6 + 7: Development of the Modern Periodic Table and the Elements Flashcards

However, there were a few anomalies in the arrangement which were later cleared by the English Physicist, Henry Moseley. Modern periodic law states that all the properties of a particular element are dependent on their atomic numbers, and elements will show similar properties at regular intervals of increasing atomic numbers. The atomic number of tellurium is 52 and the atomic number of iodine is 53, so these elements are in the correct order in the modern periodic table. Modern Periodic Table: The modern Features of Modern Periodic Table In the study of chemistry, the modern periodic table holds prime importance. Get some practice of the same on our free Blocks of the Periodic Table FAQs. It would not be wrong to say that the study of the chemistry of elements would have been impossible without the existence of the modern periodic table.
Next
Modern Periodic Table and Its Significance

The elements of the group A are located on the left and right sides of the table. In this theory, all substances were made of fundamental building blocks. For the nonmetallic elements, electron affinity likewise somewhat correlates with reactivity, but not perfectly since other factors are involved. What are the advantages of the modern periodic table? Seaborg, Dmitri Mendeleev, and many others. For example, fluorine has a lower electron affinity than chlorine, but is more reactive. As it is in the first shell, this is called the 1s orbital. According to the modern periodic table,the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
Next
Development of Modern Periodic Table

Modern Periodic Law Henry Moseley propounded the modern periodic law. In group 14, both metallic and covalent bonding become possible. Down a group: All the elements present in a group have the same valence shell electronic configuration of their atoms. What is Modern Periodic Table? Therefore, helium is nearly universally placed in group 18 2 element before the alkaline earth metals stands out as anomalous in a way that helium as the first noble gas does not. Later on, it was found that this law of triads was not true for each element and hence, it was not proven to be successful. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph. It also contained some gaps which were later filled after the discovery of new elements.
Next







