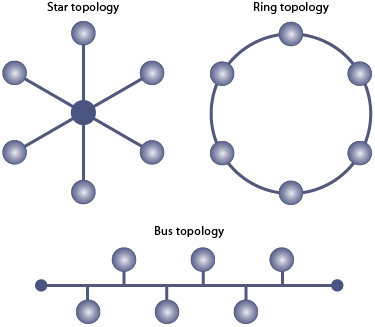
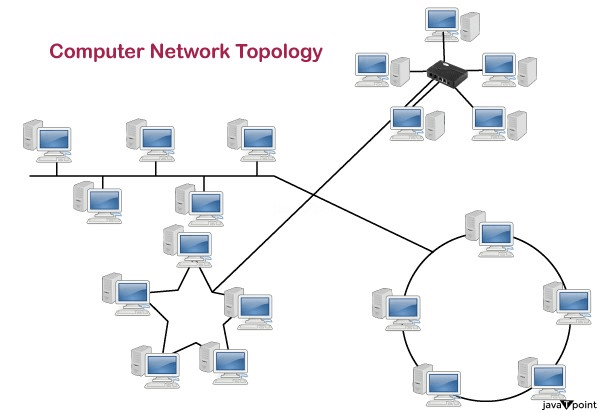
A bus topology and a ring topology are two different network configurations that are used to connect devices in a computer network. In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a central cable, or bus, which acts as a shared communication medium. In a ring topology, devices are connected in a circular fashion, with each device being connected to two other devices on either side of it. Both bus and ring topologies have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific needs and requirements of the network.
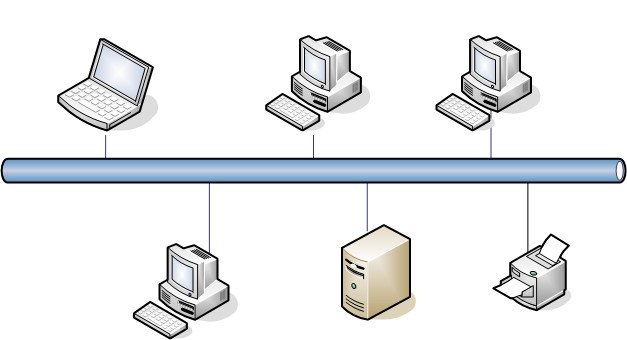
One of the main differences between a bus topology and a ring topology is the way in which data is transmitted between devices. In a bus topology, data is transmitted by sending a signal down the central bus. All devices on the network can see the signal, but only the device that the data is intended for will process it. This means that the bus topology is relatively simple, as it only requires a single central cable for communication. However, it can also be prone to data collisions, where two devices try to transmit data at the same time and the signals interfere with each other.
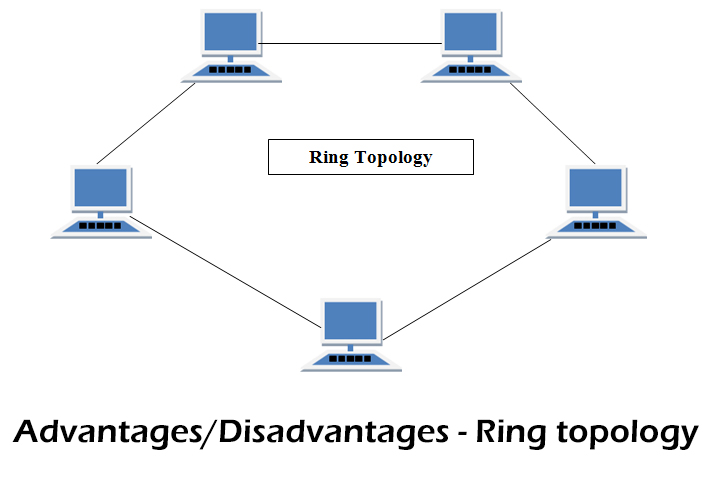
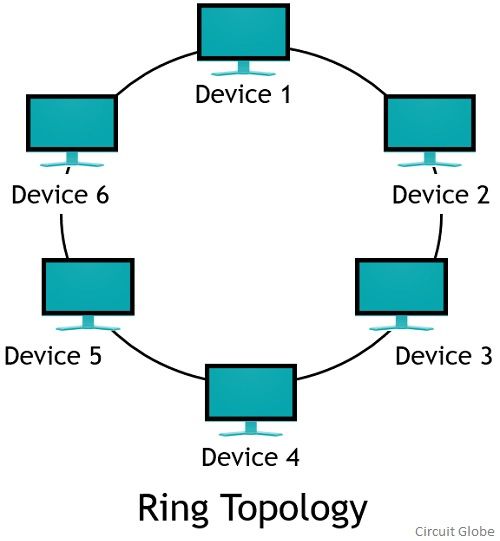
In a ring topology, data is transmitted in a circular fashion, with each device passing the data on to the next device in the ring. This means that the data travels in a specific direction around the ring, and each device only processes the data if it is intended for it. This reduces the chances of data collisions, as there is only one direction in which data can travel. However, it also means that the ring topology is slightly more complex, as it requires multiple connections between devices.
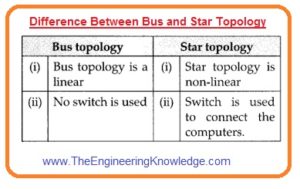
Another key difference between bus and ring topologies is the way in which they are laid out physically. A bus topology typically consists of a single central cable, with devices connected to it at various points along its length. This can make it relatively easy to install and maintain, as it only requires a single cable to be run between devices. However, it can also be prone to problems if the central cable becomes damaged, as this can disrupt communication for all devices on the network.
A ring topology, on the other hand, typically consists of a series of devices connected in a circular fashion, with each device being connected to two others on either side of it. This can make it slightly more complex to install and maintain, as it requires multiple connections between devices. However, it can also be more resilient to failures, as the ring can continue to function even if one device goes offline.
In terms of performance, both bus and ring topologies have their own strengths and weaknesses. A bus topology is generally faster than a ring topology, as it requires less processing power and has fewer connections between devices. However, it can also be more prone to congestion, as all devices share the same central cable for communication. A ring topology is generally slower than a bus topology, as it requires more processing power and has more connections between devices. However, it can also be more efficient, as it allows for more efficient use of bandwidth and can be less prone to congestion.
In conclusion, bus and ring topologies are two different network configurations that are used to connect devices in a computer network. A bus topology is relatively simple and fast, but can be prone to congestion and data collisions. A ring topology is slightly more complex and slower, but can be more efficient and resilient to failures. The choice of which one to use depends on the specific needs and requirements of the network.