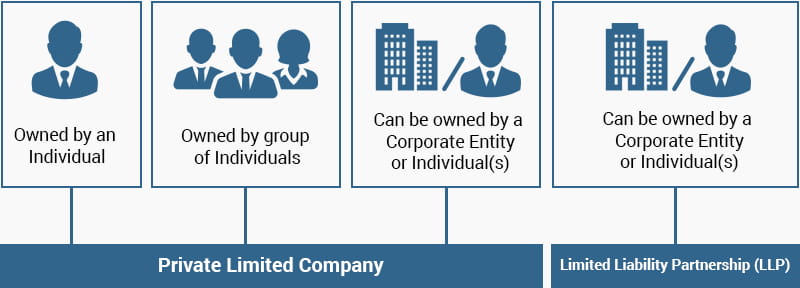
A limited company is a type of business structure that offers limited liability protection to its owners, also known as shareholders. This means that the shareholders of a limited company are only liable for the amount of money they have invested in the company and are not personally responsible for any debts or legal issues that the company may incur.
On the other hand, a proprietary limited company, also known as a private limited company, is a specific type of limited company that is privately owned and has a smaller number of shareholders, typically less than 50. Proprietary limited companies also have certain restrictions on the transfer of shares, which means that the shareholders must obtain the consent of the other shareholders before selling their shares.
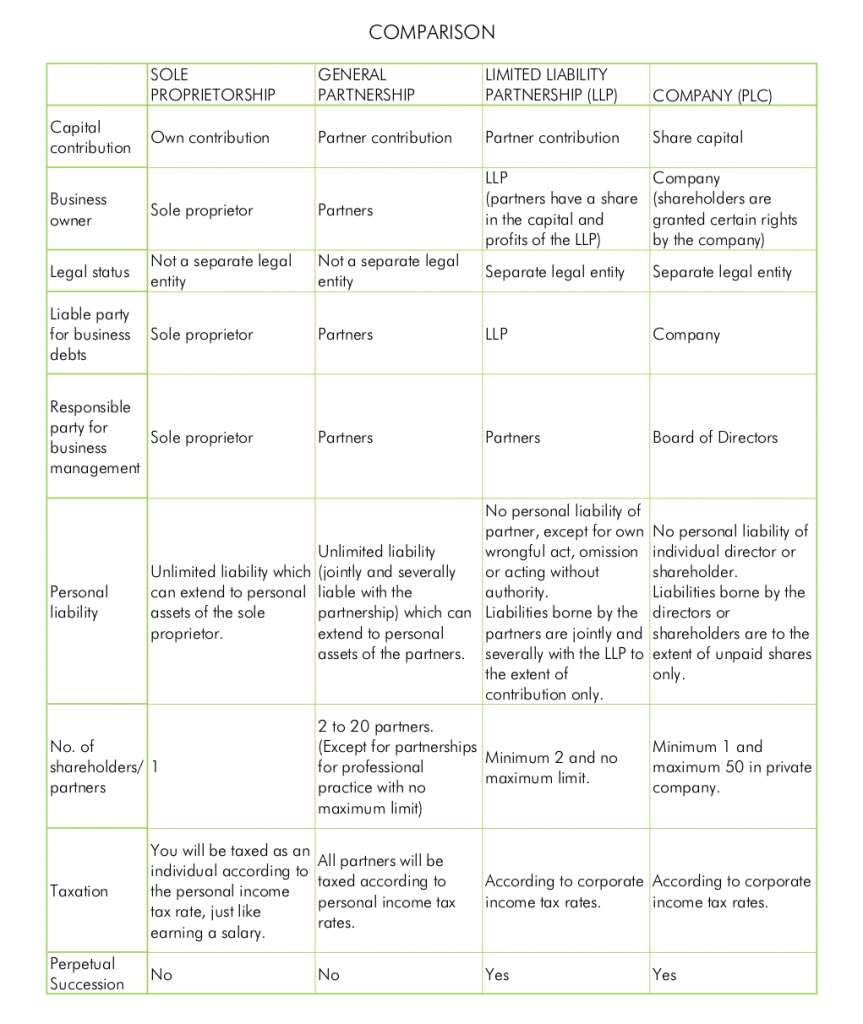
One key difference between limited and proprietary limited companies is the level of liability protection offered to the shareholders. In a limited company, the shareholders are only liable for the amount of money they have invested in the company, which is known as their "limited liability." This means that if the company incurs debts or faces legal issues, the shareholders are not personally responsible and cannot be sued for the company's debts. In contrast, in a proprietary limited company, the shareholders have unlimited liability, which means that they can be held personally responsible for the company's debts and legal issues.
Another key difference between the two types of companies is the level of transparency and reporting requirements. Limited companies are required to publicly disclose their financial statements and other important information, such as their annual report and accounts. In contrast, proprietary limited companies are not required to disclose this information publicly, and their financial statements and other important documents are typically only available to shareholders and other stakeholders.
In terms of tax implications, limited companies are generally taxed at the corporate tax rate, which is currently set at 27.5% for small businesses and 30% for larger businesses in Australia. Proprietary limited companies, on the other hand, are taxed at the individual tax rate, which ranges from 0% to 45% depending on the amount of income earned.
In conclusion, limited and proprietary limited companies are two different types of business structures that offer different levels of liability protection and have different reporting and transparency requirements. Limited companies offer limited liability protection to their shareholders and are required to publicly disclose their financial statements and other important information, while proprietary limited companies offer unlimited liability protection to their shareholders and are not required to disclose this information publicly.

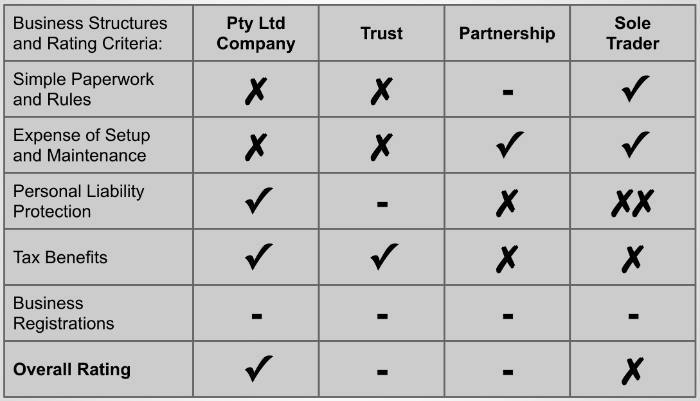
.webp)