The difference between old markets and new markets can be understood in terms of the characteristics and features that define each type of market. Old markets, also known as traditional markets, are those that have been in existence for a long time and are characterized by the presence of established businesses and a well-defined customer base. These markets are often characterized by a high degree of stability and predictability, as the businesses and customers within them are typically well-established and have a long history of interaction.
On the other hand, new markets are those that are emerging or growing rapidly, and are characterized by the presence of new businesses and a less defined customer base. These markets are often characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and risk, as the businesses within them are still establishing themselves and are often competing with one another for market share.
One key difference between old markets and new markets is the level of competition. In old markets, the businesses that have been around for a long time are often well-established and have a strong presence in the market. This can make it difficult for new businesses to enter the market and compete, as they may not have the same level of experience or resources as their established counterparts. In new markets, on the other hand, there may be more opportunities for new businesses to enter and compete, as the market is less saturated and there are fewer established players.
Another difference between old markets and new markets is the level of innovation. In old markets, the businesses that have been around for a long time are often more focused on maintaining their position in the market, rather than trying to introduce new products or services. In new markets, on the other hand, there is often more room for innovation, as businesses are trying to establish themselves and differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Overall, the key difference between old markets and new markets is the level of stability and predictability versus uncertainty and risk. Old markets are typically more stable and predictable, while new markets are characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and risk. This can have significant implications for businesses operating in each type of market, as they must adapt their strategies and tactics to the unique characteristics of the market in which they operate.
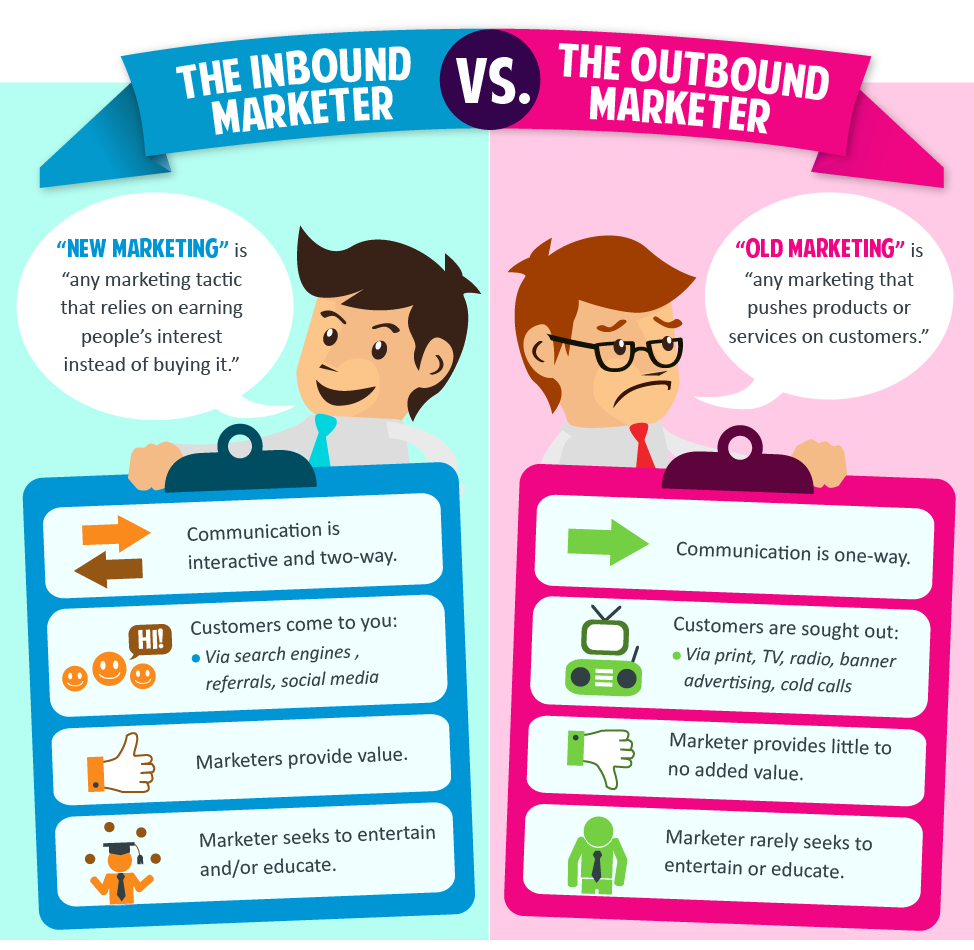
Difference between Traditional Marketing and Modern Marketing

One notable aspect is his giving back to the community through social responsibility program such as charity. It also cut down the cost of employing cooks and the waste of ingredients when their products did not turn out good. This is the reason he opts to settle among the Grimworth community where according to his insight, is well located, had a potential for future growth, with no competition and therefore an ideal location to set up a business. They were used to a particular way of life and consumption. David comes out well as if he had scanned the place well before deciding to venture into his business. What is new-old approach entrepreneurship? He earned the Chartered Financial Consultant® designation for advanced financial planning, the Chartered Life Underwriter® designation for advanced insurance specialization, the Accredited Financial Counselor® for Financial Counseling and both the Retirement Income Certified Professional®, and Certified Retirement Counselor designations for advance retirement planning. A bazaar or souk is a marketplace consisting of multiple small stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East and India.
New Market and Market Types

While traditional marketing uses traditional media like magazines and newspapers, digital marketing uses digital media, such as social media or websites. He portrays modern advertising as much better than the old method in the face of stiff competition from other companies in the same line of production. On the other hand, he offered his products at a lower price than what the customer would incur preparing mince pies and other products. Strive hard to promote your website and products through both mediums: Internet and manual process. It turns out that there are four distinct types of entrepreneurial organizations; small businesses, scalable startups, large companies and social entrepreneurs. Further, amongst the first customers is the rector's wife who goes to the shop under pretext of welcoming the shopkeeper to the community as well as to the church. A Greater Variety of Available Goods and Services: Today, a person can order almost anything over the internet: furniture, washing machines, Books, etc.
What is the difference between old approach and new approach?

The first impression of an advertiser matters a lot. As a consequence, salespeople spend less time ensuring the satisfaction of existing customers, with the result that some current customers defect. As the central argument in this context, the differences in advertisement and marketing both in the past and the present will be analyzed. David Faux combined friendliness, kindness, service to poor and openness. This acted as his pricing strategy.
OEM Parts vs. Aftermarket Parts: What's the Difference?

The Old Economy does not also pay attention to customer retention but rather focuses on customer acquisition. Further, organizations ought to foster on good public relations so that the community will have a good image about them hence good response on their products. A Substantial Increase in Buying Power: Buyers today are only a click away from comparing competitor prices and product attributes. The 4 Ps are used by companies to identify some key factors for their business, including what consumers want from them, how their product or service meets or fails to meet those needs, how their product or service is perceived in the world, how they stand out from their competitors, and how they interact with their … Is modern market organic? A few companies dominate existing markets while simultaneously opening new markets. In the old Marketing Economy, companies organize themselves by way of product units.