Social change refers to the transformation of culture, behavior, social institutions, and social structure over time. It can be a slow process that occurs gradually, or it can be a rapid and dramatic shift. Social change can be driven by various factors, including technological advancements, economic shifts, political revolutions, and cultural movements.
Social mobility, on the other hand, refers to the movement of individuals or groups from one social class to another. It can be upward mobility, which refers to movement from a lower social class to a higher one, or downward mobility, which refers to movement from a higher social class to a lower one. Social mobility can be driven by various factors, including education, career opportunities, and personal ambition.
One key difference between social change and social mobility is that social change affects society as a whole, while social mobility only affects individuals or groups. Social change can be a result of social mobility, as individuals or groups who achieve upward mobility may contribute to the transformation of social norms and values. However, social mobility does not necessarily lead to social change.
Another difference is that social change tends to be a long-term process, while social mobility can occur more quickly. For example, a person who earns a degree and secures a high-paying job may experience upward mobility within a relatively short period of time. However, the changes that result from this individual's increased economic status may not necessarily lead to significant social change.
In summary, social change refers to the transformation of society over time, while social mobility refers to the movement of individuals or groups from one social class to another. While the two concepts are related, they are distinct and should not be conflated. Understanding the difference between social change and social mobility is important for understanding the complex dynamics of society and the factors that shape it.
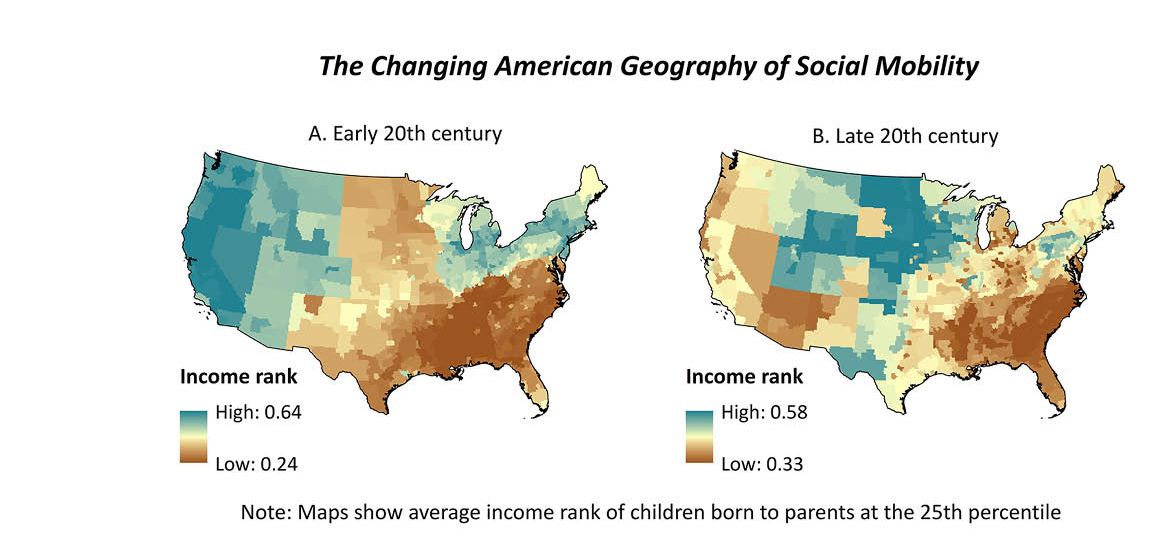
Social Mobility

Types of Crowds and Groups Crowds are also a common type of collective behavior. He has a diploma in electrical engineering from the industrial training institute, Gurgaon. When Zamindari Abolition Act was passed, most of the tenant cultivators became owner cultivators which indicates improvement in their status i. Occupational mobility, in short, stands for change of occupation of lower prestige to higher and vice-versa. Inter-Generational Mobility: This type of mobility means that one generation changes its social status in contrast to preceding generation. It offers online resources like the Radicalendar, a calendar for connecting and becoming radical, as well as activities like an alternative to the traditional Fourth of July picnic. After two or three generations their new position may be recognized.
What is the difference between social class and social mobility?
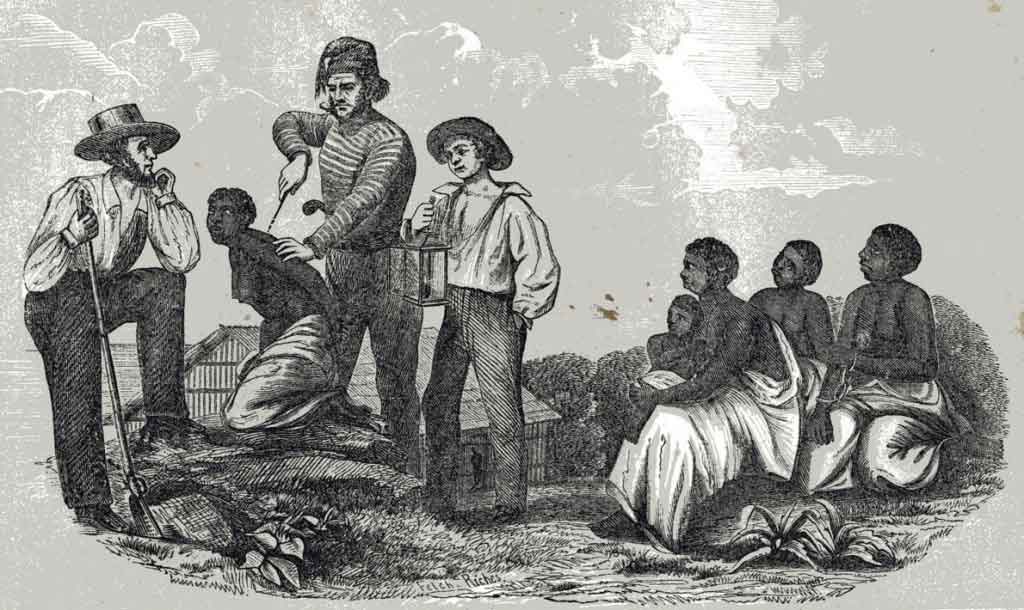

After a brief burst of activity, they fade away due to an inability to gather sufficient support. Persons are motivated according to a complex variety of factors to work toward new roles, with their higher status and greater rewards. Social movements often begin out of a feeling of injustice. La Grande Bretagne évolue dans le même sens, mais plus lentement et l'Australie peut-être plus lentement encore. The shift can either be higher, lower, inter-generational, or intra-generational, and it cannot necessarily be determined if the change is for good or bad. They acquired new vocational training and got jobs in industries. Springer is one of the leading international scientific publishing companies, publishing over 1,200 journals and more than 3,000 new books annually, covering a wide range of subjects including biomedicine and the life sciences, clinical medicine, physics, engineering, mathematics, computer sciences, and economics.
What is the Difference Between Social Stratification and Social Mobility

There are also various types of social movements. Also, a positive political discourse around migration is needed to increase geographic and social mobility. In such systems, social position is based on ascribed status, or social position you inherit at birth. However, you may now recognize the social change that has occurred in relation to legalizing marijuana. For example, the Indian Figure 1: Indian Caste System Open system, on the other hand, allows more change and freedom.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/conflict-theory-Final-66da57019fd84b9e906d0a6114cb79a8.png)
