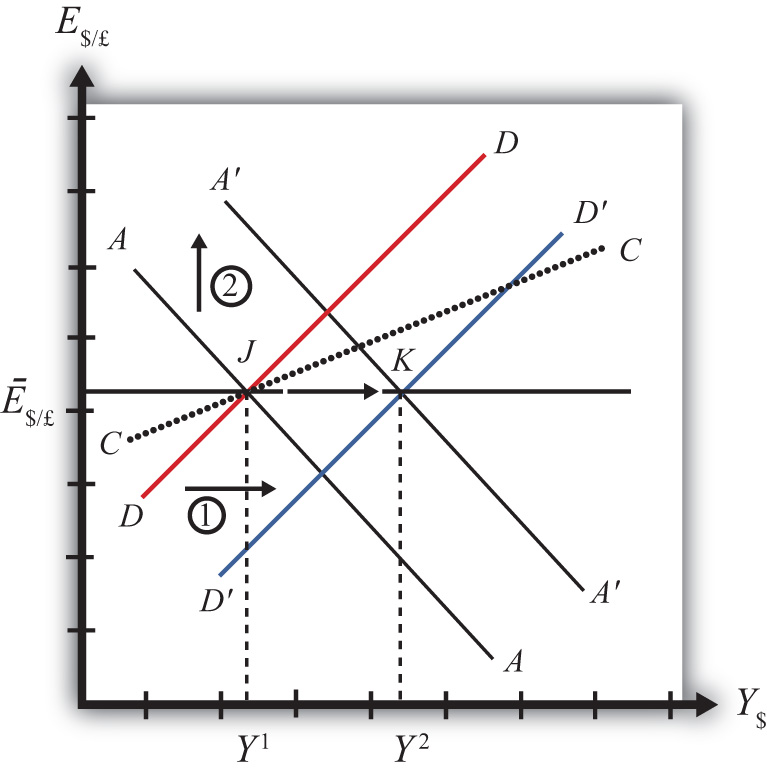
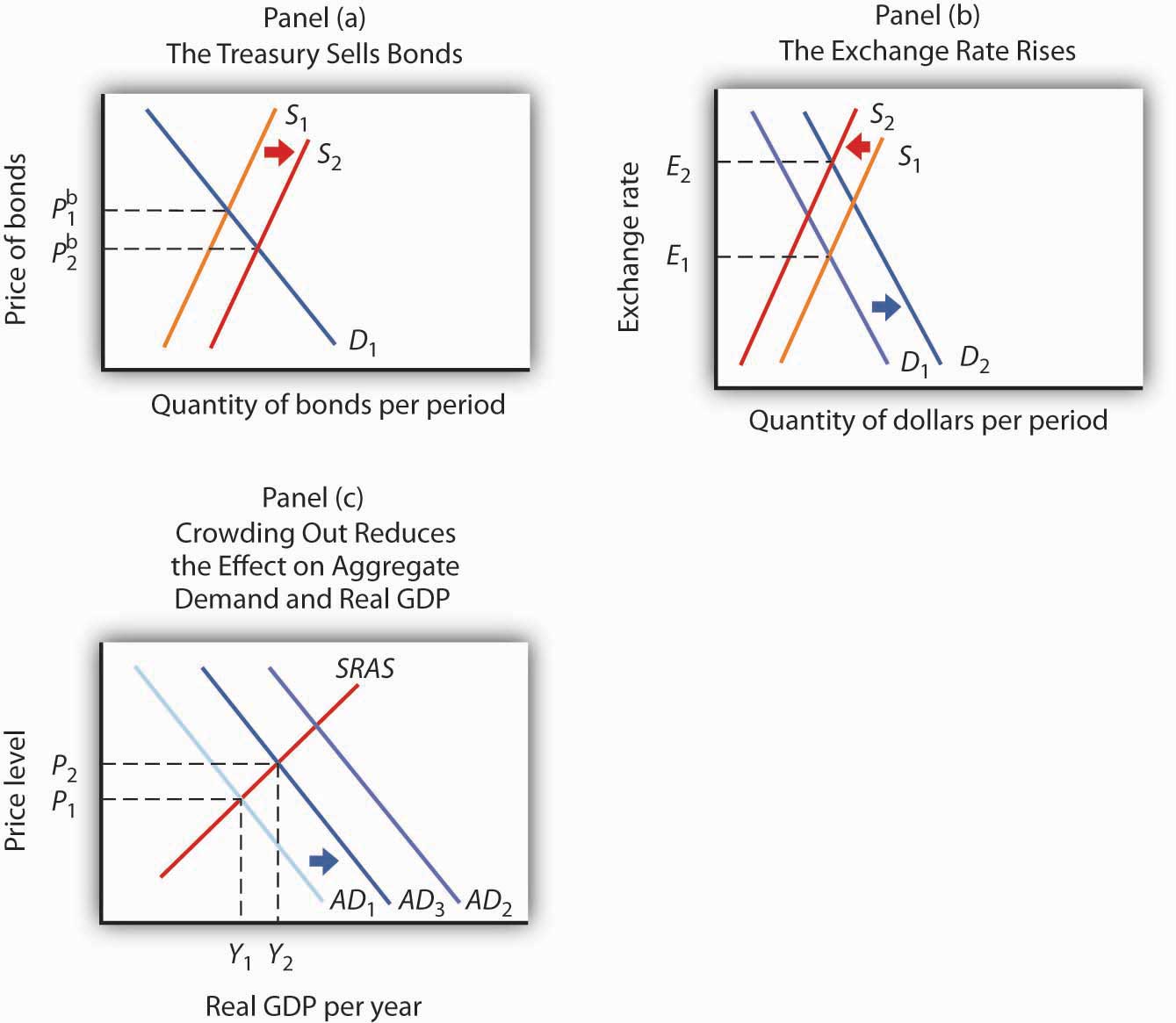
Expansionary monetary policy refers to actions taken by a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, to increase the supply of money in the economy and stimulate economic growth. While expansionary monetary policy can be effective in boosting economic activity in the short term, it can also have some disadvantages.
One potential disadvantage of expansionary monetary policy is that it can lead to higher inflation. When the central bank increases the money supply, it can lead to an excess of money chasing a limited number of goods and services. This excess demand can drive up prices, resulting in higher inflation. While some level of inflation is normal and can be beneficial for an economy, high or accelerating inflation can be a problem. It can erode the purchasing power of consumers, making it harder for them to afford basic goods and services. High inflation can also create uncertainty and disrupt financial markets.
Another potential disadvantage of expansionary monetary policy is that it can lead to asset bubbles. When the central bank lowers interest rates, it can make borrowing cheaper and more attractive for individuals and businesses. This can lead to increased demand for assets such as stocks, real estate, and other investments. If the demand for these assets outstrips their fundamental value, it can lead to an asset bubble, where the prices of these assets become artificially inflated. When the bubble eventually bursts, it can lead to significant losses for investors and a sharp downturn in the economy.
Expansionary monetary policy can also have distributional effects, as it can benefit some groups more than others. For example, lower interest rates can make it easier for businesses to borrow and invest, which can lead to increased economic activity and job growth. However, lower interest rates can also make it harder for savers to earn a decent return on their savings, as they may receive lower interest rates on their deposits. This can disproportionately affect those who rely on their savings for income, such as retirees.
Finally, expansionary monetary policy can lead to a buildup of debt. When the central bank lowers interest rates, it can encourage borrowing, as it becomes cheaper for individuals and businesses to take on debt. This can lead to a buildup of debt over time, which can become unsustainable if the economy slows or interest rates eventually rise. High levels of debt can also make an economy more vulnerable to financial shocks and economic downturns.
In summary, while expansionary monetary policy can be effective in boosting economic activity in the short term, it can also have some disadvantages, such as higher inflation, asset bubbles, distributional effects, and a buildup of debt. It is important for central banks to carefully consider the potential trade-offs of using expansionary monetary policy and to use it in a responsible manner.