Precast concrete is a type of construction material that is cast and cured in a factory setting before being transported to the construction site. While precast concrete has a number of benefits, it also has a number of disadvantages that must be considered when determining if it is the right choice for a particular construction project.
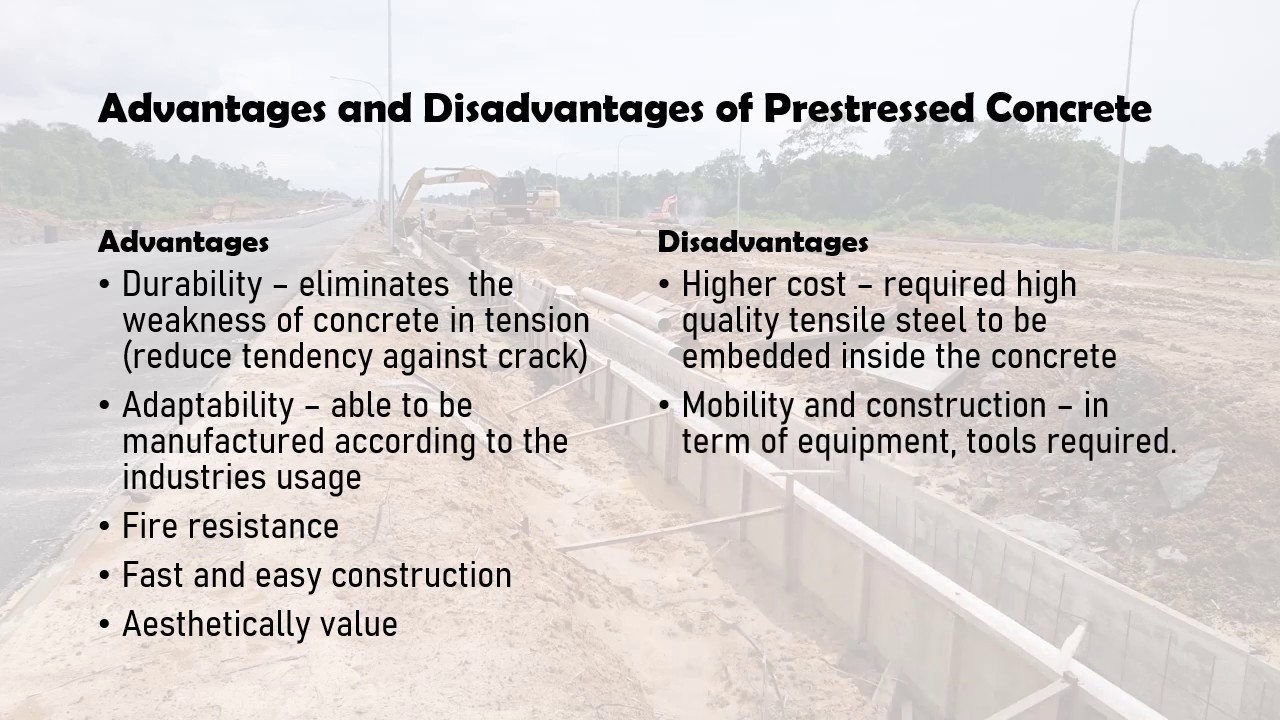
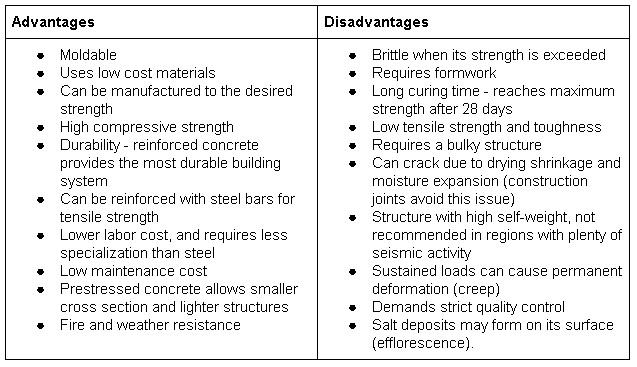
One major disadvantage of precast concrete is its cost. Precast concrete is generally more expensive than other types of construction materials, such as steel or wood. This is due to the additional costs associated with transportation, handling, and storage of the precast concrete elements. In addition, the specialized equipment and facilities needed to manufacture precast concrete can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
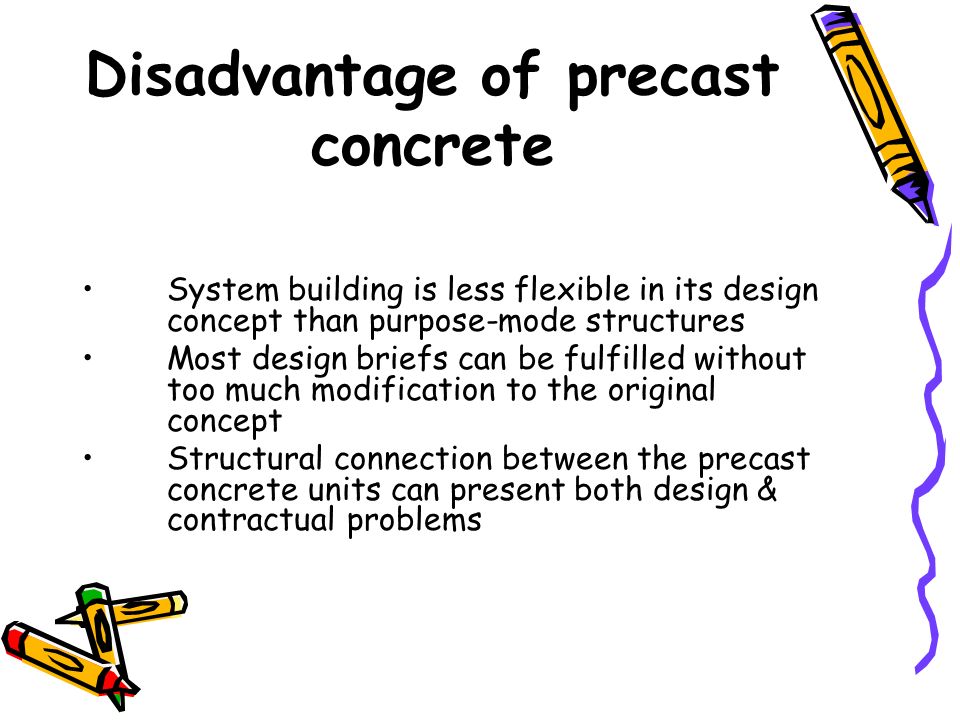
Another disadvantage of precast concrete is its limited design flexibility. Because the concrete is cast and cured in a factory setting, it is difficult to make changes or modifications to the design once the process has begun. This can be a problem if changes need to be made to the design after construction has started, as it may require the entire process to be restarted, which can lead to delays and additional costs.
Precast concrete can also be difficult to repair if it is damaged. Because the concrete is cast in a factory and then transported to the construction site, it can be difficult to access the internal structure of the precast elements to make repairs. This can be a problem if the concrete is damaged during construction or if it becomes damaged over time.
Finally, precast concrete can be difficult to work with on site. The elements are heavy and require specialized equipment to move and place them. This can make the construction process more complex and time-consuming, which can lead to delays and additional costs.
In conclusion, while precast concrete has a number of benefits, it also has a number of disadvantages that must be considered when determining if it is the right choice for a particular construction project. These disadvantages include its high cost, limited design flexibility, difficulty in repair, and complexity of use on site.