Protectionism refers to the economic policy of restricting trade between countries through the use of tariffs, quotas, and other measures designed to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. While protectionism can provide some short-term benefits to domestic industries and workers, it also has several disadvantages that can ultimately harm the economy and the welfare of consumers.
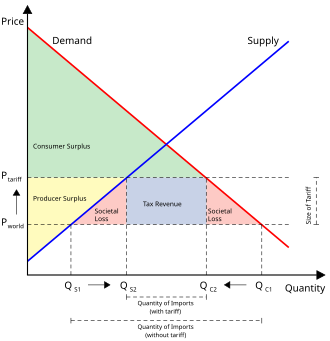
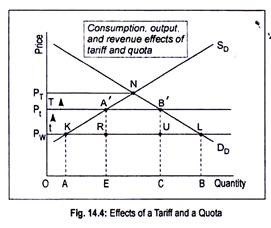
One disadvantage of protectionism is that it can lead to higher prices for consumers. When tariffs are placed on imported goods, the cost of those goods will increase, leading to higher prices for consumers. This can lead to reduced purchasing power, as consumers may not be able to afford the same amount of goods as they could before the tariffs were implemented. This can particularly affect lower-income households, who may struggle to afford basic necessities.
Another disadvantage of protectionism is that it can lead to reduced efficiency and innovation. When domestic industries are protected from foreign competition, they may not have the same incentives to improve their efficiency and reduce costs. This can lead to a decline in productivity and competitiveness, ultimately hurting the domestic economy. In addition, protectionist policies can reduce the ability of domestic firms to access new technologies and innovations from abroad, which can stifle innovation and progress.
Protectionism can also lead to trade wars and other forms of economic conflict between countries. When one country imposes tariffs on imported goods, other countries may respond by imposing tariffs on their own imported goods, leading to a spiral of retaliatory tariffs and trade barriers. This can lead to reduced trade between countries, which can harm global economic growth and stability.
Furthermore, protectionism can lead to a decline in international relations and cooperation. When countries engage in protectionist policies, they may be viewed as acting in their own self-interest rather than in the interests of the global community. This can lead to strained relations and a lack of cooperation on issues such as climate change, terrorism, and other global challenges.
In conclusion, while protectionism can provide some short-term benefits to domestic industries and workers, it also has several disadvantages that can ultimately harm the economy and the welfare of consumers. It can lead to higher prices for consumers, reduced efficiency and innovation, trade wars, and a decline in international relations and cooperation.