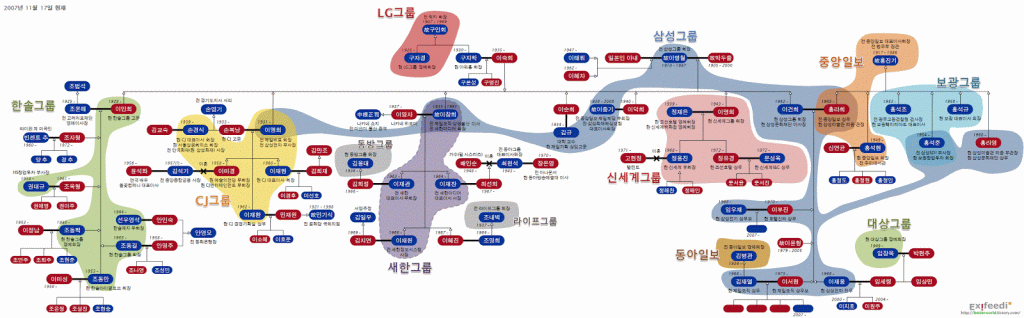
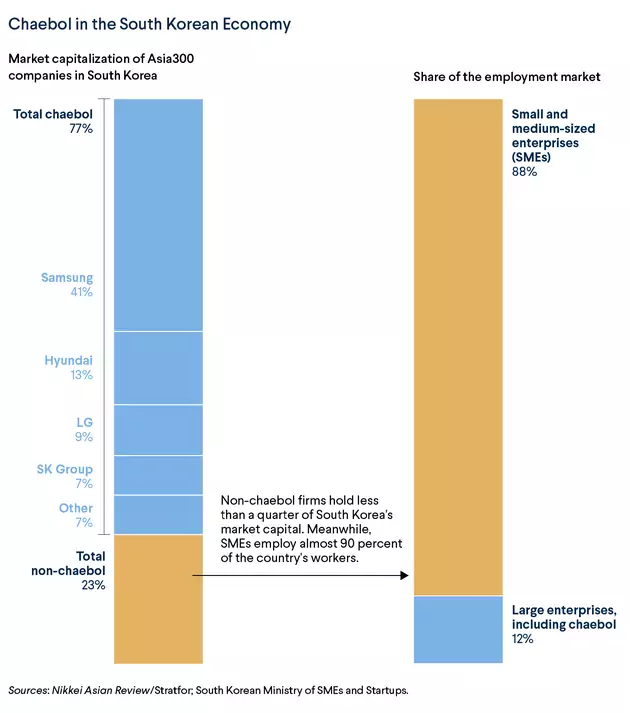
A South Korean multinational conglomerate company, also known as a chaebol, is a large business group that typically consists of a holding company and its subsidiaries. These companies are some of the largest and most influential in South Korea, and they have a significant impact on the country's economy and business landscape.
The history of chaebols in South Korea can be traced back to the 1960s, when the government implemented policies to encourage the growth of large, export-oriented businesses. These companies, which included Samsung, Hyundai, and LG, played a key role in South Korea's rapid economic development and transformation into a major global player.
One of the defining characteristics of chaebols is their vertical integration, which means that they own or control all aspects of their supply chain, from raw materials to production to distribution. This allows them to maintain a high level of control over their operations and ensure efficiency and quality.
However, chaebols have also faced criticism for their concentration of power and influence. Many of these companies have been accused of using their size and influence to unfairly advantage themselves, and there have been concerns about the impact on smaller businesses and the potential for corruption.
Despite these criticisms, chaebols continue to be a major force in South Korea's economy. They have expanded globally, establishing a presence in a wide range of industries, including electronics, automobiles, construction, and finance.
In conclusion, South Korean multinational conglomerate companies, or chaebols, have played a significant role in the country's economic development and have become major players in the global business world. While they have faced criticism for their concentration of power, they continue to be a major force in South Korea's economy and have a significant impact on the country's business landscape.