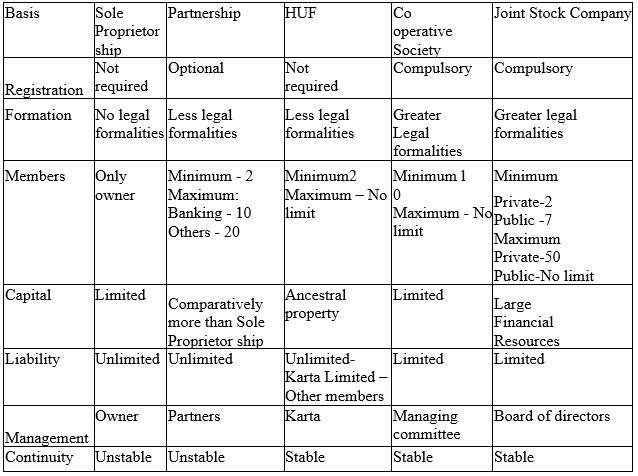
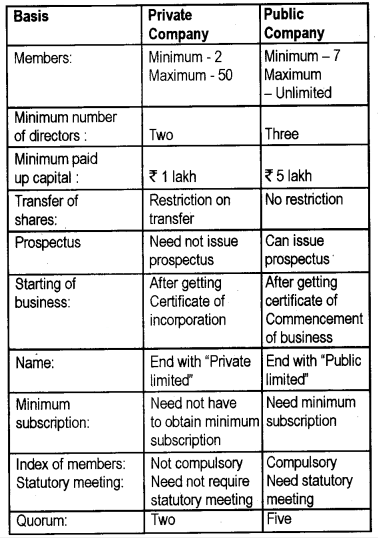
A partnership and a company are two different business structures that are commonly used by entrepreneurs and business owners. While both forms of business allow for the ownership and operation of a business by more than one person, there are several key differences between a partnership and a company that are important to understand.
One of the main differences between a partnership and a company is the level of liability that the owners have for the business. In a partnership, the owners, also known as partners, are personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. This means that if the partnership incurs any debts or liabilities, the partners are personally responsible for paying them off. In contrast, a company is a separate legal entity from its owners, and the owners, also known as shareholders, are not personally liable for the debts and obligations of the company. This means that if the company incurs any debts or liabilities, the shareholders are not personally responsible for paying them off.
Another key difference between a partnership and a company is the way in which they are taxed. Partnerships are taxed as pass-through entities, which means that the profits and losses of the business are passed through to the partners and are taxed at the individual level. Companies, on the other hand, are taxed as separate entities, and the profits and losses of the company are taxed at the corporate level. This means that the company pays taxes on its profits, and the shareholders pay taxes on any dividends they receive from the company.
In terms of governance and management, partnerships and companies also differ. In a partnership, the partners are typically involved in the day-to-day management and decision-making of the business, and they often have equal say in how the business is run. In a company, the management and decision-making are typically the responsibility of a board of directors, and the shareholders elect the board members. The shareholders also have the right to vote on major business decisions, such as the appointment of new directors or the approval of major financial transactions.
Finally, partnerships and companies also differ in terms of their lifespan. Partnerships are often formed for a specific project or a set period of time, and they typically dissolve when the project is completed or when the term of the partnership expires. Companies, on the other hand, are more permanent entities and can continue to exist indefinitely, even if the owners or shareholders change.
In conclusion, while partnerships and companies are both forms of business that allow for the ownership and operation of a business by more than one person, they differ in terms of liability, taxation, governance, and lifespan. Understanding the differences between these two business structures can help entrepreneurs and business owners choose the structure that is most appropriate for their needs.