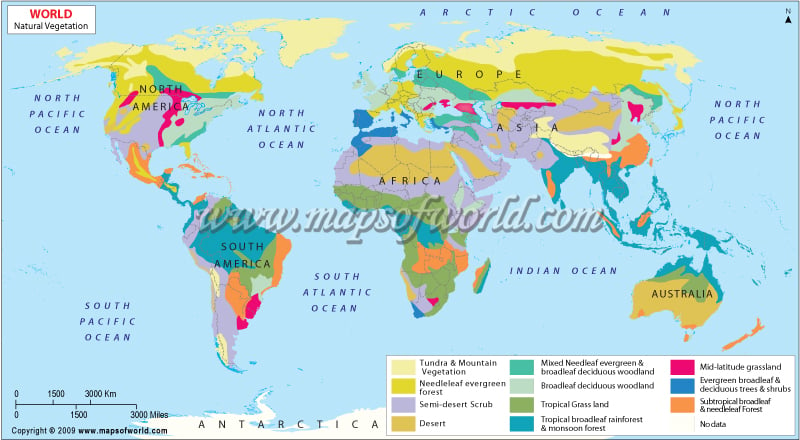
Natural vegetation refers to the plant life that grows naturally in a specific region, without human intervention. The distribution of natural vegetation around the world is influenced by a variety of factors, including climate, topography, soil type, and the presence of other plant and animal species.
One of the most important factors influencing the distribution of natural vegetation is climate. Different climates support different types of vegetation, and this is largely due to the availability of water. In general, areas with a lot of rainfall, such as tropical rainforests, support a diverse array of plant life. These regions are typically characterized by high humidity, warm temperatures, and abundant sunlight, which creates a favorable environment for plant growth.
On the other hand, areas with little rainfall, such as deserts and grasslands, support relatively sparse vegetation. These regions are typically characterized by low humidity, high temperatures, and limited sunlight, which can be hostile to plant growth. However, some plant species are able to thrive in these conditions by adapting to the harsh conditions, such as by developing deep roots to access underground water sources or by producing waxy leaves to retain moisture.
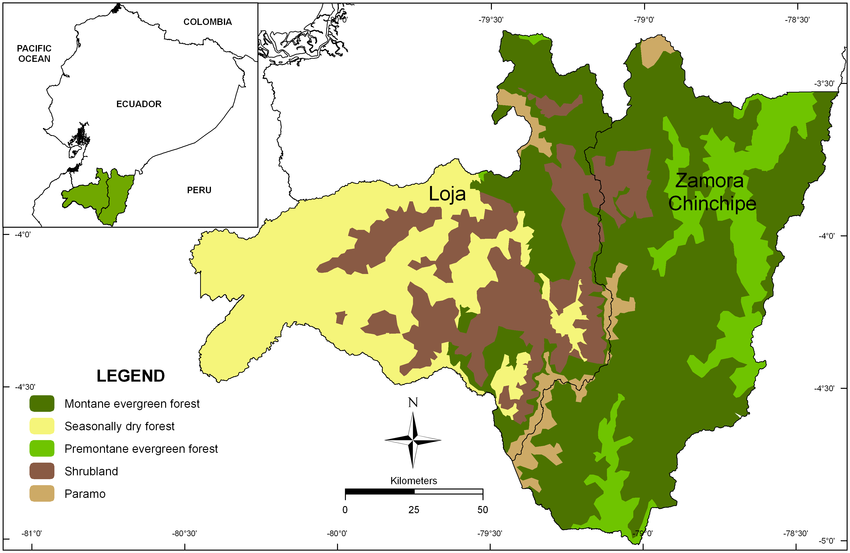
Topography, or the physical features of the land, also plays a role in the distribution of natural vegetation. For example, mountain ranges often have a variety of different vegetation types due to the range of altitudes and microclimates found within them. At higher altitudes, where temperatures are cooler and there is less sunlight, alpine or tundra vegetation may be found. As one moves down the mountain, the vegetation may change to coniferous forests, deciduous forests, or even grasslands or savannas.
Soil type is another factor that can influence the distribution of natural vegetation. Different soil types have different nutrient levels and pH levels, which can affect the types of plants that are able to grow in a given area. For example, acidic soils may support coniferous forests or heathlands, while alkaline soils may support grasslands or savannas.
Finally, the presence of other plant and animal species can also impact the distribution of natural vegetation. For example, certain plant species may only be able to grow in an area if they have specific pollinators or seed dispersers, such as insects or birds. Similarly, certain herbivores may preferentially graze on certain plant species, which can affect the distribution and abundance of those plants.
Overall, the distribution of natural vegetation around the world is the result of a complex interplay of factors, including climate, topography, soil type, and the presence of other plant and animal species. Understanding these factors can help us to better understand the patterns of plant life on our planet and how they may be impacted by human activities and climate change.