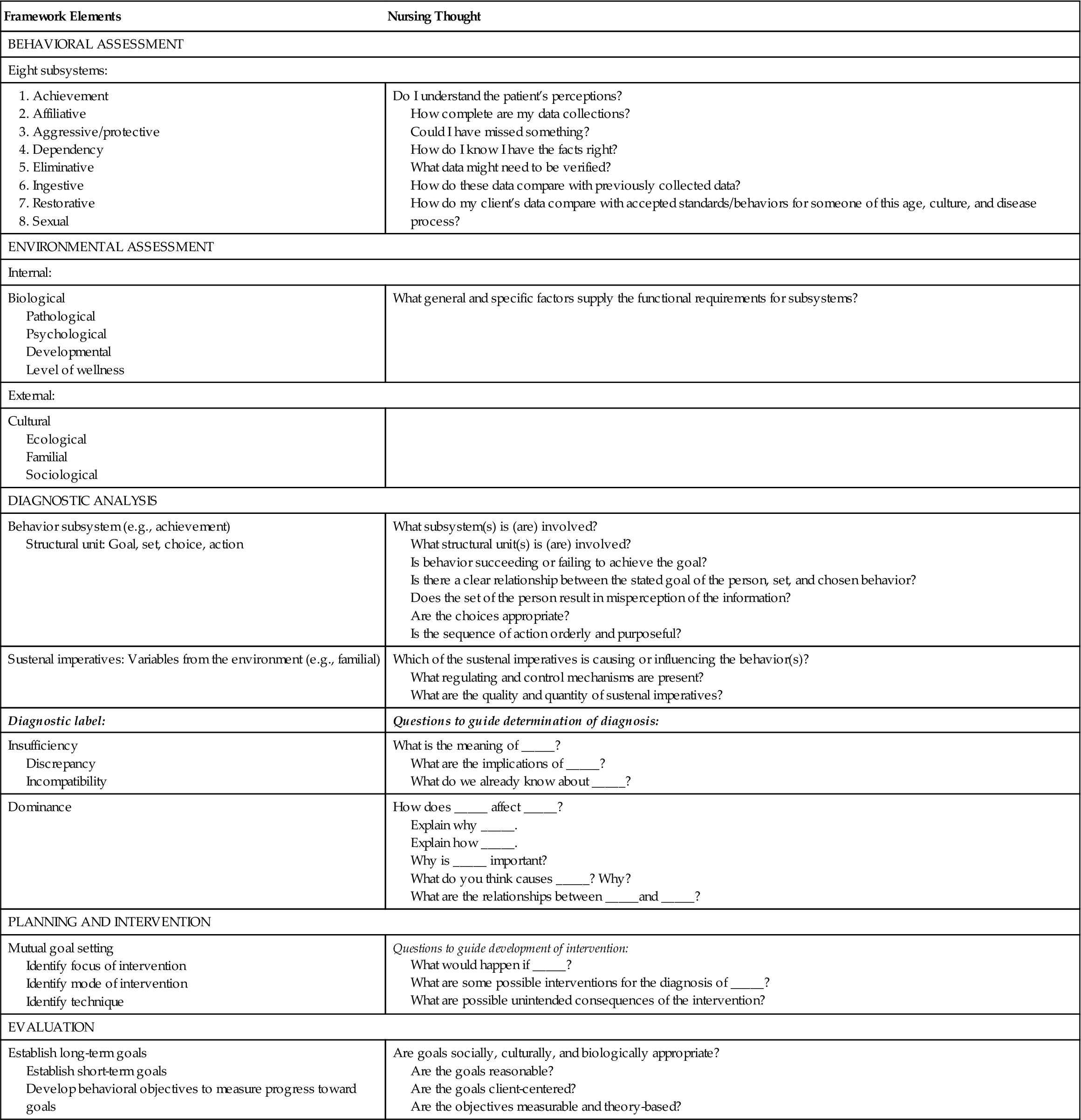
The Dorothy Johnson Behavioral System Model is a nursing theory that was developed in the 1970s by Dorothy Johnson, a nursing theorist and professor at the University of Colorado. This model is based on the belief that human behavior is a function of the interaction between the individual and their environment. It is a holistic approach to nursing that takes into account the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of the patient.
The Johnson Behavioral System Model is based on the concept of a behavioral system, which is a set of interacting parts that work together to achieve a common goal. In this case, the goal is the health and well-being of the patient. The model consists of three interacting systems: the personal system, the social system, and the environmental system.
The personal system is made up of the patient's physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. It includes the patient's beliefs, values, and coping mechanisms, as well as their physical health and functional abilities. The social system consists of the patient's relationships with others, including family, friends, and healthcare providers. The environmental system includes the physical environment in which the patient lives, including the climate, geography, and culture, as well as the larger societal and political systems that may impact the patient's health.
The Johnson Behavioral System Model is a metaparadigm for nursing, meaning that it provides a framework for understanding the key concepts and principles that guide the practice of nursing. One of the key principles of this model is the concept of mutual goal setting, in which the nurse and patient work together to set realistic and achievable goals for improving the patient's health. This involves ongoing communication and collaboration between the nurse and the patient, as well as a willingness to adapt the care plan as needed in response to changes in the patient's health or circumstances.
Another key principle of the Johnson Behavioral System Model is the idea that nursing is a process of continuous learning and growth. Nurses are expected to continually assess and evaluate the patient's needs and adjust their care plan accordingly. This requires ongoing education and training to stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices in nursing.
In summary, the Dorothy Johnson Behavioral System Model is a holistic approach to nursing that recognizes the complex interaction between the individual, their environment, and their relationships with others. It emphasizes the importance of mutual goal setting and continuous learning and growth in the practice of nursing. This model has had a significant impact on the field of nursing and continues to be a valuable guide for nursing practice today.