Testing a leaf for starch is a common experiment in biology classrooms, as it allows students to understand the process of photosynthesis and how plants use energy. In this lab report, we will outline the materials and methods used, describe the results of the experiment, and discuss the implications of these results.
Materials:
- Fresh leaf from a green plant
- Iodine solution
- Beaker
- Test tube
- Glass stirring rod
- Dropper
- Paper towels
Methods:
- Obtain a fresh leaf from a green plant and gently wash it with water to remove any dirt or debris.
- Fill a beaker with water and add a few drops of iodine solution.
- Use a dropper to place a small drop of the iodine solution onto the leaf.
- Observe the color of the iodine on the leaf. If the leaf contains starch, the iodine will turn blue or black. If the leaf does not contain starch, the iodine will remain yellow or orange.
- Repeat the process with a few additional drops of iodine to confirm the results.
- If necessary, use a glass stirring rod to scrape a small piece of tissue from the leaf and place it in a test tube. Add a few drops of iodine solution to the test tube and observe the color change.
Results:
In our experiment, we found that the iodine turned blue or black when applied to the leaf, indicating the presence of starch. When a small piece of tissue was placed in a test tube and mixed with iodine solution, the solution also turned blue or black. These results suggest that the leaf we tested contains starch.
Discussion:
Starch is a complex carbohydrate that plants use to store energy. It is produced during photosynthesis, when the plant uses energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. The glucose is then converted into starch and stored in the plant's tissues, such as leaves, stems, and roots.
The presence of starch in the leaf we tested confirms that the plant is able to carry out photosynthesis and produce glucose. This is important for the plant's survival, as it allows the plant to store energy for times when sunlight is not available, such as at night or during periods of low light intensity.
Overall, testing a leaf for starch is a simple and effective way to understand the process of photosynthesis and the role of starch in plant metabolism. It also helps students learn how to use scientific equipment and follow experimental procedures, which are important skills for any aspiring scientist.
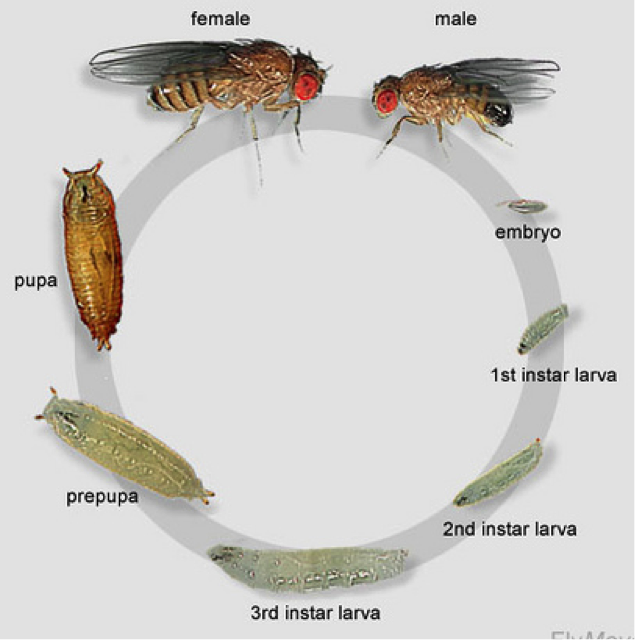
Drosophila Cross Lab Report: Comparing the Given Genotype to the Phenotype

Additionally, his Law of Independent Assortment states that different alleles that are passed from first had to undergo a process of of being anesthetized. These include a fast reproduction cycle of approximately 30 days, small physical size, cost-effective culture and growth in large quantities, and a small genome size of 4 pairs of chromosomes. Then, they were taken to be examined quickly before waking up. Related Articles Surfactants to Enhance Bioavailability of Recalcitrant Residual Petroleum Contamination A rhamnolipid biosurfactant altered microbial community composition and hindered hydrocarbon biodegradation in fire-impacted contaminated soils from Lac Megantic, Quebec. In this experiment, it was used the actual sample 4 and the ago sample 3. Genetics Lab Handout 1 Manning, G.
Drosophila Melanogaster Lab Report Essay
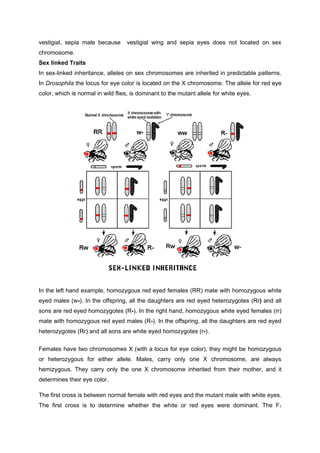
To conclude this experiment, Mendelian genetics set a good standard to what this experiment should be. Many different species, and a large number and wide variety of naturally-occurring and artificially-induced genetic variants are available. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work in 1933 and the Division of Biology that he founded at Caltech produced seven more Nobel laureates. Normal wings Normal wings No wings white No wings Red eyes White Drosophila Melanogaster Lab Report Identifying unknown phenotypes and determining mechanisms of inheritance of various genes in mutations of Drosophila melanogaster Michael Fisher, Tori Hall, Lindsey Theodore Crosses carried out with Drosophila melanogaster can be used to determine mechanisms that modify ratios of Mendelian inheritance, such as autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance, genetic linkage, and epistasis. We can conclude this considering our F1 generation ratio between male and female flies were closer to equal. The Drosophila melanogaster In this experiment, the species Drosophila melanogaster, the common fruit fly, was studied to examine the processes of natural selection and genetic drift in the laboratory. Once 2 minutes was up, the flies were taken out of the freezer and dumped onto the petri dish to be quickly examined for phenotype.
Drosophila Melanogaster Lab blog.sigma-systems.com

The result of the coefficient of selection should be at the rate between 0 and 1. Along with sex-linkage, epistatic inheritance occurs when multiple genes affect a single phenotype such as eye-color Klug, 2014. After this time period, data was collected and a Chi Squared test was run to test the deviance from this expected ratio. These grownup flies were anesthetized and the phenotypes sex and oculus colour were observed and recorded. To prepare a food vile, one scoop of dry food and one scoop of water was added to an empty vile. Acknowledgements I would like to thank my lab partners, Andrea Nichols, Madison Sanders, and Tiffany Taylor for all the hard work they do and help getting me through this lab.
Drosophila melanogaster lab report
There were a few ways to differentiate between a female and male fly. The drosophila egg is about half a millimeter long. Drosophila Melanogaster, also known as fruit flies, are good to experiment with due to their high number of offspring, can produce new adults in two weeks, and only have four pairs of chromosomes which makes it easy when locating a specific gene Mlotshwa Raymond. Six red-eyed fruit flies genotype RR of one sex and six sepia-eyed fruit flies genotype rr of the other sex were transferred into the civilization bottle after being anesthetized. This data was tested at the.
Drosophila melanogaster lab report
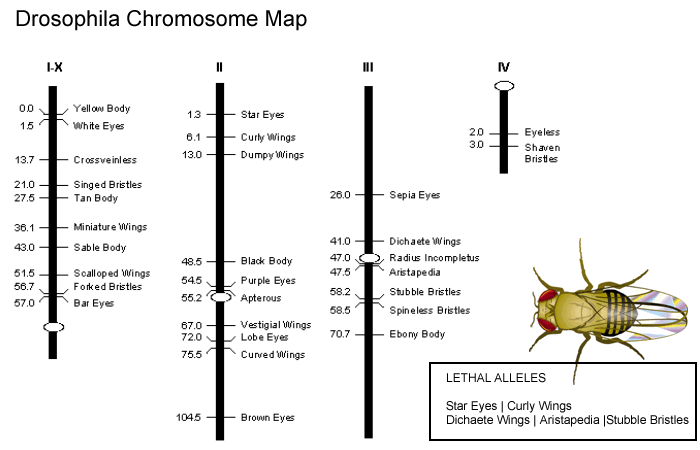
After years of research, Morgan discovered white-eyed flies appearing among the normal red-eyed flies. He reported different wing patterns and, by 1908, had noticed the proliferation of dwarf mutants. Drosophila fruit flies share about seventy percent of the genes that cause disease with humans so… Drosophila Melanogaster Research Paper Drosophila melanogaster, more commonly known as the fruit fly, is commonly used as a model organism in genetic research. The Chi-Square figure for our experiment was 62. In his study he concluded that ebony flies reproduced much more thoroughly if they remained in the dark throughout their lifespan. Life Stages of Drosophila melanogaster GSA, n.