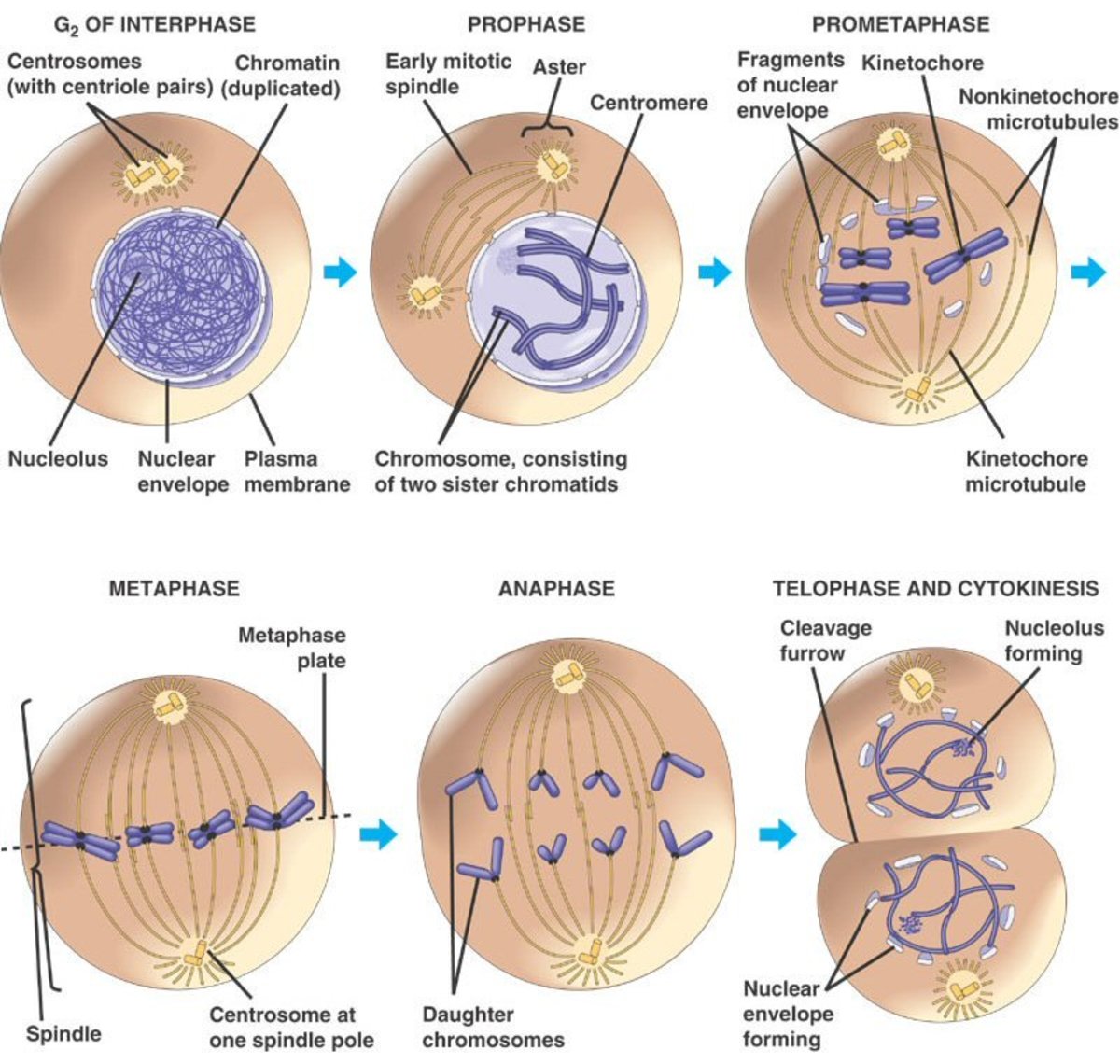
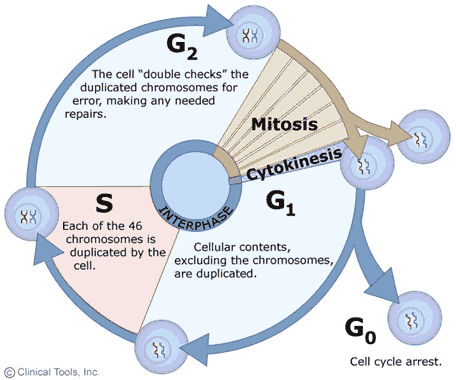
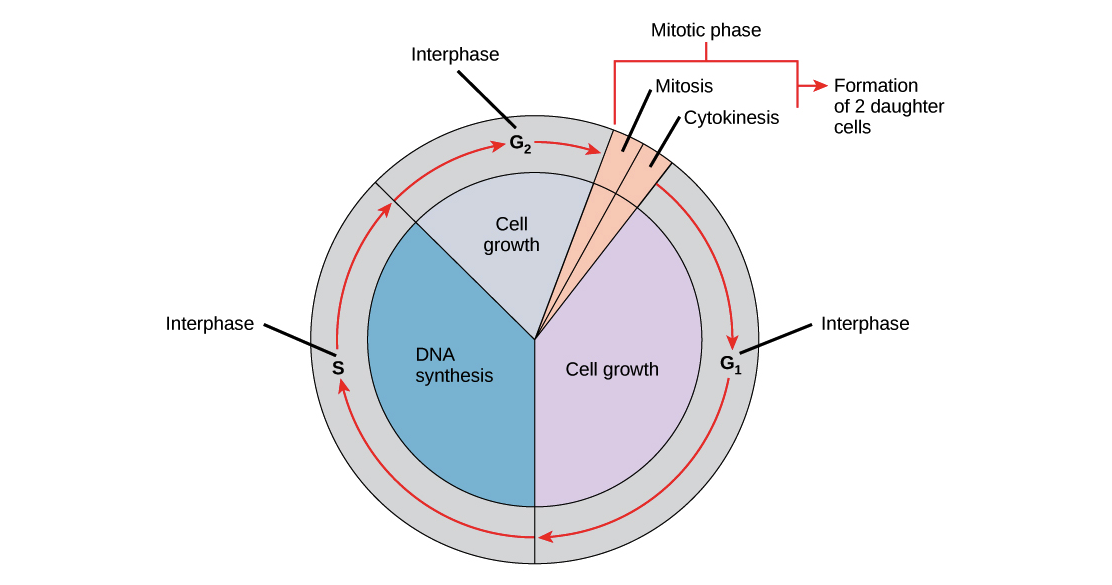
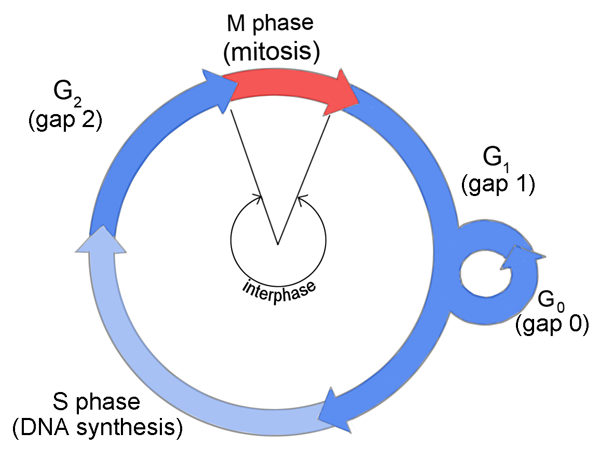
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell divides its nucleus and cytoplasm into two identical daughter cells. It is a vital process that occurs in all multicellular organisms and is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction. Mitosis consists of four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. During prophase, the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, breaks down, and the chromatin, the material that makes up the chromosomes, becomes more visible. The centrosomes, which are responsible for forming the mitotic spindle, also begin to move to opposite poles of the cell.
Metaphase is the second phase of mitosis. During metaphase, the mitotic spindle is fully formed and the chromosomes line up at the equatorial plane of the cell, which is the center of the cell. The chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle by their centromere, a region of DNA that connects the two sister chromatids, or copies of the chromosome.
Anaphase is the third phase of mitosis. During anaphase, the centromere of each chromosome splits and the sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the mitotic spindle. This results in the separation of the genetic material and the creation of two identical sets of chromosomes in each daughter cell.
Telophase is the final phase of mitosis. During telophase, a new nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and the cell begins to divide into two daughter cells. The cell also begins to form a new cell wall, called the cell plate, which will eventually become the cell membrane of the daughter cells.
Overall, mitosis is a complex process that is essential for the proper growth and function of multicellular organisms. Each phase of mitosis plays a vital role in ensuring that the genetic material is accurately replicated and distributed to the daughter cells, ensuring the continuation of life.